András Antos
Department of Artificial Intelligence and Systems Engineering, Budapest University of Technology and Economics
Semi-overlapping Multi-bandit Best Arm Identification for Sequential Support Network Learning
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Many modern AI and ML problems require evaluating partners' contributions through shared yet asymmetric, computationally intensive processes and the simultaneous selection of the most beneficial candidates. Sequential approaches to these problems can be unified under a new framework, Sequential Support Network Learning (SSNL), in which the goal is to select the most beneficial candidate set of partners for all participants using trials; that is, to learn a directed graph that represents the highest-performing contributions. We demonstrate that a new pure-exploration model, the semi-overlapping multi-(multi-armed) bandit (SOMMAB), in which a single evaluation provides distinct feedback to multiple bandits due to structural overlap among their arms, can be used to learn a support network from sparse candidate lists efficiently. We develop a generalized GapE algorithm for SOMMABs and derive new exponential error bounds that improve the best known constant in the exponent for multi-bandit best-arm identification. The bounds scale linearly with the degree of overlap, revealing significant sample-complexity gains arising from shared evaluations. From an application point of view, this work provides a theoretical foundation and improved performance guarantees for sequential learning tools for identifying support networks from sparse candidates in multiple learning problems, such as in multi-task learning (MTL), auxiliary task learning (ATL), federated learning (FL), and in multi-agent systems (MAS).
BandiK: Efficient Multi-Task Decomposition Using a Multi-Bandit Framework
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:The challenge of effectively transferring knowledge across multiple tasks is of critical importance and is also present in downstream tasks with foundation models. However, the nature of transfer, its transitive-intransitive nature, is still an open problem, and negative transfer remains a significant obstacle. Selection of beneficial auxiliary task sets in multi-task learning is frequently hindered by the high computational cost of their evaluation, the high number of plausible candidate auxiliary sets, and the varying complexity of selection across target tasks. To address these constraints, we introduce BandiK, a novel three-stage multi-task auxiliary task subset selection method using multi-bandits, where each arm pull evaluates candidate auxiliary sets by training and testing a multiple output neural network on a single random train-test dataset split. Firstly, BandiK estimates the pairwise transfers between tasks, which helps in identifying which tasks are likely to benefit from joint learning. In the second stage, it constructs a linear number of candidate sets of auxiliary tasks (in the number of all tasks) for each target task based on the initial estimations, significantly reducing the exponential number of potential auxiliary task sets. Thirdly, it employs a Multi-Armed Bandit (MAB) framework for each task, where the arms correspond to the performance of candidate auxiliary sets realized as multiple output neural networks over train-test data set splits. To enhance efficiency, BandiK integrates these individual task-specific MABs into a multi-bandit structure. The proposed multi-bandit solution exploits that the same neural network realizes multiple arms of different individual bandits corresponding to a given candidate set. This semi-overlapping arm property defines a novel multi-bandit cost/reward structure utilized in BandiK.
Upper-Confidence-Bound Algorithms for Active Learning in Multi-Armed Bandits
Jul 16, 2015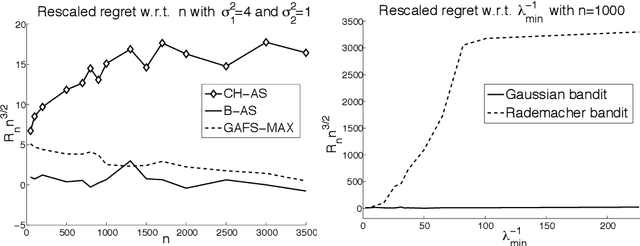
Abstract:In this paper, we study the problem of estimating uniformly well the mean values of several distributions given a finite budget of samples. If the variance of the distributions were known, one could design an optimal sampling strategy by collecting a number of independent samples per distribution that is proportional to their variance. However, in the more realistic case where the distributions are not known in advance, one needs to design adaptive sampling strategies in order to select which distribution to sample from according to the previously observed samples. We describe two strategies based on pulling the distributions a number of times that is proportional to a high-probability upper-confidence-bound on their variance (built from previous observed samples) and report a finite-sample performance analysis on the excess estimation error compared to the optimal allocation. We show that the performance of these allocation strategies depends not only on the variances but also on the full shape of the distributions.
Toward a Classification of Finite Partial-Monitoring Games
Oct 11, 2011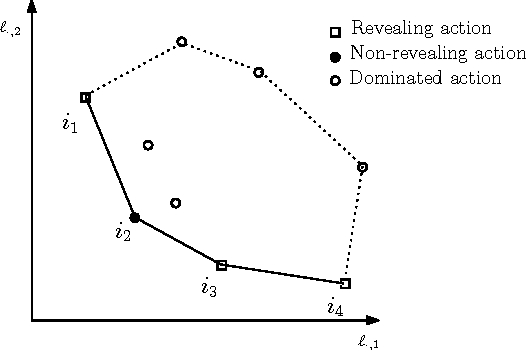


Abstract:Partial-monitoring games constitute a mathematical framework for sequential decision making problems with imperfect feedback: The learner repeatedly chooses an action, opponent responds with an outcome, and then the learner suffers a loss and receives a feedback signal, both of which are fixed functions of the action and the outcome. The goal of the learner is to minimize his total cumulative loss. We make progress towards the classification of these games based on their minimax expected regret. Namely, we classify almost all games with two outcomes and finite number of actions: We show that their minimax expected regret is either zero, $\widetilde{\Theta}(\sqrt{T})$, $\Theta(T^{2/3})$, or $\Theta(T)$ and we give a simple and efficiently computable classification of these four classes of games. Our hope is that the result can serve as a stepping stone toward classifying all finite partial-monitoring games.
Non-trivial two-armed partial-monitoring games are bandits
Aug 24, 2011Abstract:We consider online learning in partial-monitoring games against an oblivious adversary. We show that when the number of actions available to the learner is two and the game is nontrivial then it is reducible to a bandit-like game and thus the minimax regret is $\Theta(\sqrt{T})$.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge