Alberto Poncelas
Using Multiple Subwords to Improve English-Esperanto Automated Literary Translation Quality
Nov 28, 2020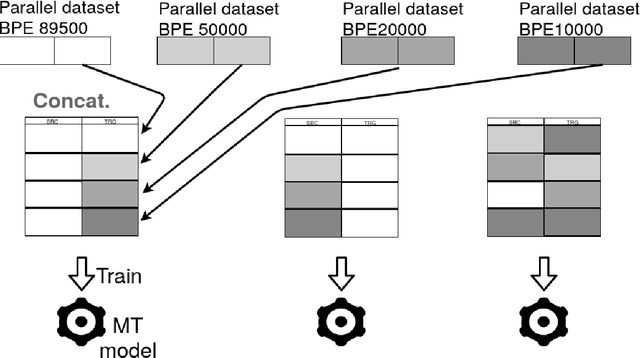



Abstract:Building Machine Translation (MT) systems for low-resource languages remains challenging. For many language pairs, parallel data are not widely available, and in such cases MT models do not achieve results comparable to those seen with high-resource languages. When data are scarce, it is of paramount importance to make optimal use of the limited material available. To that end, in this paper we propose employing the same parallel sentences multiple times, only changing the way the words are split each time. For this purpose we use several Byte Pair Encoding models, with various merge operations used in their configuration. In our experiments, we use this technique to expand the available data and improve an MT system involving a low-resource language pair, namely English-Esperanto. As an additional contribution, we made available a set of English-Esperanto parallel data in the literary domain.
The Impact of Indirect Machine Translation on Sentiment Classification
Aug 25, 2020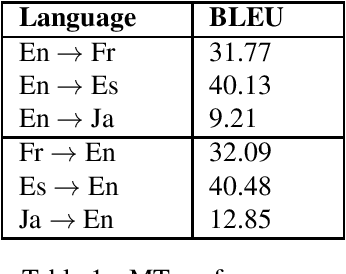
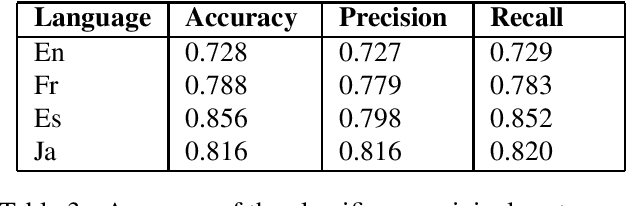
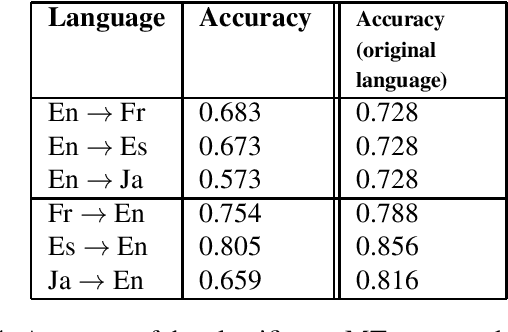
Abstract:Sentiment classification has been crucial for many natural language processing (NLP) applications, such as the analysis of movie reviews, tweets, or customer feedback. A sufficiently large amount of data is required to build a robust sentiment classification system. However, such resources are not always available for all domains or for all languages. In this work, we propose employing a machine translation (MT) system to translate customer feedback into another language to investigate in which cases translated sentences can have a positive or negative impact on an automatic sentiment classifier. Furthermore, as performing a direct translation is not always possible, we explore the performance of automatic classifiers on sentences that have been translated using a pivot MT system. We conduct several experiments using the above approaches to analyse the performance of our proposed sentiment classification system and discuss the advantages and drawbacks of classifying translated sentences.
Selecting Backtranslated Data from Multiple Sources for Improved Neural Machine Translation
May 01, 2020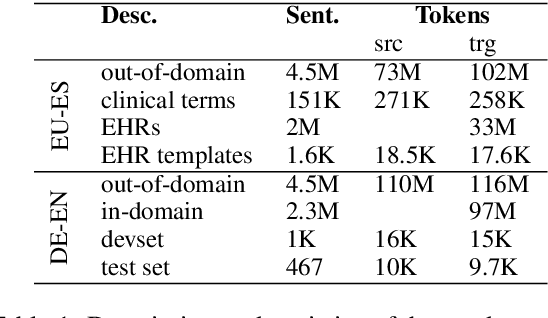
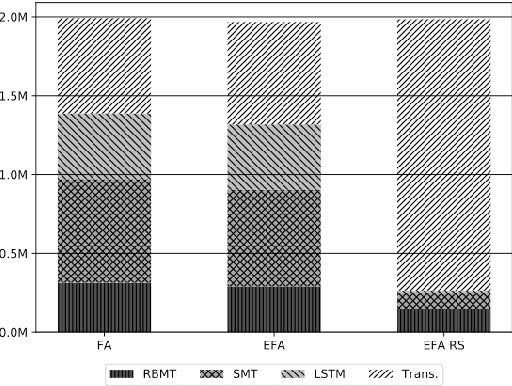

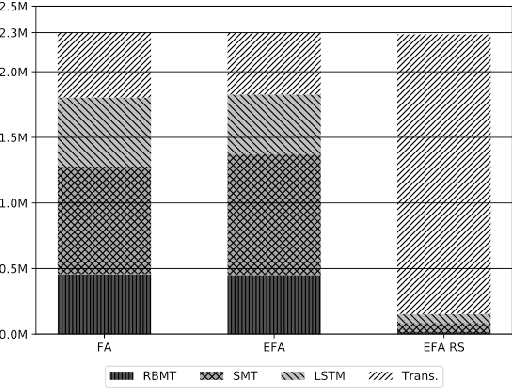
Abstract:Machine translation (MT) has benefited from using synthetic training data originating from translating monolingual corpora, a technique known as backtranslation. Combining backtranslated data from different sources has led to better results than when using such data in isolation. In this work we analyse the impact that data translated with rule-based, phrase-based statistical and neural MT systems has on new MT systems. We use a real-world low-resource use-case (Basque-to-Spanish in the clinical domain) as well as a high-resource language pair (German-to-English) to test different scenarios with backtranslation and employ data selection to optimise the synthetic corpora. We exploit different data selection strategies in order to reduce the amount of data used, while at the same time maintaining high-quality MT systems. We further tune the data selection method by taking into account the quality of the MT systems used for backtranslation and lexical diversity of the resulting corpora. Our experiments show that incorporating backtranslated data from different sources can be beneficial, and that availing of data selection can yield improved performance.
Facilitating Access to Multilingual COVID-19 Information via Neural Machine Translation
May 01, 2020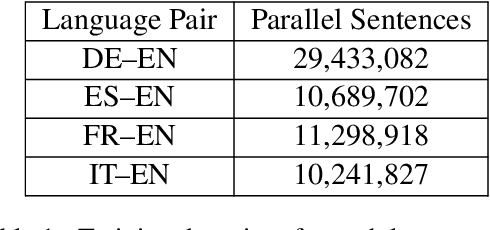
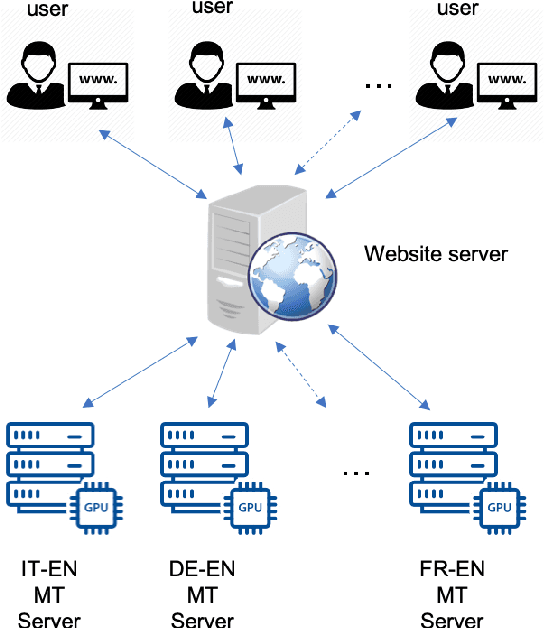

Abstract:Every day, more people are becoming infected and dying from exposure to COVID-19. Some countries in Europe like Spain, France, the UK and Italy have suffered particularly badly from the virus. Others such as Germany appear to have coped extremely well. Both health professionals and the general public are keen to receive up-to-date information on the effects of the virus, as well as treatments that have proven to be effective. In cases where language is a barrier to access of pertinent information, machine translation (MT) may help people assimilate information published in different languages. Our MT systems trained on COVID-19 data are freely available for anyone to use to help translate information published in German, French, Italian, Spanish into English, as well as the reverse direction.
Multiple Segmentations of Thai Sentences for Neural Machine Translation
Apr 23, 2020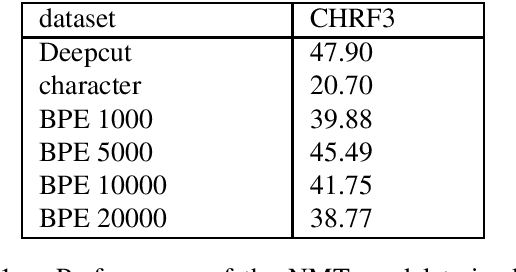
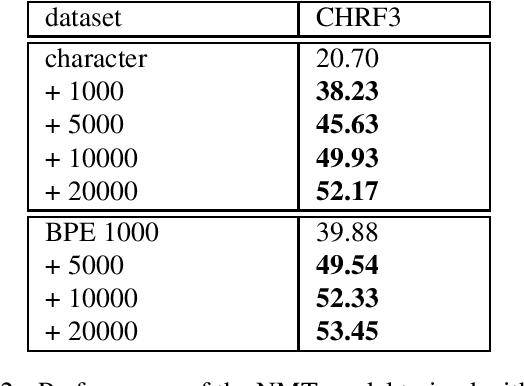

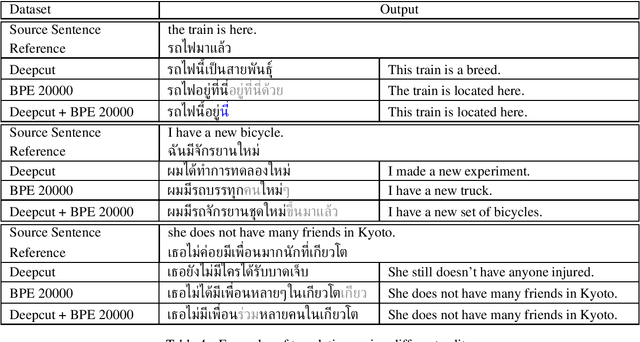
Abstract:Thai is a low-resource language, so it is often the case that data is not available in sufficient quantities to train an Neural Machine Translation (NMT) model which perform to a high level of quality. In addition, the Thai script does not use white spaces to delimit the boundaries between words, which adds more complexity when building sequence to sequence models. In this work, we explore how to augment a set of English--Thai parallel data by replicating sentence-pairs with different word segmentation methods on Thai, as training data for NMT model training. Using different merge operations of Byte Pair Encoding, different segmentations of Thai sentences can be obtained. The experiments show that combining these datasets, performance is improved for NMT models trained with a dataset that has been split using a supervised splitting tool.
A Tool for Facilitating OCR Postediting in Historical Documents
Apr 23, 2020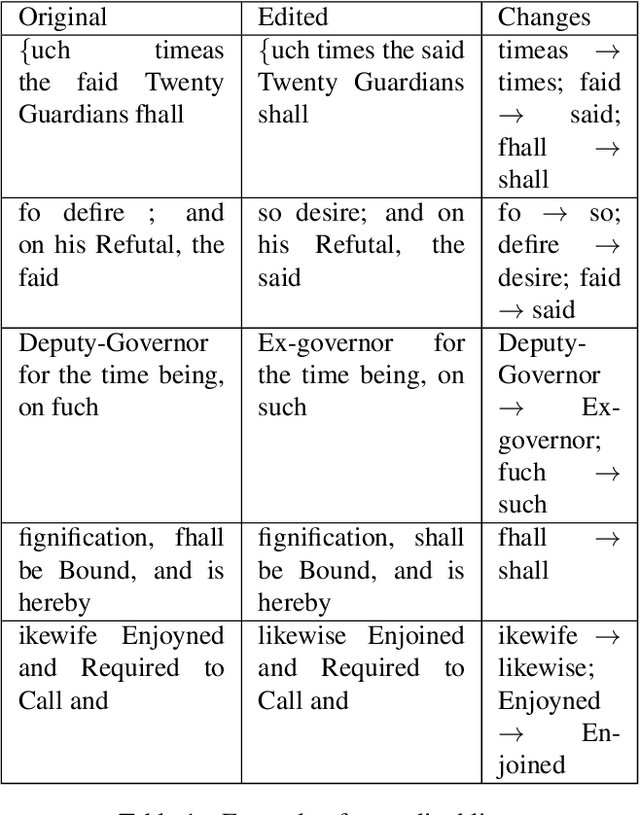

Abstract:Optical character recognition (OCR) for historical documents is a complex procedure subject to a unique set of material issues, including inconsistencies in typefaces and low quality scanning. Consequently, even the most sophisticated OCR engines produce errors. This paper reports on a tool built for postediting the output of Tesseract, more specifically for correcting common errors in digitized historical documents. The proposed tool suggests alternatives for word forms not found in a specified vocabulary. The assumed error is replaced by a presumably correct alternative in the post-edition based on the scores of a Language Model (LM). The tool is tested on a chapter of the book An Essay Towards Regulating the Trade and Employing the Poor of this Kingdom (Cary ,1719). As demonstrated below, the tool is successful in correcting a number of common errors. If sometimes unreliable, it is also transparent and subject to human intervention.
Transductive Data-Selection Algorithms for Fine-Tuning Neural Machine Translation
Oct 08, 2019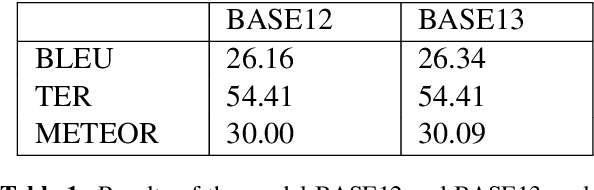
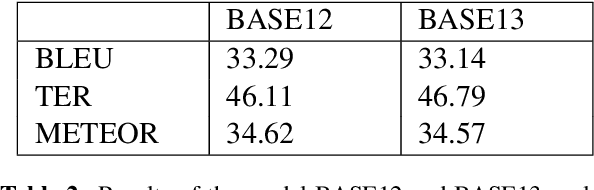
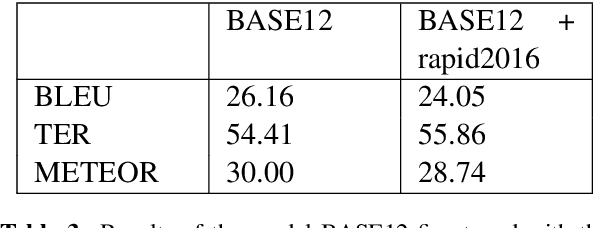
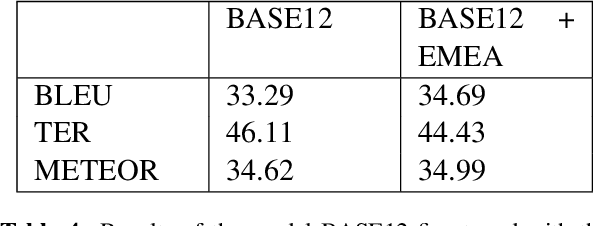
Abstract:Machine Translation models are trained to translate a variety of documents from one language into another. However, models specifically trained for a particular characteristics of the documents tend to perform better. Fine-tuning is a technique for adapting an NMT model to some domain. In this work, we want to use this technique to adapt the model to a given test set. In particular, we are using transductive data selection algorithms which take advantage the information of the test set to retrieve sentences from a larger parallel set. In cases where the model is available at translation time (when the test set is provided), it can be adapted with a small subset of data, thereby achieving better performance than a generic model or a domain-adapted model.
* Proceedings of The 8th Workshop on Patent and Scientific Literature Translation, 2019, pages 13--23, Dublin
Selecting Artificially-Generated Sentences for Fine-Tuning Neural Machine Translation
Sep 26, 2019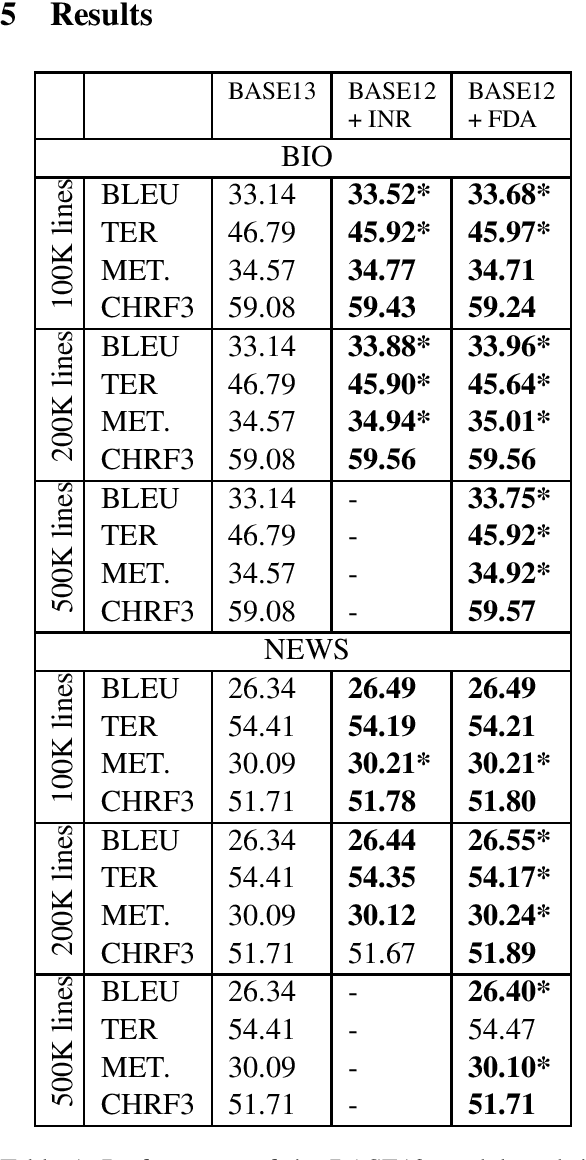
Abstract:Neural Machine Translation (NMT) models tend to achieve best performance when larger sets of parallel sentences are provided for training. For this reason, augmenting the training set with artificially-generated sentence pairs can boost performance. Nonetheless, the performance can also be improved with a small number of sentences if they are in the same domain as the test set. Accordingly, we want to explore the use of artificially-generated sentences along with data-selection algorithms to improve German-to-English NMT models trained solely with authentic data. In this work, we show how artificially-generated sentences can be more beneficial than authentic pairs, and demonstrate their advantages when used in combination with data-selection algorithms.
* Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Natural Language Generation (INLG 2019)
Combining SMT and NMT Back-Translated Data for Efficient NMT
Sep 09, 2019



Abstract:Neural Machine Translation (NMT) models achieve their best performance when large sets of parallel data are used for training. Consequently, techniques for augmenting the training set have become popular recently. One of these methods is back-translation (Sennrich et al., 2016), which consists on generating synthetic sentences by translating a set of monolingual, target-language sentences using a Machine Translation (MT) model. Generally, NMT models are used for back-translation. In this work, we analyze the performance of models when the training data is extended with synthetic data using different MT approaches. In particular we investigate back-translated data generated not only by NMT but also by Statistical Machine Translation (SMT) models and combinations of both. The results reveal that the models achieve the best performances when the training set is augmented with back-translated data created by merging different MT approaches.
Adaptation of Machine Translation Models with Back-translated Data using Transductive Data Selection Methods
Jun 18, 2019

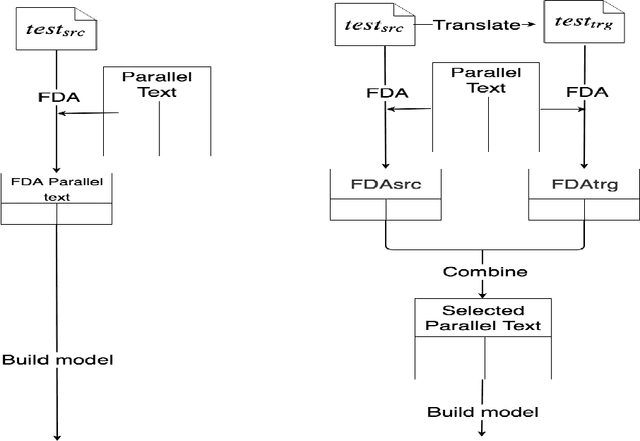

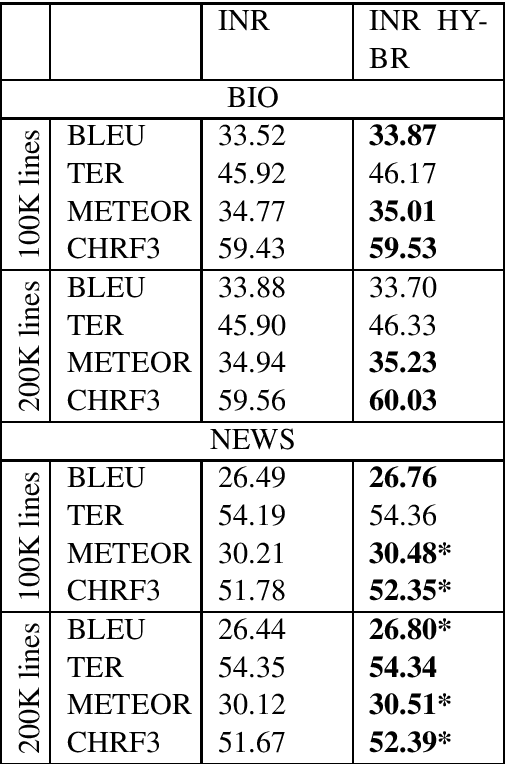
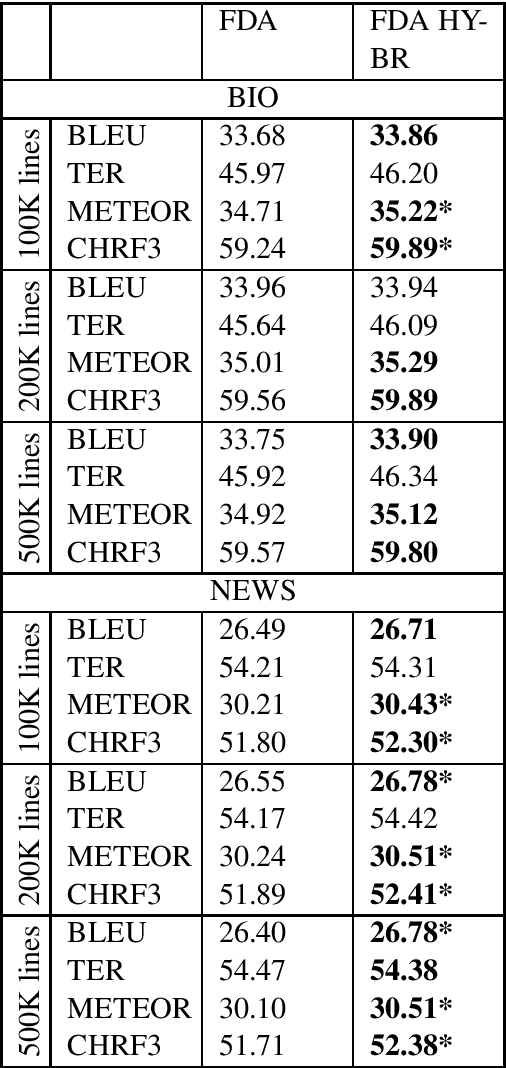
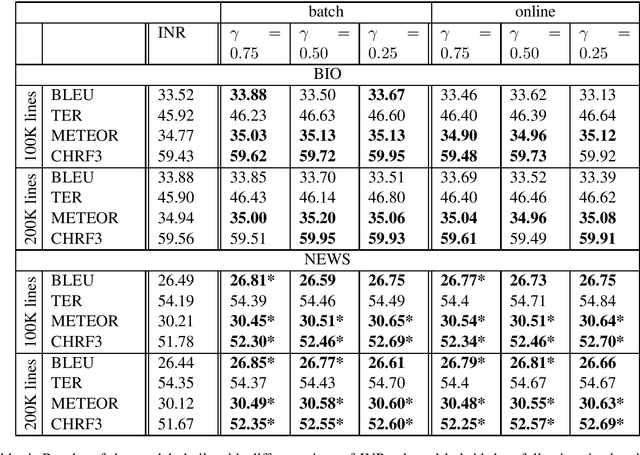
Abstract:Data selection has proven its merit for improving Neural Machine Translation (NMT), when applied to authentic data. But the benefit of using synthetic data in NMT training, produced by the popular back-translation technique, raises the question if data selection could also be useful for synthetic data? In this work we use Infrequent N-gram Recovery (INR) and Feature Decay Algorithms (FDA), two transductive data selection methods to obtain subsets of sentences from synthetic data. These methods ensure that selected sentences share n-grams with the test set so the NMT model can be adapted to translate it. Performing data selection on back-translated data creates new challenges as the source-side may contain noise originated by the model used in the back-translation. Hence, finding n-grams present in the test set become more difficult. Despite that, in our work we show that adapting a model with a selection of synthetic data is an useful approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge