Ajay Kulkarni
A Review of Cybersecurity Incidents in the Food and Agriculture Sector
Mar 12, 2024Abstract:The increasing utilization of emerging technologies in the Food & Agriculture (FA) sector has heightened the need for security to minimize cyber risks. Considering this aspect, this manuscript reviews disclosed and documented cybersecurity incidents in the FA sector. For this purpose, thirty cybersecurity incidents were identified, which took place between July 2011 and April 2023. The details of these incidents are reported from multiple sources such as: the private industry and flash notifications generated by the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), internal reports from the affected organizations, and available media sources. Considering the available information, a brief description of the security threat, ransom amount, and impact on the organization are discussed for each incident. This review reports an increased frequency of cybersecurity threats to the FA sector. To minimize these cyber risks, popular cybersecurity frameworks and recent agriculture-specific cybersecurity solutions are also discussed. Further, the need for AI assurance in the FA sector is explained, and the Farmer-Centered AI (FCAI) framework is proposed. The main aim of the FCAI framework is to support farmers in decision-making for agricultural production, by incorporating AI assurance. Lastly, the effects of the reported cyber incidents on other critical infrastructures, food security, and the economy are noted, along with specifying the open issues for future development.
Rationalization for Explainable NLP: A Survey
Jan 21, 2023



Abstract:Recent advances in deep learning have improved the performance of many Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks such as translation, question-answering, and text classification. However, this improvement comes at the expense of model explainability. Black-box models make it difficult to understand the internals of a system and the process it takes to arrive at an output. Numerical (LIME, Shapley) and visualization (saliency heatmap) explainability techniques are helpful; however, they are insufficient because they require specialized knowledge. These factors led rationalization to emerge as a more accessible explainable technique in NLP. Rationalization justifies a model's output by providing a natural language explanation (rationale). Recent improvements in natural language generation have made rationalization an attractive technique because it is intuitive, human-comprehensible, and accessible to non-technical users. Since rationalization is a relatively new field, it is disorganized. As the first survey, rationalization literature in NLP from 2007-2022 is analyzed. This survey presents available methods, explainable evaluations, code, and datasets used across various NLP tasks that use rationalization. Further, a new subfield in Explainable AI (XAI), namely, Rational AI (RAI), is introduced to advance the current state of rationalization. A discussion on observed insights, challenges, and future directions is provided to point to promising research opportunities.
Measuring Outcomes in Healthcare Economics using Artificial Intelligence: with Application to Resource Management
Nov 15, 2021Abstract:The quality of service in healthcare is constantly challenged by outlier events such as pandemics (i.e. Covid-19) and natural disasters (such as hurricanes and earthquakes). In most cases, such events lead to critical uncertainties in decision making, as well as in multiple medical and economic aspects at a hospital. External (geographic) or internal factors (medical and managerial), lead to shifts in planning and budgeting, but most importantly, reduces confidence in conventional processes. In some cases, support from other hospitals proves necessary, which exacerbates the planning aspect. This manuscript presents three data-driven methods that provide data-driven indicators to help healthcare managers organize their economics and identify the most optimum plan for resources allocation and sharing. Conventional decision-making methods fall short in recommending validated policies for managers. Using reinforcement learning, genetic algorithms, traveling salesman, and clustering, we experimented with different healthcare variables and presented tools and outcomes that could be applied at health institutes. Experiments are performed; the results are recorded, evaluated, and presented.
* This paper is published at Cambridge University Press Journal of Data & Policy
Foundations of data imbalance and solutions for a data democracy
Jul 30, 2021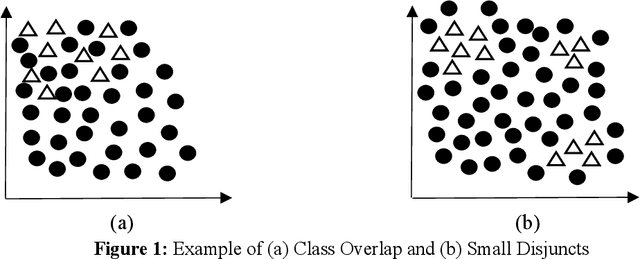

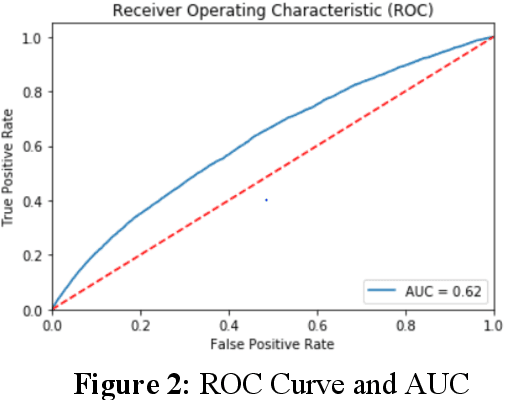

Abstract:Dealing with imbalanced data is a prevalent problem while performing classification on the datasets. Many times, this problem contributes to bias while making decisions or implementing policies. Thus, it is vital to understand the factors which cause imbalance in the data (or class imbalance). Such hidden biases and imbalances can lead to data tyranny and a major challenge to a data democracy. In this chapter, two essential statistical elements are resolved: the degree of class imbalance and the complexity of the concept; solving such issues helps in building the foundations of a data democracy. Furthermore, statistical measures which are appropriate in these scenarios are discussed and implemented on a real-life dataset (car insurance claims). In the end, popular data-level methods such as random oversampling, random undersampling, synthetic minority oversampling technique, Tomek link, and others are implemented in Python, and their performance is compared.
Towards Understanding the Impact of Real-Time AI-Powered Educational Dashboards on Providing Guidance to Instructors
Jul 30, 2021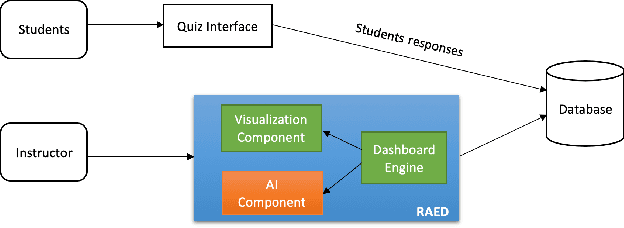
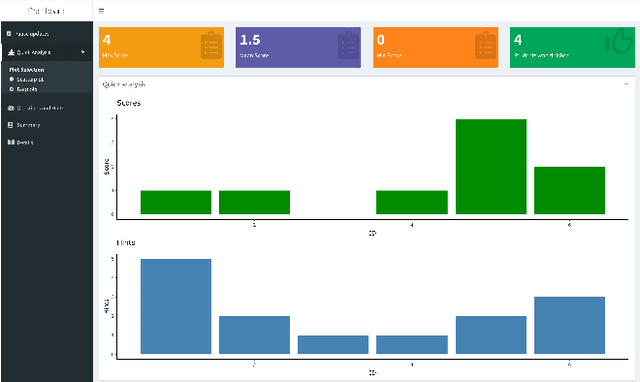
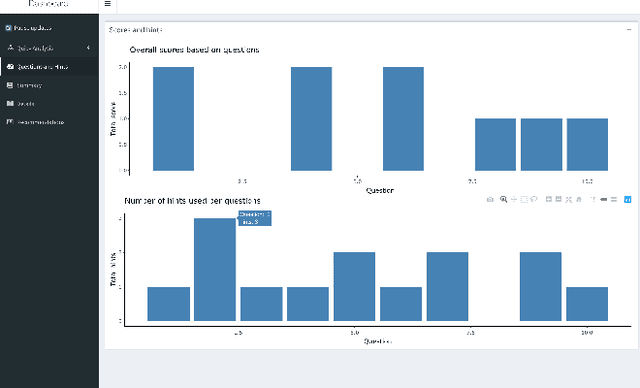
Abstract:The objectives of this ongoing research are to build Real-Time AI-Powered Educational Dashboard (RAED) as a decision support tool for instructors, and to measure its impact on them while making decisions. Current developments in AI can be combined with the educational dashboards to make them AI-Powered. Thus, AI can help in providing recommendations based on the students' performances. AI-Powered educational dashboards can also assist instructors in tracking real-time student activities. In this ongoing research, our aim is to develop the AI component as well as improve the existing design component of the RAED. Further, we will conduct experiments to study its impact on instructors, and understand how much they trust RAED to guide them while making decisions. This paper elaborates on the ongoing research and future direction.
Demonstrating REACT: a Real-time Educational AI-powered Classroom Tool
Jul 30, 2021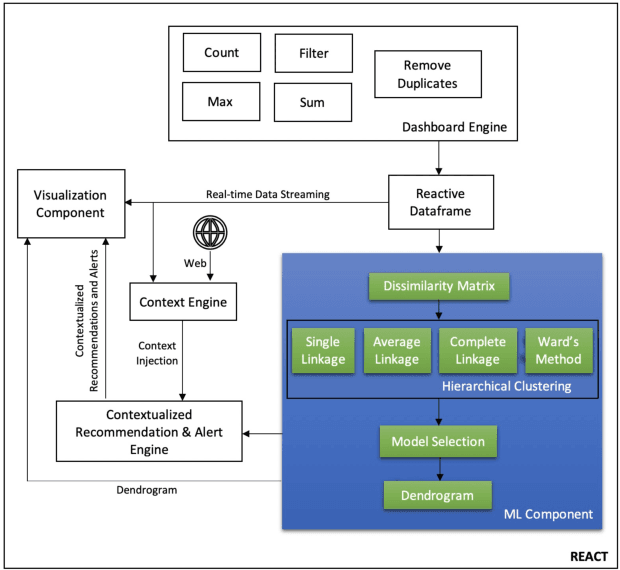
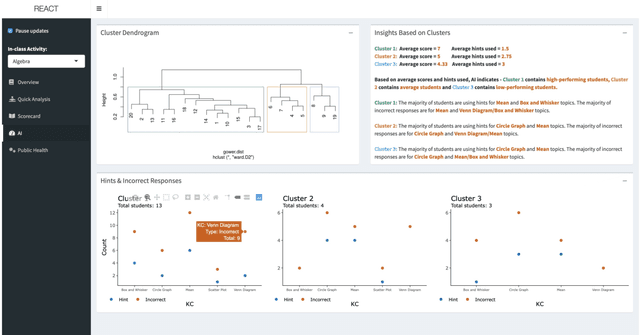
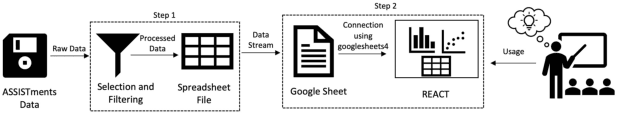
Abstract:We present a demonstration of REACT, a new Real-time Educational AI-powered Classroom Tool that employs EDM techniques for supporting the decision-making process of educators. REACT is a data-driven tool with a user-friendly graphical interface. It analyzes students' performance data and provides context-based alerts as well as recommendations to educators for course planning. Furthermore, it incorporates model-agnostic explanations for bringing explainability and interpretability in the process of decision making. This paper demonstrates a use case scenario of our proposed tool using a real-world dataset and presents the design of its architecture and user interface. This demonstration focuses on the agglomerative clustering of students based on their performance (i.e., incorrect responses and hints used) during an in-class activity. This formation of clusters of students with similar strengths and weaknesses may help educators to improve their course planning by identifying at-risk students, forming study groups, or encouraging tutoring between students of different strengths.
Context-Driven Data Mining through Bias Removal and Data Incompleteness Mitigation
Oct 19, 2019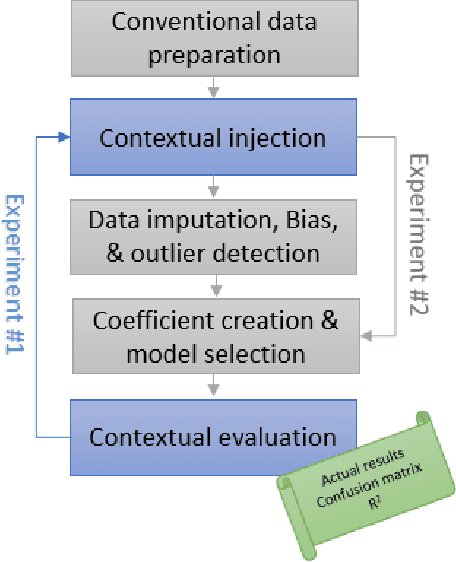
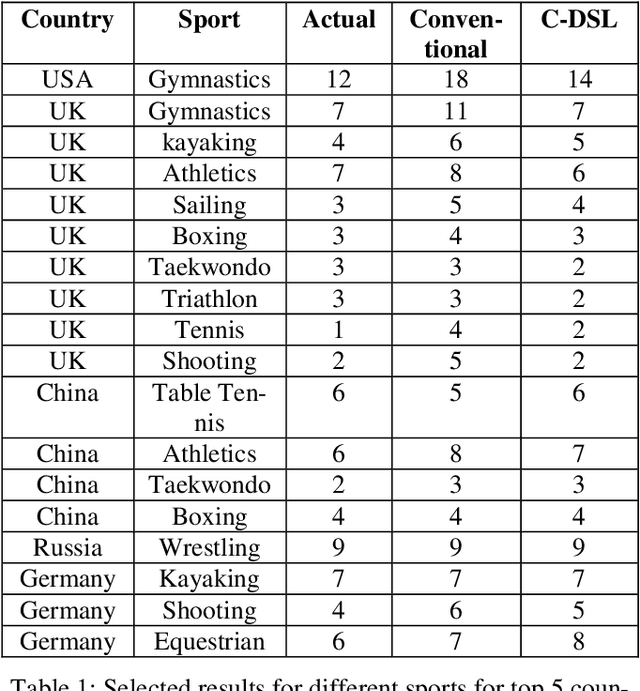
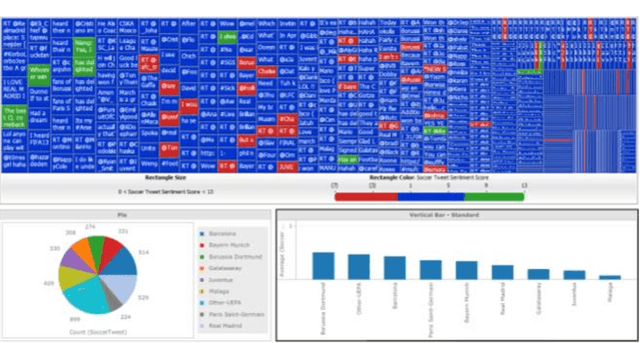

Abstract:The results of data mining endeavors are majorly driven by data quality. Throughout these deployments, serious show-stopper problems are still unresolved, such as: data collection ambiguities, data imbalance, hidden biases in data, the lack of domain information, and data incompleteness. This paper is based on the premise that context can aid in mitigating these issues. In a traditional data science lifecycle, context is not considered. Context-driven Data Science Lifecycle (C-DSL); the main contribution of this paper, is developed to address these challenges. Two case studies (using data-sets from sports events) are developed to test C-DSL. Results from both case studies are evaluated using common data mining metrics such as: coefficient of determination (R2 value) and confusion matrices. The work presented in this paper aims to re-define the lifecycle and introduce tangible improvements to its outcomes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge