Ali Pourramezan Fard
AffectNet+: A Database for Enhancing Facial Expression Recognition with Soft-Labels
Oct 29, 2024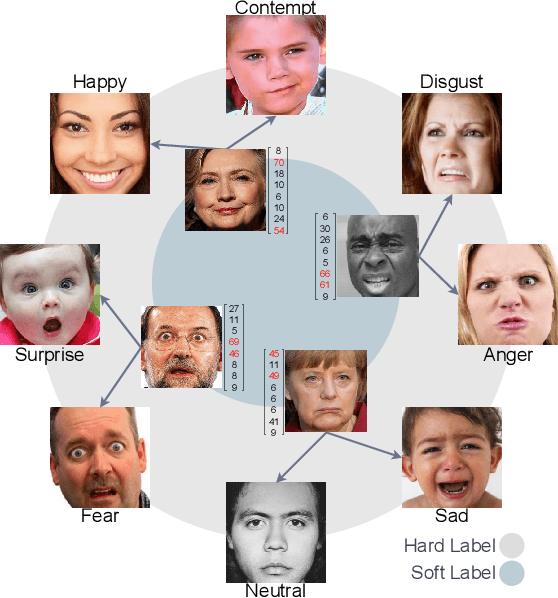
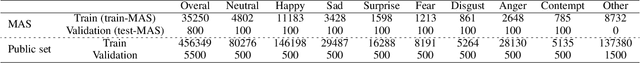
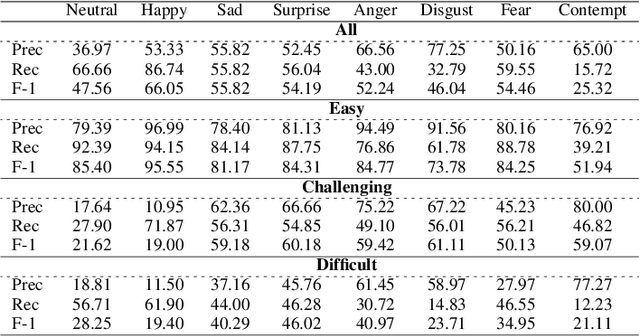
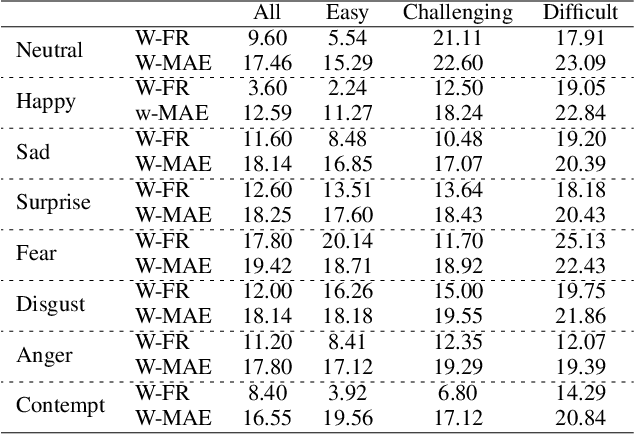
Abstract:Automated Facial Expression Recognition (FER) is challenging due to intra-class variations and inter-class similarities. FER can be especially difficult when facial expressions reflect a mixture of various emotions (aka compound expressions). Existing FER datasets, such as AffectNet, provide discrete emotion labels (hard-labels), where a single category of emotion is assigned to an expression. To alleviate inter- and intra-class challenges, as well as provide a better facial expression descriptor, we propose a new approach to create FER datasets through a labeling method in which an image is labeled with more than one emotion (called soft-labels), each with different confidences. Specifically, we introduce the notion of soft-labels for facial expression datasets, a new approach to affective computing for more realistic recognition of facial expressions. To achieve this goal, we propose a novel methodology to accurately calculate soft-labels: a vector representing the extent to which multiple categories of emotion are simultaneously present within a single facial expression. Finding smoother decision boundaries, enabling multi-labeling, and mitigating bias and imbalanced data are some of the advantages of our proposed method. Building upon AffectNet, we introduce AffectNet+, the next-generation facial expression dataset. This dataset contains soft-labels, three categories of data complexity subsets, and additional metadata such as age, gender, ethnicity, head pose, facial landmarks, valence, and arousal. AffectNet+ will be made publicly accessible to researchers.
A Review of Deep Learning Approaches for Non-Invasive Cognitive Impairment Detection
Oct 25, 2024



Abstract:This review paper explores recent advances in deep learning approaches for non-invasive cognitive impairment detection. We examine various non-invasive indicators of cognitive decline, including speech and language, facial, and motoric mobility. The paper provides an overview of relevant datasets, feature-extracting techniques, and deep-learning architectures applied to this domain. We have analyzed the performance of different methods across modalities and observed that speech and language-based methods generally achieved the highest detection performance. Studies combining acoustic and linguistic features tended to outperform those using a single modality. Facial analysis methods showed promise for visual modalities but were less extensively studied. Most papers focused on binary classification (impaired vs. non-impaired), with fewer addressing multi-class or regression tasks. Transfer learning and pre-trained language models emerged as popular and effective techniques, especially for linguistic analysis. Despite significant progress, several challenges remain, including data standardization and accessibility, model explainability, longitudinal analysis limitations, and clinical adaptation. Lastly, we propose future research directions, such as investigating language-agnostic speech analysis methods, developing multi-modal diagnostic systems, and addressing ethical considerations in AI-assisted healthcare. By synthesizing current trends and identifying key obstacles, this review aims to guide further development of deep learning-based cognitive impairment detection systems to improve early diagnosis and ultimately patient outcomes.
Linguistic-Based Mild Cognitive Impairment Detection Using Informative Loss
Jan 23, 2024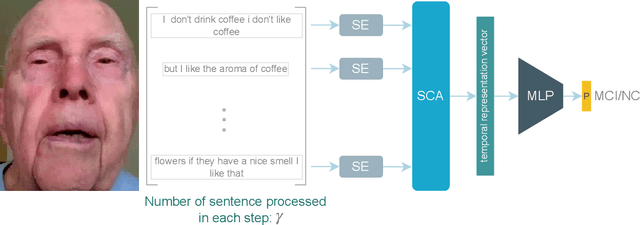

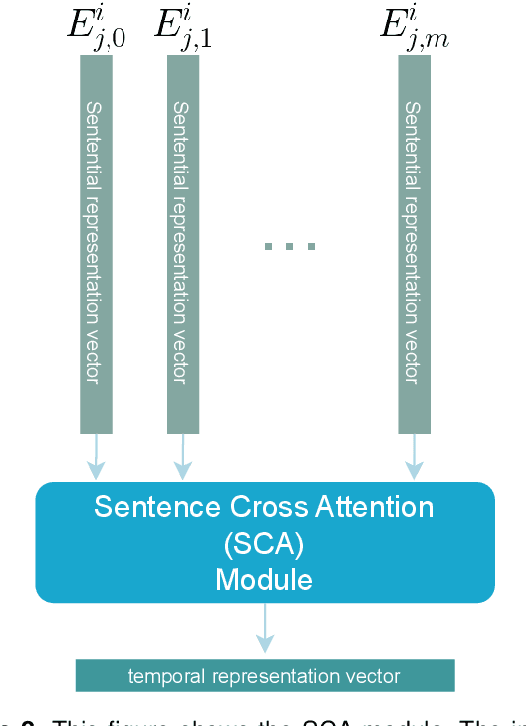
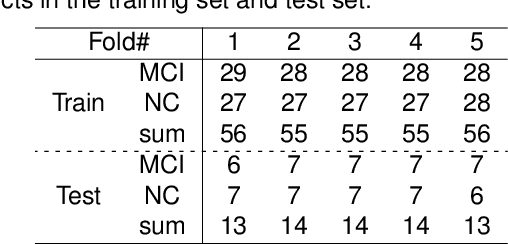
Abstract:This paper presents a deep learning method using Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques, to distinguish between Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Normal Cognitive (NC) conditions in older adults. We propose a framework that analyzes transcripts generated from video interviews collected within the I-CONECT study project, a randomized controlled trial aimed at improving cognitive functions through video chats. Our proposed NLP framework consists of two Transformer-based modules, namely Sentence Embedding (SE) and Sentence Cross Attention (SCA). First, the SE module captures contextual relationships between words within each sentence. Subsequently, the SCA module extracts temporal features from a sequence of sentences. This feature is then used by a Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) for the classification of subjects into MCI or NC. To build a robust model, we propose a novel loss function, called InfoLoss, that considers the reduction in entropy by observing each sequence of sentences to ultimately enhance the classification accuracy. The results of our comprehensive model evaluation using the I-CONECT dataset show that our framework can distinguish between MCI and NC with an average area under the curve of 84.75%.
GANalyzer: Analysis and Manipulation of GANs Latent Space for Controllable Face Synthesis
Feb 02, 2023Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are capable of synthesizing high-quality facial images. Despite their success, GANs do not provide any information about the relationship between the input vectors and the generated images. Currently, facial GANs are trained on imbalanced datasets, which generate less diverse images. For example, more than 77% of 100K images that we randomly synthesized using the StyleGAN3 are classified as Happy, and only around 3% are Angry. The problem even becomes worse when a mixture of facial attributes is desired: less than 1% of the generated samples are Angry Woman, and only around 2% are Happy Black. To address these problems, this paper proposes a framework, called GANalyzer, for the analysis, and manipulation of the latent space of well-trained GANs. GANalyzer consists of a set of transformation functions designed to manipulate latent vectors for a specific facial attribute such as facial Expression, Age, Gender, and Race. We analyze facial attribute entanglement in the latent space of GANs and apply the proposed transformation for editing the disentangled facial attributes. Our experimental results demonstrate the strength of GANalyzer in editing facial attributes and generating any desired faces. We also create and release a balanced photo-realistic human face dataset. Our code is publicly available on GitHub.
ACR Loss: Adaptive Coordinate-based Regression Loss for Face Alignment
Mar 29, 2022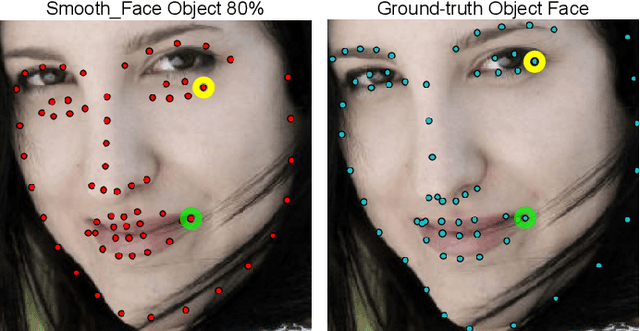


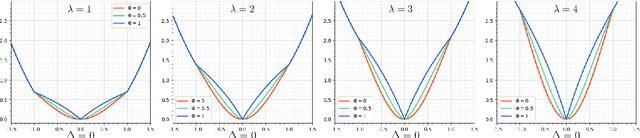
Abstract:Although deep neural networks have achieved reasonable accuracy in solving face alignment, it is still a challenging task, specifically when we deal with facial images, under occlusion, or extreme head poses. Heatmap-based Regression (HBR) and Coordinate-based Regression (CBR) are among the two mainly used methods for face alignment. CBR methods require less computer memory, though their performance is less than HBR methods. In this paper, we propose an Adaptive Coordinate-based Regression (ACR) loss to improve the accuracy of CBR for face alignment. Inspired by the Active Shape Model (ASM), we generate Smooth-Face objects, a set of facial landmark points with less variations compared to the ground truth landmark points. We then introduce a method to estimate the level of difficulty in predicting each landmark point for the network by comparing the distribution of the ground truth landmark points and the corresponding Smooth-Face objects. Our proposed ACR Loss can adaptively modify its curvature and the influence of the loss based on the difficulty level of predicting each landmark point in a face. Accordingly, the ACR Loss guides the network toward challenging points than easier points, which improves the accuracy of the face alignment task. Our extensive evaluation shows the capabilities of the proposed ACR Loss in predicting facial landmark points in various facial images.
XnODR and XnIDR: Two Accurate and Fast Fully Connected Layers For Convolutional Neural Networks
Nov 21, 2021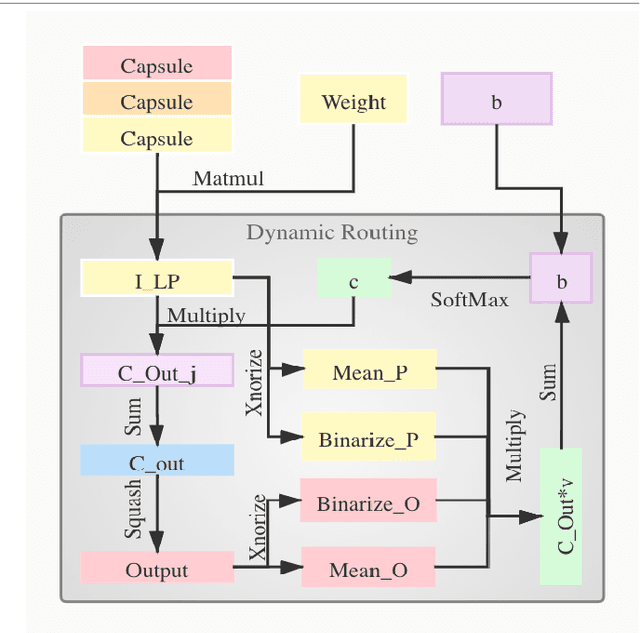
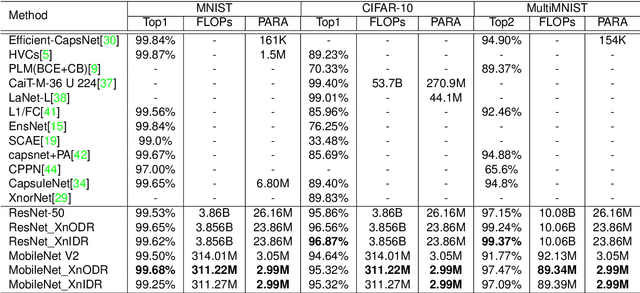
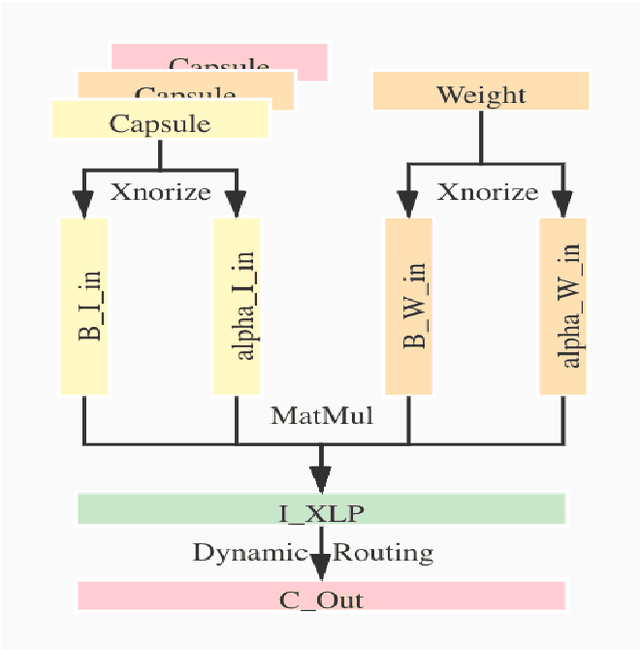
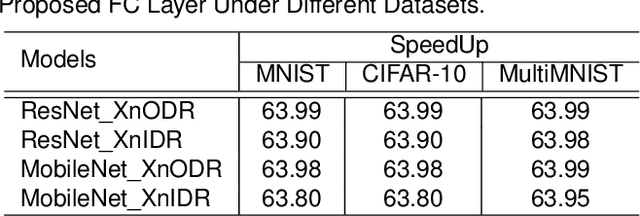
Abstract:Although Capsule Networks show great abilities in defining the position relationship between features in deep neural networks for visual recognition tasks, they are computationally expensive and not suitable for running on mobile devices. The bottleneck is in the computational complexity of the Dynamic Routing mechanism used between capsules. On the other hand, neural networks such as XNOR-Net are fast and computationally efficient but have relatively low accuracy because of their information loss in the binarization process. This paper proposes a new class of Fully Connected (FC) Layers by xnorizing the linear projector outside or inside the Dynamic Routing within the CapsFC layer. Specifically, our proposed FC layers have two versions, XnODR (Xnorizing Linear Projector Outside Dynamic Routing) and XnIDR (Xnorizing Linear Projector Inside Dynamic Routing). To test their generalization, we insert them into MobileNet V2 and ResNet-50 separately. Experiments on three datasets, MNIST, CIFAR-10, MultiMNIST validate their effectiveness. Our experimental results demonstrate that both XnODR and XnIDR help networks to have high accuracy with lower FLOPs and fewer parameters (e.g., 95.32\% accuracy with 2.99M parameters and 311.22M FLOPs on CIFAR-10).
Facial Landmark Points Detection Using Knowledge Distillation-Based Neural Networks
Nov 13, 2021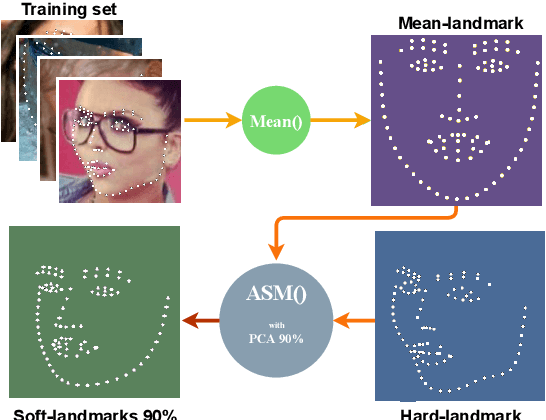
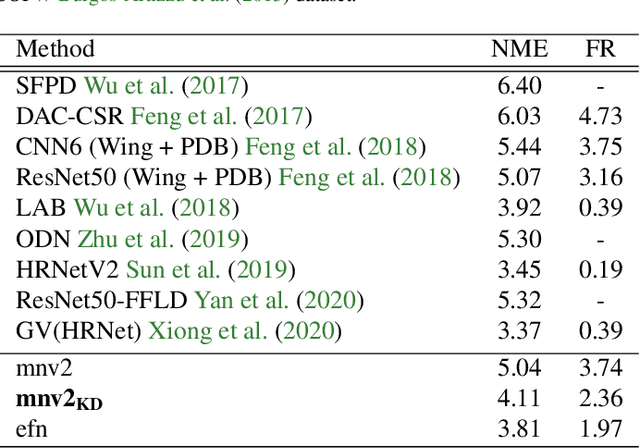

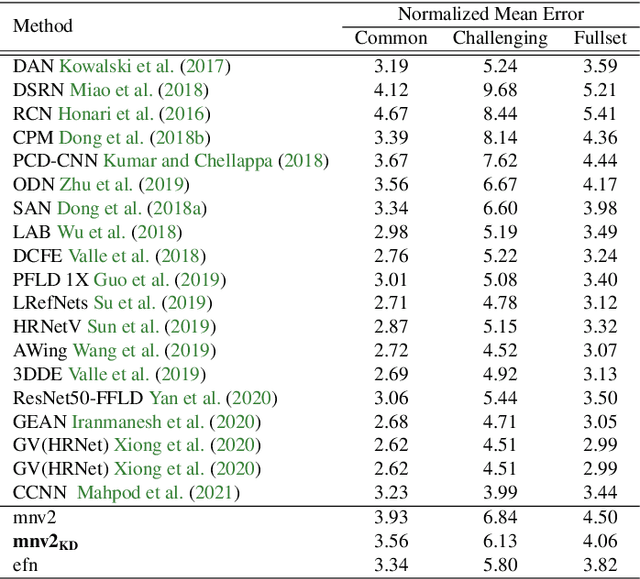
Abstract:Facial landmark detection is a vital step for numerous facial image analysis applications. Although some deep learning-based methods have achieved good performances in this task, they are often not suitable for running on mobile devices. Such methods rely on networks with many parameters, which makes the training and inference time-consuming. Training lightweight neural networks such as MobileNets are often challenging, and the models might have low accuracy. Inspired by knowledge distillation (KD), this paper presents a novel loss function to train a lightweight Student network (e.g., MobileNetV2) for facial landmark detection. We use two Teacher networks, a Tolerant-Teacher and a Tough-Teacher in conjunction with the Student network. The Tolerant-Teacher is trained using Soft-landmarks created by active shape models, while the Tough-Teacher is trained using the ground truth (aka Hard-landmarks) landmark points. To utilize the facial landmark points predicted by the Teacher networks, we define an Assistive Loss (ALoss) for each Teacher network. Moreover, we define a loss function called KD-Loss that utilizes the facial landmark points predicted by the two pre-trained Teacher networks (EfficientNet-b3) to guide the lightweight Student network towards predicting the Hard-landmarks. Our experimental results on three challenging facial datasets show that the proposed architecture will result in a better-trained Student network that can extract facial landmark points with high accuracy.
Deep Active Shape Model for Face Alignment and Pose Estimation in Mobile Environment
Mar 11, 2021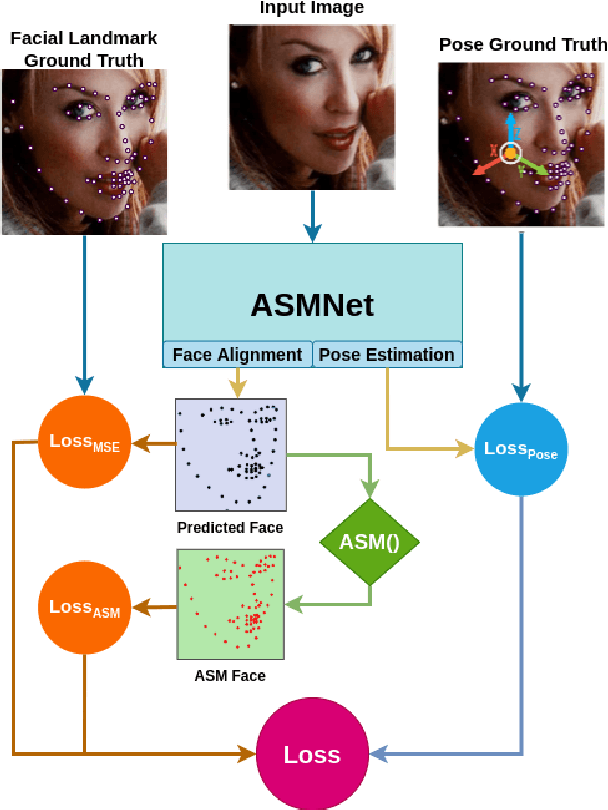
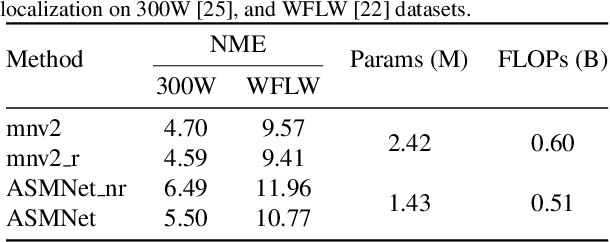
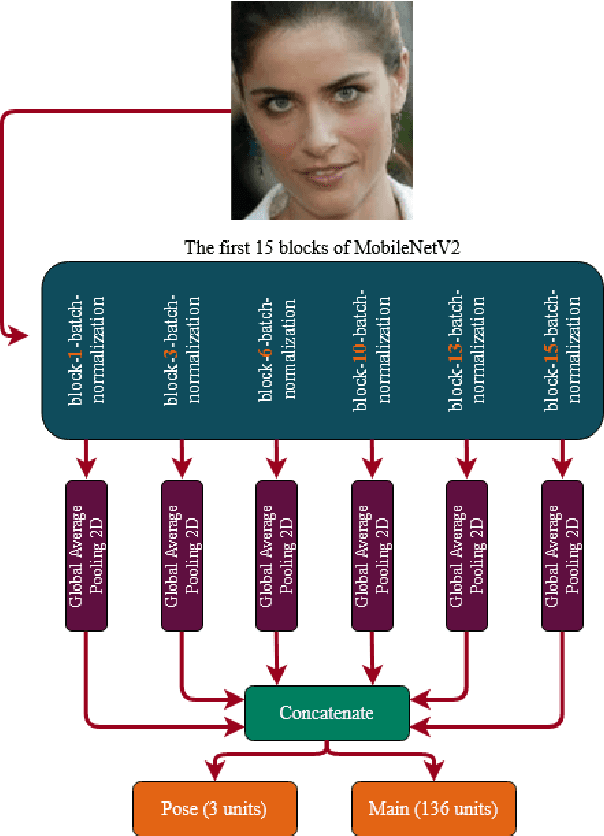
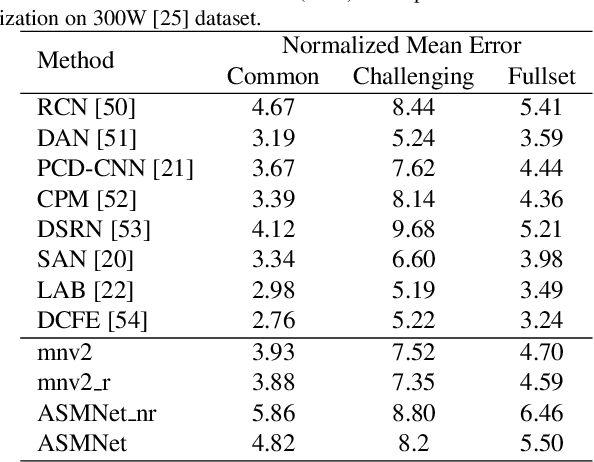
Abstract:Active Shape Model (ASM) is a statistical model of object shapes that represents a target structure. ASM can guide machine learning algorithms to fit a set of points representing an object (e.g., face) onto an image. This paper presents a lightweight Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture with a loss function being assisted by ASM for face alignment and estimating head pose in the wild. We use ASM to first guide the network towards learning the smoother distribution of the facial landmark points. Then, during the training process, inspired by the transfer learning, we gradually harden the regression problem and lead the network towards learning the original landmark points distribution. We define multi-tasks in our loss function that are responsible for detecting facial landmark points, as well as estimating face pose. Learning multiple correlated tasks simultaneously builds synergy and improves the performance of individual tasks. We compare the performance of our proposed CNN, ASMNet with MobileNetV2 (which is about 2 times bigger ASMNet) in both face alignment and pose estimation tasks. Experimental results on challenging datasets show that by using the proposed ASM assisted loss function, ASMNet performance is comparable with MobileNetV2 in face alignment task. Besides, for face pose estimation, ASMNet performs much better than MobileNetV2. Moreover, overall ASMNet achieves an acceptable performance for facial landmark points detection and pose estimation while having a significantly smaller number of parameters and floating-point operations comparing to many CNN-based proposed models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge