Alessandro Serra
The Narrow Gate: Localized Image-Text Communication in Vision-Language Models
Dec 09, 2024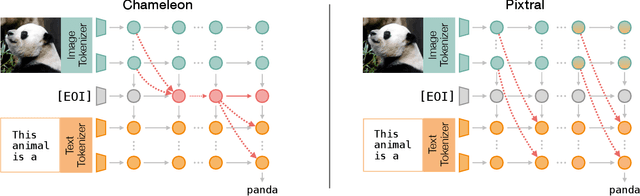
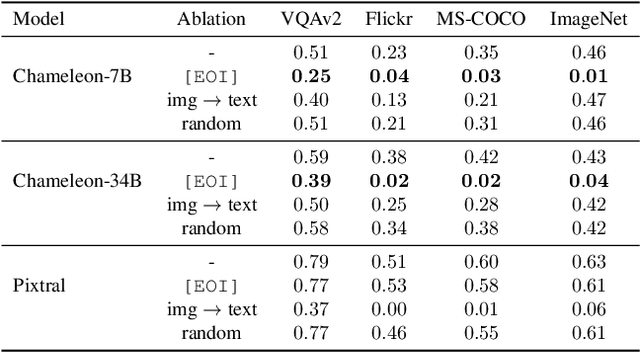
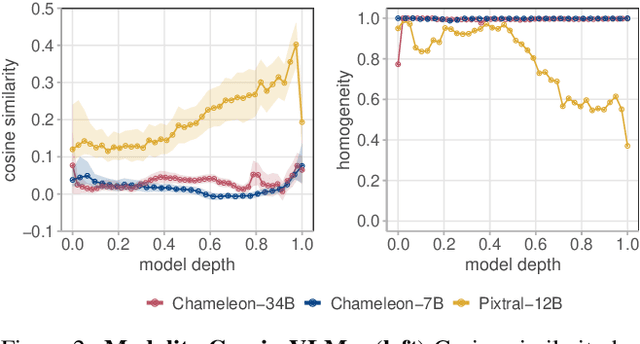
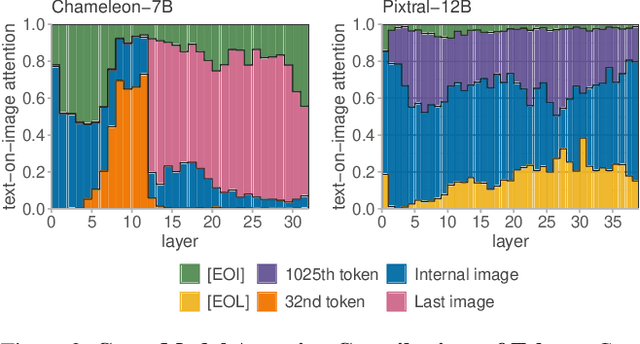
Abstract:Recent advances in multimodal training have significantly improved the integration of image understanding and generation within a unified model. This study investigates how vision-language models (VLMs) handle image-understanding tasks, specifically focusing on how visual information is processed and transferred to the textual domain. We compare VLMs that generate both images and text with those that output only text, highlighting key differences in information flow. We find that in models with multimodal outputs, image and text embeddings are more separated within the residual stream. Additionally, models vary in how information is exchanged from visual to textual tokens. VLMs that only output text exhibit a distributed communication pattern, where information is exchanged through multiple image tokens. In contrast, models trained for image and text generation rely on a single token that acts as a narrow gate for the visual information. We demonstrate that ablating this single token significantly deteriorates performance on image understanding tasks. Furthermore, modifying this token enables effective steering of the image semantics, showing that targeted, local interventions can reliably control the model's global behavior.
The representation landscape of few-shot learning and fine-tuning in large language models
Sep 05, 2024Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) and supervised fine-tuning (SFT) are two common strategies for improving the performance of modern large language models (LLMs) on specific tasks. Despite their different natures, these strategies often lead to comparable performance gains. However, little is known about whether they induce similar representations inside LLMs. We approach this problem by analyzing the probability landscape of their hidden representations in the two cases. More specifically, we compare how LLMs solve the same question-answering task, finding that ICL and SFT create very different internal structures, in both cases undergoing a sharp transition in the middle of the network. In the first half of the network, ICL shapes interpretable representations hierarchically organized according to their semantic content. In contrast, the probability landscape obtained with SFT is fuzzier and semantically mixed. In the second half of the model, the fine-tuned representations develop probability modes that better encode the identity of answers, while the landscape of ICL representations is characterized by less defined peaks. Our approach reveals the diverse computational strategies developed inside LLMs to solve the same task across different conditions, allowing us to make a step towards designing optimal methods to extract information from language models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge