Amir Roshan Zamir
Unsupervised Semantic Action Discovery from Video Collections
May 11, 2016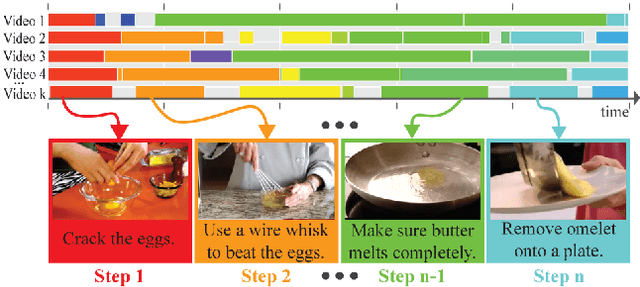
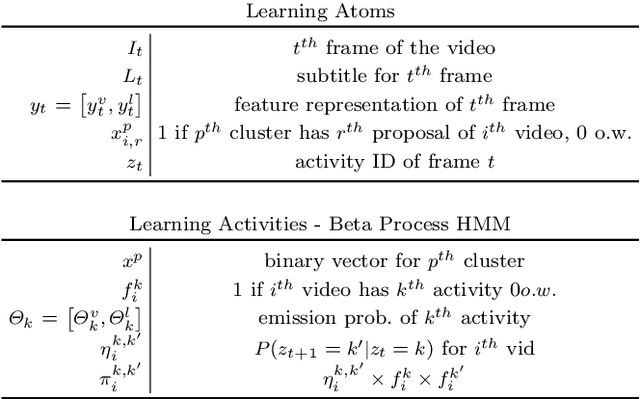

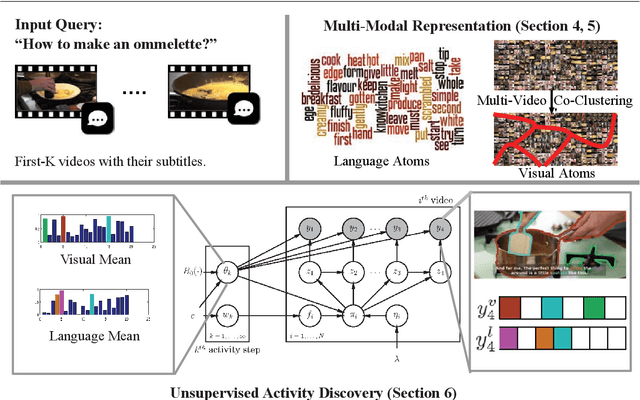
Abstract:Human communication takes many forms, including speech, text and instructional videos. It typically has an underlying structure, with a starting point, ending, and certain objective steps between them. In this paper, we consider instructional videos where there are tens of millions of them on the Internet. We propose a method for parsing a video into such semantic steps in an unsupervised way. Our method is capable of providing a semantic "storyline" of the video composed of its objective steps. We accomplish this using both visual and language cues in a joint generative model. Our method can also provide a textual description for each of the identified semantic steps and video segments. We evaluate our method on a large number of complex YouTube videos and show that our method discovers semantically correct instructions for a variety of tasks.
Action Recognition by Hierarchical Mid-level Action Elements
Aug 31, 2015



Abstract:Realistic videos of human actions exhibit rich spatiotemporal structures at multiple levels of granularity: an action can always be decomposed into multiple finer-grained elements in both space and time. To capture this intuition, we propose to represent videos by a hierarchy of mid-level action elements (MAEs), where each MAE corresponds to an action-related spatiotemporal segment in the video. We introduce an unsupervised method to generate this representation from videos. Our method is capable of distinguishing action-related segments from background segments and representing actions at multiple spatiotemporal resolutions. Given a set of spatiotemporal segments generated from the training data, we introduce a discriminative clustering algorithm that automatically discovers MAEs at multiple levels of granularity. We develop structured models that capture a rich set of spatial, temporal and hierarchical relations among the segments, where the action label and multiple levels of MAE labels are jointly inferred. The proposed model achieves state-of-the-art performance in multiple action recognition benchmarks. Moreover, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our model in real-world applications such as action recognition in large-scale untrimmed videos and action parsing.
UCF101: A Dataset of 101 Human Actions Classes From Videos in The Wild
Dec 03, 2012



Abstract:We introduce UCF101 which is currently the largest dataset of human actions. It consists of 101 action classes, over 13k clips and 27 hours of video data. The database consists of realistic user uploaded videos containing camera motion and cluttered background. Additionally, we provide baseline action recognition results on this new dataset using standard bag of words approach with overall performance of 44.5%. To the best of our knowledge, UCF101 is currently the most challenging dataset of actions due to its large number of classes, large number of clips and also unconstrained nature of such clips.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge