Abhishek Peri
Adapting Diffusion Models for Improved Prompt Compliance and Controllable Image Synthesis
Oct 29, 2024Abstract:Recent advances in generative modeling with diffusion processes (DPs) enabled breakthroughs in image synthesis. Despite impressive image quality, these models have various prompt compliance problems, including low recall in generating multiple objects, difficulty in generating text in images, and meeting constraints like object locations and pose. For fine-grained editing and manipulation, they also require fine-grained semantic or instance maps that are tedious to produce manually. While prompt compliance can be enhanced by addition of loss functions at inference, this is time consuming and does not scale to complex scenes. To overcome these limitations, this work introduces a new family of \textit{Factor Graph Diffusion Models} (FG-DMs) that models the joint distribution of images and conditioning variables, such as semantic, sketch, depth or normal maps via a factor graph decomposition. This joint structure has several advantages, including support for efficient sampling based prompt compliance schemes, which produce images of high object recall, semi-automated fine-grained editing, text-based editing of conditions with noise inversion, explainability at intermediate levels, ability to produce labeled datasets for the training of downstream models such as segmentation or depth, training with missing data, and continual learning where new conditioning variables can be added with minimal or no modifications to the existing structure. We propose an implementation of FG-DMs by adapting a pre-trained Stable Diffusion (SD) model to implement all FG-DM factors, using only COCO dataset, and show that it is effective in generating images with 15\% higher recall than SD while retaining its generalization ability. We introduce an attention distillation loss that encourages consistency among the attention maps of all factors, improving the fidelity of the generated conditions and image.
ReF -- Rotation Equivariant Features for Local Feature Matching
Mar 10, 2022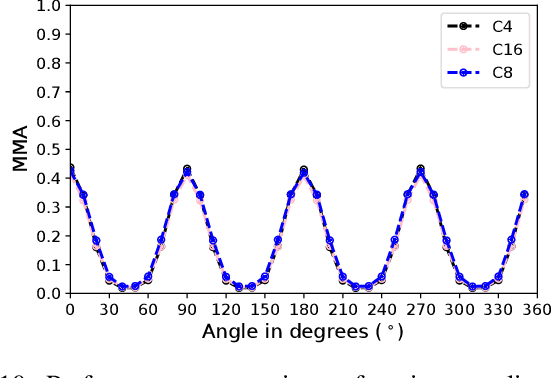
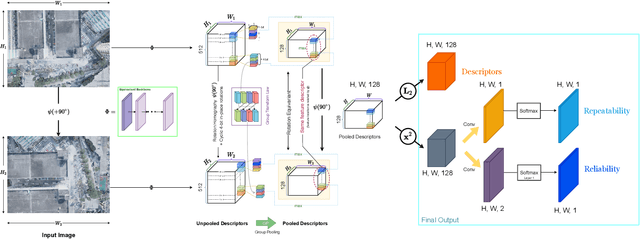
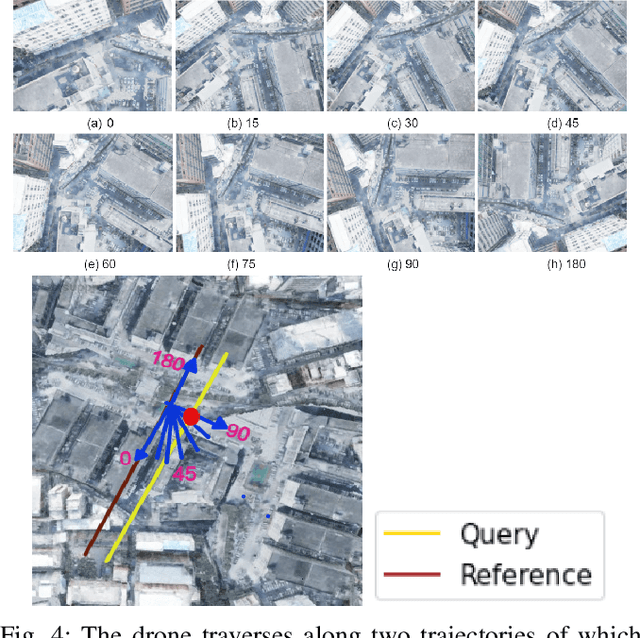
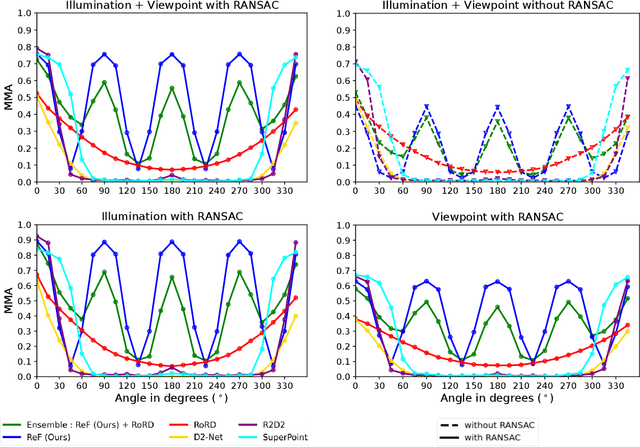
Abstract:Sparse local feature matching is pivotal for many computer vision and robotics tasks. To improve their invariance to challenging appearance conditions and viewing angles, and hence their usefulness, existing learning-based methods have primarily focused on data augmentation-based training. In this work, we propose an alternative, complementary approach that centers on inducing bias in the model architecture itself to generate `rotation-specific' features using Steerable E2-CNNs, that are then group-pooled to achieve rotation-invariant local features. We demonstrate that this high performance, rotation-specific coverage from the steerable CNNs can be expanded to all rotation angles by combining it with augmentation-trained standard CNNs which have broader coverage but are often inaccurate, thus creating a state-of-the-art rotation-robust local feature matcher. We benchmark our proposed methods against existing techniques on HPatches and a newly proposed UrbanScenes3D-Air dataset for visual place recognition. Furthermore, we present a detailed analysis of the performance effects of ensembling, robust estimation, network architecture variations, and the use of rotation priors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge