Selecting Artificially-Generated Sentences for Fine-Tuning Neural Machine Translation
Paper and Code
Sep 26, 2019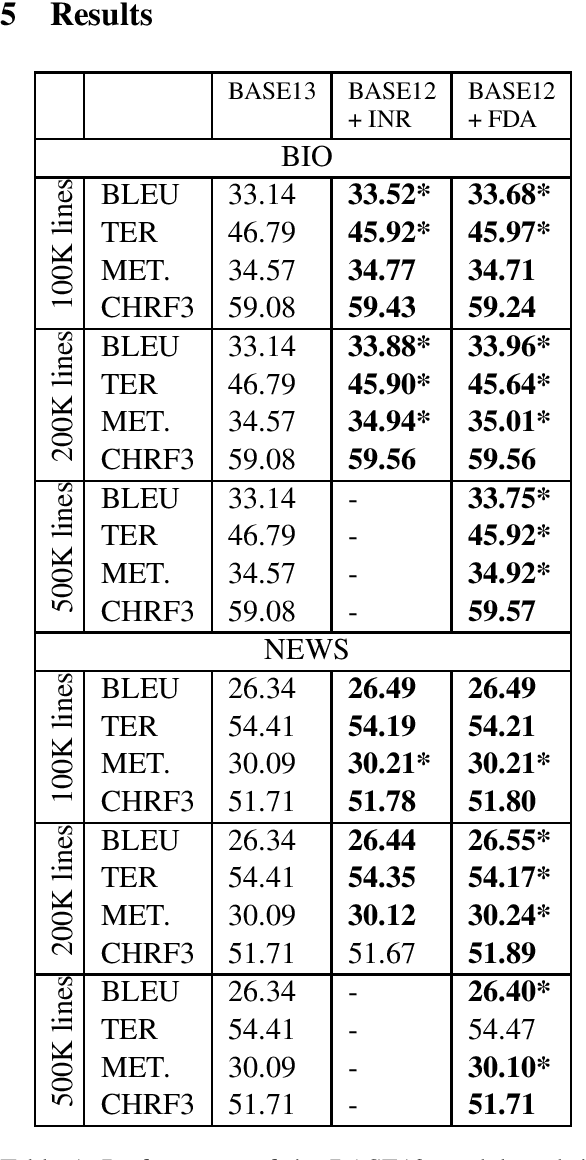
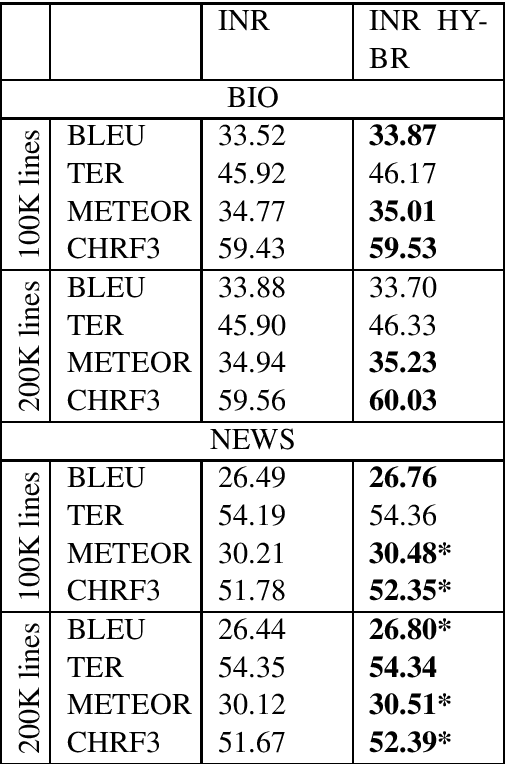
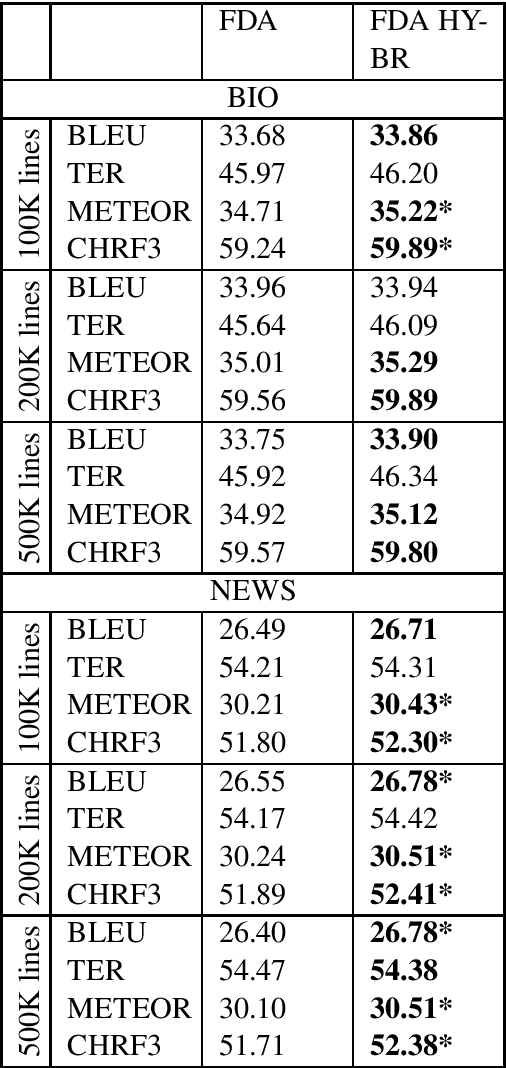
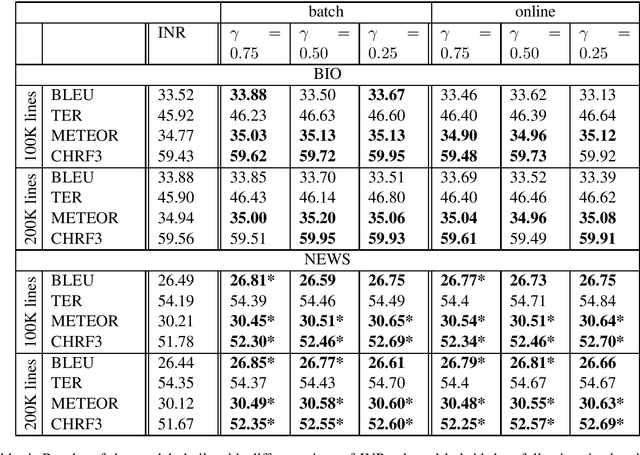
Neural Machine Translation (NMT) models tend to achieve best performance when larger sets of parallel sentences are provided for training. For this reason, augmenting the training set with artificially-generated sentence pairs can boost performance. Nonetheless, the performance can also be improved with a small number of sentences if they are in the same domain as the test set. Accordingly, we want to explore the use of artificially-generated sentences along with data-selection algorithms to improve German-to-English NMT models trained solely with authentic data. In this work, we show how artificially-generated sentences can be more beneficial than authentic pairs, and demonstrate their advantages when used in combination with data-selection algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge