Alexandr Kozlov
STC Speaker Recognition Systems for the VOiCES From a Distance Challenge
Apr 12, 2019



Abstract:This paper presents the Speech Technology Center (STC) speaker recognition (SR) systems submitted to the VOiCES From a Distance challenge 2019. The challenge's SR task is focused on the problem of speaker recognition in single channel distant/far-field audio under noisy conditions. In this work we investigate different deep neural networks architectures for speaker embedding extraction to solve the task. We show that deep networks with residual frame level connections outperform more shallow architectures. Simple energy based speech activity detector (SAD) and automatic speech recognition (ASR) based SAD are investigated in this work. We also address the problem of data preparation for robust embedding extractors training. The reverberation for the data augmentation was performed using automatic room impulse response generator. In our systems we used discriminatively trained cosine similarity metric learning model as embedding backend. Scores normalization procedure was applied for each individual subsystem we used. Our final submitted systems were based on the fusion of different subsystems. The results obtained on the VOiCES development and evaluation sets demonstrate effectiveness and robustness of the proposed systems when dealing with distant/far-field audio under noisy conditions.
STC Antispoofing Systems for the ASVspoof2019 Challenge
Apr 11, 2019



Abstract:This paper describes the Speech Technology Center (STC) antispoofing systems submitted to the ASVspoof 2019 challenge. The ASVspoof2019 is the extended version of the previous challenges and includes 2 evaluation conditions: logical access use-case scenario with speech synthesis and voice conversion attack types and physical access use-case scenario with replay attacks. During the challenge we developed anti-spoofing solutions for both scenarios. The proposed systems are implemented using deep learning approach and are based on different types of acoustic features. We enhanced Light CNN architecture previously considered by the authors for replay attacks detection and which performed high spoofing detection quality during the ASVspoof2017 challenge. In particular here we investigate the efficiency of angular margin based softmax activation for training robust deep Light CNN classifier to solve the mentioned-above tasks. Submitted systems achieved EER of 1.86% in logical access scenario and 0.54% in physical access scenario on the evaluation part of the Challenge corpora. High performance obtained for the unknown types of spoofing attacks demonstrates the stability of the offered approach in both evaluation conditions.
On deep speaker embeddings for text-independent speaker recognition
Apr 26, 2018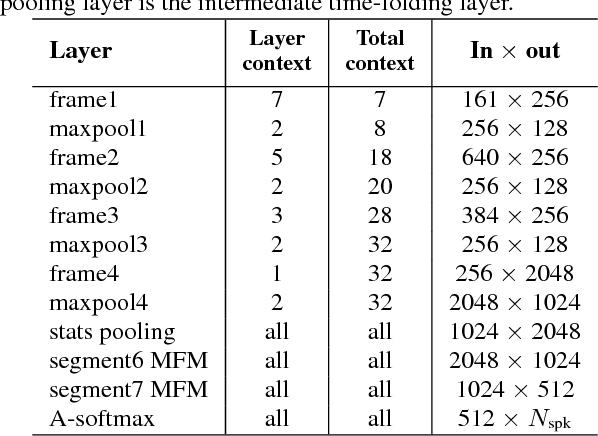
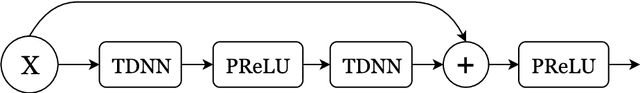
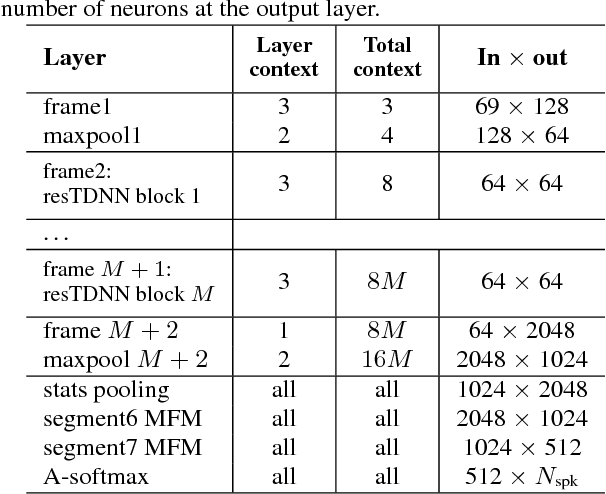
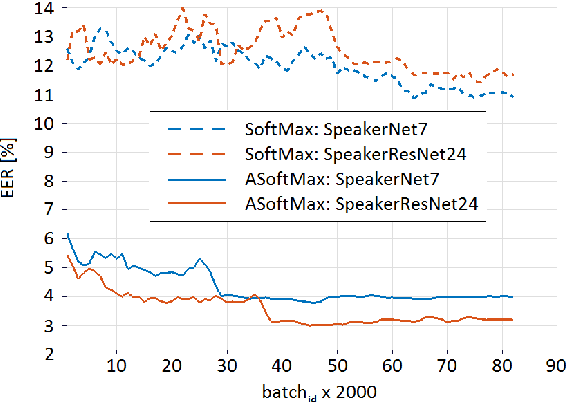
Abstract:We investigate deep neural network performance in the textindependent speaker recognition task. We demonstrate that using angular softmax activation at the last classification layer of a classification neural network instead of a simple softmax activation allows to train a more generalized discriminative speaker embedding extractor. Cosine similarity is an effective metric for speaker verification in this embedding space. We also address the problem of choosing an architecture for the extractor. We found that deep networks with residual frame level connections outperform wide but relatively shallow architectures. This paper also proposes several improvements for previous DNN-based extractor systems to increase the speaker recognition accuracy. We show that the discriminatively trained similarity metric learning approach outperforms the standard LDA-PLDA method as an embedding backend. The results obtained on Speakers in the Wild and NIST SRE 2016 evaluation sets demonstrate robustness of the proposed systems when dealing with close to real-life conditions.
STC Anti-spoofing Systems for the ASVspoof 2015 Challenge
Jul 29, 2015



Abstract:This paper presents the Speech Technology Center (STC) systems submitted to Automatic Speaker Verification Spoofing and Countermeasures (ASVspoof) Challenge 2015. In this work we investigate different acoustic feature spaces to determine reliable and robust countermeasures against spoofing attacks. In addition to the commonly used front-end MFCC features we explored features derived from phase spectrum and features based on applying the multiresolution wavelet transform. Similar to state-of-the-art ASV systems, we used the standard TV-JFA approach for probability modelling in spoofing detection systems. Experiments performed on the development and evaluation datasets of the Challenge demonstrate that the use of phase-related and wavelet-based features provides a substantial input into the efficiency of the resulting STC systems. In our research we also focused on the comparison of the linear (SVM) and nonlinear (DBN) classifiers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge