Alif Munim
EchoJEPA: A Latent Predictive Foundation Model for Echocardiography
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Foundation models for echocardiography promise to reduce annotation burden and improve diagnostic consistency by learning generalizable representations from large unlabeled video archives. However, current approaches fail to disentangle anatomical signal from the stochastic speckle and acquisition artifacts that dominate ultrasound imagery. We present EchoJEPA, a foundation model for echocardiography trained on 18 million echocardiograms across 300K patients, the largest pretraining corpus for this modality to date. We also introduce a novel multi-view probing framework with factorized stream embeddings that standardizes evaluation under frozen backbones. Compared to prior methods, EchoJEPA reduces left ventricular ejection fraction estimation error by 19% and achieves 87.4% view classification accuracy. EchoJEPA exhibits strong sample efficiency, reaching 78.6% accuracy with only 1% of labeled data versus 42.1% for the best baseline trained on 100%. Under acoustic perturbations, EchoJEPA degrades by only 2.3% compared to 16.8% for the next best model, and transfers zero-shot to pediatric patients with 15% lower error than the next best model, outperforming all fine-tuned baselines. These results establish latent prediction as a superior paradigm for ultrasound foundation models.
Benchmarking and Adapting On-Device Large Language Models for Clinical Decision Support
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have rapidly advanced in clinical decision-making, yet the deployment of proprietary systems is hindered by privacy concerns and reliance on cloud-based infrastructure. Open-source alternatives allow local inference but often require large model sizes that limit their use in resource-constrained clinical settings. Here, we benchmark two on-device LLMs, gpt-oss-20b and gpt-oss-120b, across three representative clinical tasks: general disease diagnosis, specialty-specific (ophthalmology) diagnosis and management, and simulation of human expert grading and evaluation. We compare their performance with state-of-the-art proprietary models (GPT-5 and o4-mini) and a leading open-source model (DeepSeek-R1), and we further evaluate the adaptability of on-device systems by fine-tuning gpt-oss-20b on general diagnostic data. Across tasks, gpt-oss models achieve performance comparable to or exceeding DeepSeek-R1 and o4-mini despite being substantially smaller. In addition, fine-tuning remarkably improves the diagnostic accuracy of gpt-oss-20b, enabling it to approach the performance of GPT-5. These findings highlight the potential of on-device LLMs to deliver accurate, adaptable, and privacy-preserving clinical decision support, offering a practical pathway for broader integration of LLMs into routine clinical practice.
MedRAX: Medical Reasoning Agent for Chest X-ray
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:Chest X-rays (CXRs) play an integral role in driving critical decisions in disease management and patient care. While recent innovations have led to specialized models for various CXR interpretation tasks, these solutions often operate in isolation, limiting their practical utility in clinical practice. We present MedRAX, the first versatile AI agent that seamlessly integrates state-of-the-art CXR analysis tools and multimodal large language models into a unified framework. MedRAX dynamically leverages these models to address complex medical queries without requiring additional training. To rigorously evaluate its capabilities, we introduce ChestAgentBench, a comprehensive benchmark containing 2,500 complex medical queries across 7 diverse categories. Our experiments demonstrate that MedRAX achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to both open-source and proprietary models, representing a significant step toward the practical deployment of automated CXR interpretation systems. Data and code have been publicly available at https://github.com/bowang-lab/MedRAX
Bringing the State-of-the-Art to Customers: A Neural Agent Assistant Framework for Customer Service Support
Feb 07, 2023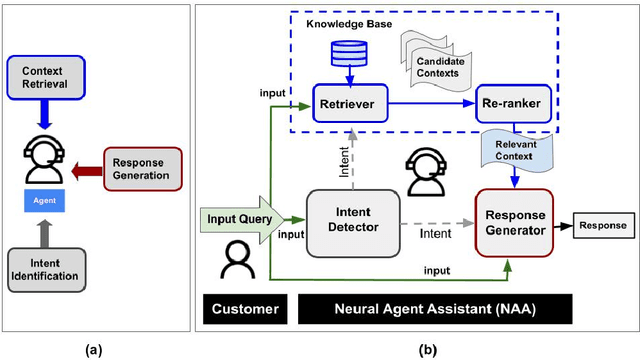
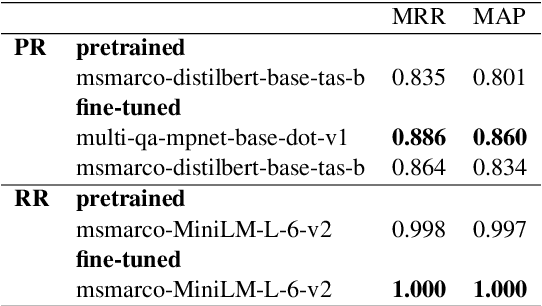
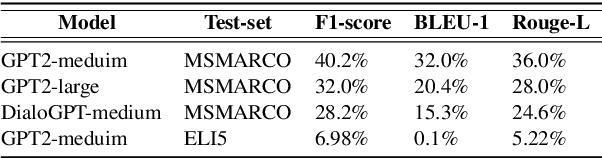
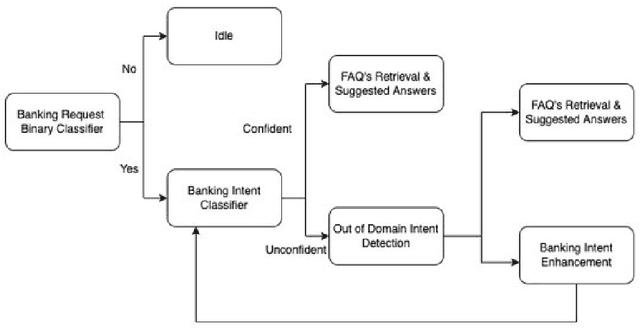
Abstract:Building Agent Assistants that can help improve customer service support requires inputs from industry users and their customers, as well as knowledge about state-of-the-art Natural Language Processing (NLP) technology. We combine expertise from academia and industry to bridge the gap and build task/domain-specific Neural Agent Assistants (NAA) with three high-level components for: (1) Intent Identification, (2) Context Retrieval, and (3) Response Generation. In this paper, we outline the pipeline of the NAA's core system and also present three case studies in which three industry partners successfully adapt the framework to find solutions to their unique challenges. Our findings suggest that a collaborative process is instrumental in spurring the development of emerging NLP models for Conversational AI tasks in industry. The full reference implementation code and results are available at \url{https://github.com/VectorInstitute/NAA}
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge