Ahmed Aldahdooh
Univ. Rennes, INSA Rennes, CNRS, IETR - UMR 6164, Rennes, France
Transformer based Models for Unsupervised Anomaly Segmentation in Brain MR Images
Jul 05, 2022
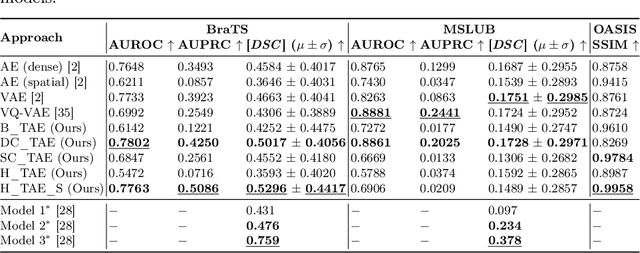


Abstract:The quality of patient care associated with diagnostic radiology is proportionate to a physician workload. Segmentation is a fundamental limiting precursor to diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Advances in Machine Learning (ML) aim to increase diagnostic efficiency to replace single application with generalized algorithms. In Unsupervised Anomaly Detection (UAD), Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based Autoencoders (AEs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) are considered as a de facto approach for reconstruction based anomaly segmentation. Looking for anomalous regions in medical images is one of the main applications that use anomaly segmentation. The restricted receptive field in CNNs limit the CNN to model the global context and hence if the anomalous regions cover parts of the image, the CNN-based AEs are not capable to bring semantic understanding of the image. On the other hand, Vision Transformers (ViTs) have emerged as a competitive alternative to CNNs. It relies on the self-attention mechanism that is capable to relate image patches to each other. To reconstruct a coherent and more realistic image, in this work, we investigate Transformer capabilities in building AEs for reconstruction based UAD task. We focus on anomaly segmentation for Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and present five Transformer-based models while enabling segmentation performance comparable or superior to State-of-The-Art (SOTA) models. The source code is available on Github https://github.com/ahmedgh970/Transformers_Unsupervised_Anomaly_Segmentation.git
Federated Adversarial Training with Transformers
Jun 05, 2022



Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has emerged to enable global model training over distributed clients' data while preserving its privacy. However, the global trained model is vulnerable to the evasion attacks especially, the adversarial examples (AEs), carefully crafted samples to yield false classification. Adversarial training (AT) is found to be the most promising approach against evasion attacks and it is widely studied for convolutional neural network (CNN). Recently, vision transformers have been found to be effective in many computer vision tasks. To the best of the authors' knowledge, there is no work that studied the feasibility of AT in a FL process for vision transformers. This paper investigates such feasibility with different federated model aggregation methods and different vision transformer models with different tokenization and classification head techniques. In order to improve the robust accuracy of the models with the not independent and identically distributed (Non-IID), we propose an extension to FedAvg aggregation method, called FedWAvg. By measuring the similarities between the last layer of the global model and the last layer of the client updates, FedWAvg calculates the weights to aggregate the local models updates. The experiments show that FedWAvg improves the robust accuracy when compared with other state-of-the-art aggregation methods.
Reveal of Vision Transformers Robustness against Adversarial Attacks
Jun 07, 2021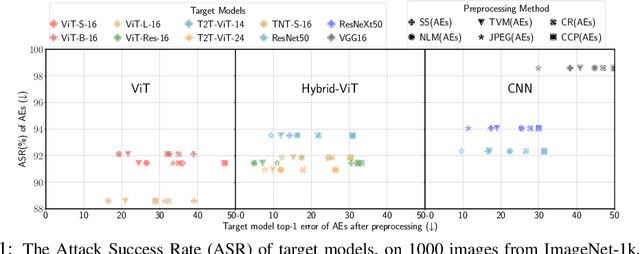
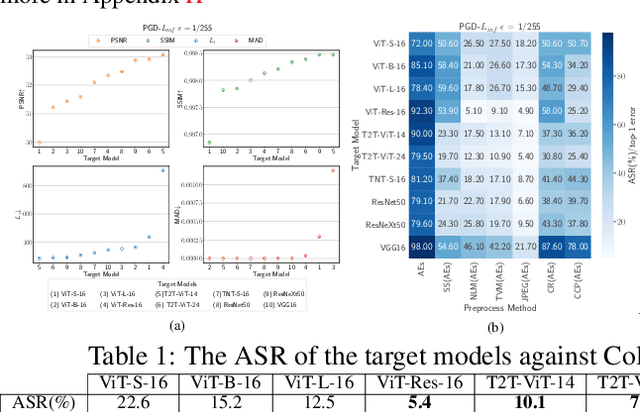
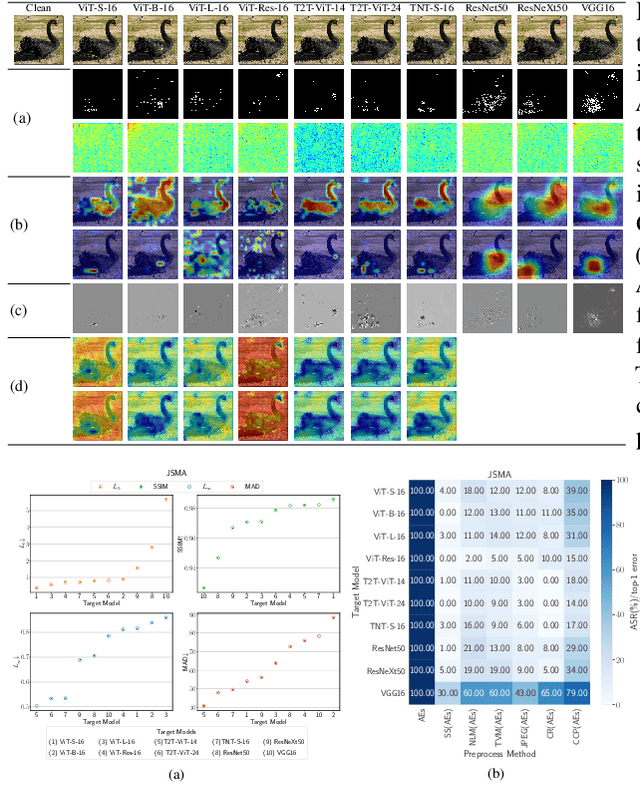
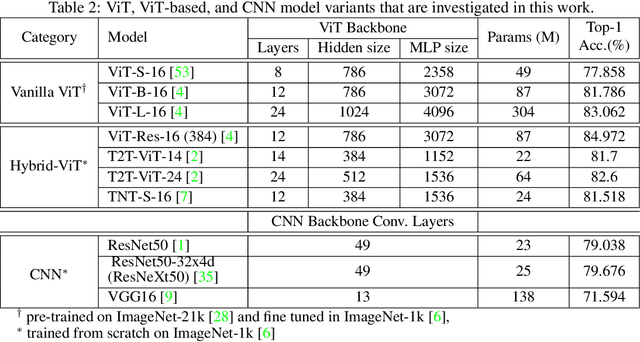
Abstract:Attention-based networks have achieved state-of-the-art performance in many computer vision tasks, such as image classification. Unlike Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), the major part of the vanilla Vision Transformer (ViT) is the attention block that brings the power of mimicking the global context of the input image. This power is data hunger and hence, the larger the training data the better the performance. To overcome this limitation, many ViT-based networks, or hybrid-ViT, have been proposed to include local context during the training. The robustness of ViTs and its variants against adversarial attacks has not been widely invested in the literature. Some robustness attributes were revealed in few previous works and hence, more insight robustness attributes are yet unrevealed. This work studies the robustness of ViT variants 1) against different $L_p$-based adversarial attacks in comparison with CNNs and 2) under Adversarial Examples (AEs) after applying preprocessing defense methods. To that end, we run a set of experiments on 1000 images from ImageNet-1k and then provide an analysis that reveals that vanilla ViT or hybrid-ViT are more robust than CNNs. For instance, we found that 1) Vanilla ViTs or hybrid-ViTs are more robust than CNNs under $L_0$, $L_1$, $L_2$, $L_\infty$-based, and Color Channel Perturbations (CCP) attacks. 2) Vanilla ViTs are not responding to preprocessing defenses that mainly reduce the high frequency components while, hybrid-ViTs are more responsive to such defense. 3) CCP can be used as a preprocessing defense and larger ViT variants are found to be more responsive than other models. Furthermore, feature maps, attention maps, and Grad-CAM visualization jointly with image quality measures, and perturbations' energy spectrum are provided for an insight understanding of attention-based models.
Adversarial Example Detection for DNN Models: A Review
May 01, 2021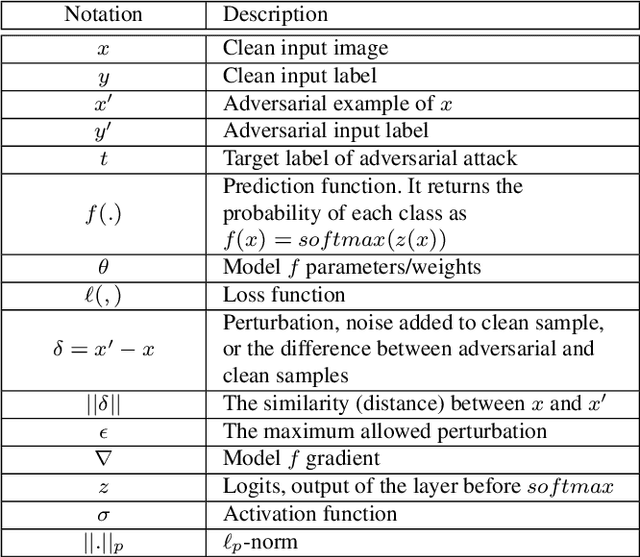
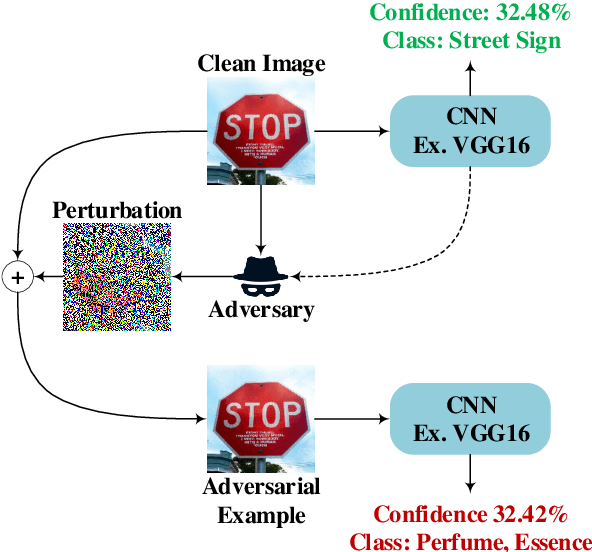
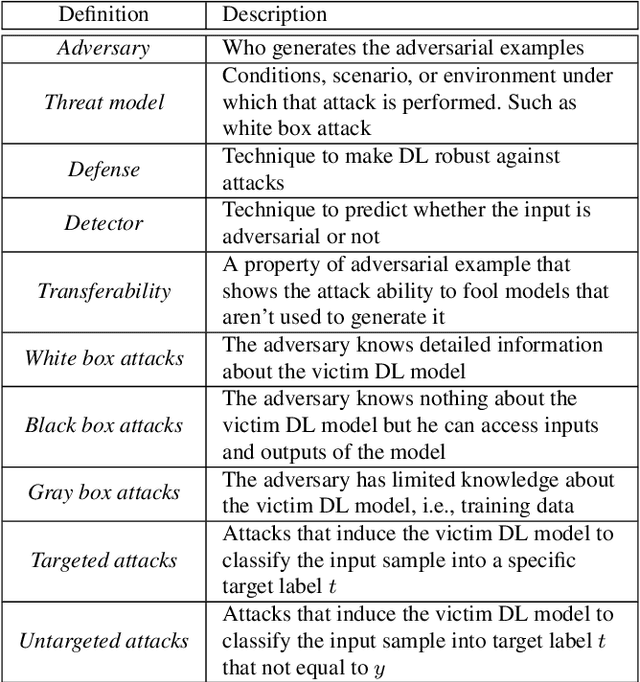
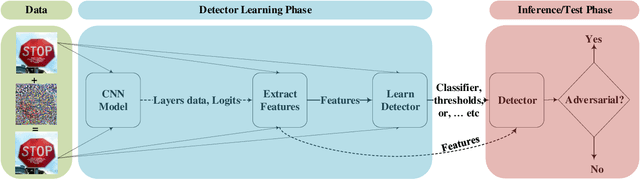
Abstract:Deep Learning (DL) has shown great success in many human-related tasks, which has led to its adoption in many computer vision based applications, such as security surveillance system, autonomous vehicles and healthcare. Such safety-critical applications have to draw its path to success deployment once they have the capability to overcome safety-critical challenges. Among these challenges are the defense against or/and the detection of the adversarial example (AE). Adversary can carefully craft small, often imperceptible, noise called perturbations, to be added to the clean image to generate the AE. The aim of AE is to fool the DL model which makes it a potential risk for DL applications. Many test-time evasion attacks and countermeasures, i.e., defense or detection methods, are proposed in the literature. Moreover, few reviews and surveys were published and theoretically showed the taxonomy of the threats and the countermeasure methods with little focus in AE detection methods. In this paper, we attempt to provide a theoretical and experimental review for AE detection methods. A detailed discussion for such methods is provided and experimental results for eight state-of-the-art detectors are presented under different scenarios on four datasets. We also provide potential challenges and future perspectives for this research direction.
Selective and Features based Adversarial Example Detection
Mar 09, 2021



Abstract:Security-sensitive applications that relay on Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are vulnerable to small perturbations crafted to generate Adversarial Examples (AEs) that are imperceptible to human and cause DNN to misclassify them. Many defense and detection techniques have been proposed. The state-of-the-art detection techniques have been designed for specific attacks or broken by others, need knowledge about the attacks, are not consistent, increase model parameters overhead, are time-consuming, or have latency in inference time. To trade off these factors, we propose a novel unsupervised detection mechanism that uses the selective prediction, processing model layers outputs, and knowledge transfer concepts in a multi-task learning setting. It is called Selective and Feature based Adversarial Detection (SFAD). Experimental results show that the proposed approach achieves comparable results to the state-of-the-art methods against tested attacks in white box scenario and better results in black and gray boxes scenarios. Moreover, results show that SFAD is fully robust against High Confidence Attacks (HCAs) for MNIST and partially robust for CIFAR-10 datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge