Ivan Kremnev
On deep speaker embeddings for text-independent speaker recognition
Apr 26, 2018
Abstract:We investigate deep neural network performance in the textindependent speaker recognition task. We demonstrate that using angular softmax activation at the last classification layer of a classification neural network instead of a simple softmax activation allows to train a more generalized discriminative speaker embedding extractor. Cosine similarity is an effective metric for speaker verification in this embedding space. We also address the problem of choosing an architecture for the extractor. We found that deep networks with residual frame level connections outperform wide but relatively shallow architectures. This paper also proposes several improvements for previous DNN-based extractor systems to increase the speaker recognition accuracy. We show that the discriminatively trained similarity metric learning approach outperforms the standard LDA-PLDA method as an embedding backend. The results obtained on Speakers in the Wild and NIST SRE 2016 evaluation sets demonstrate robustness of the proposed systems when dealing with close to real-life conditions.
Deep CNN based feature extractor for text-prompted speaker recognition
Mar 13, 2018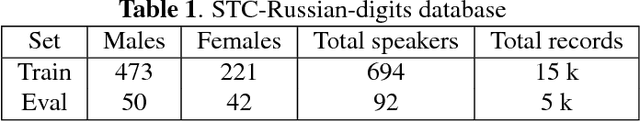
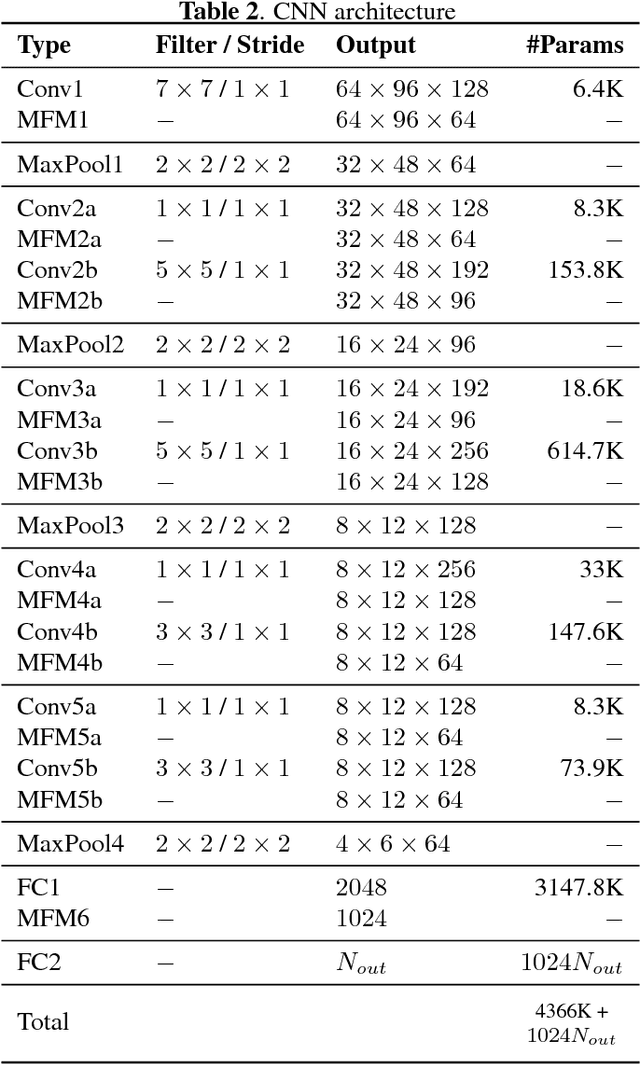
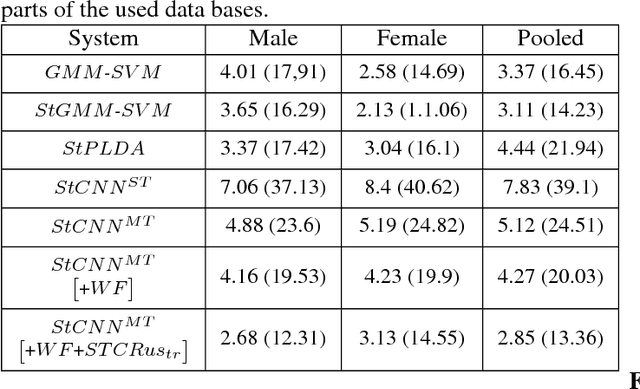
Abstract:Deep learning is still not a very common tool in speaker verification field. We study deep convolutional neural network performance in the text-prompted speaker verification task. The prompted passphrase is segmented into word states - i.e. digits -to test each digit utterance separately. We train a single high-level feature extractor for all states and use cosine similarity metric for scoring. The key feature of our network is the Max-Feature-Map activation function, which acts as an embedded feature selector. By using multitask learning scheme to train the high-level feature extractor we were able to surpass the classic baseline systems in terms of quality and achieved impressive results for such a novice approach, getting 2.85% EER on the RSR2015 evaluation set. Fusion of the proposed and the baseline systems improves this result.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge