Abhijnan Nath
Owen-Shapley Policy Optimization (OSPO): A Principled RL Algorithm for Generative Search LLMs
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Large language models are increasingly trained via reinforcement learning for personalized recommendation tasks, but standard methods like GRPO rely on sparse, sequence-level rewards that create a credit assignment gap, obscuring which tokens drive success. This gap is especially problematic when models must infer latent user intent from under-specified language without ground truth labels, a reasoning pattern rarely seen during pretraining. We introduce Owen-Shapley Policy Optimization (OSPO), a framework that redistributes sequence-level advantages based on tokens' marginal contributions to outcomes. Unlike value-model-based methods requiring additional computation, OSPO employs potential-based reward shaping via Shapley-Owen attributions to assign segment-level credit while preserving the optimal policy, learning directly from task feedback without parametric value models. By forming coalitions of semantically coherent units (phrases describing product attributes or sentences capturing preferences), OSPO identifies which response parts drive performance. Experiments on Amazon ESCI and H&M Fashion datasets show consistent gains over baselines, with notable test-time robustness to out-of-distribution retrievers unseen during training.
Learning "Partner-Aware" Collaborators in Multi-Party Collaboration
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly bring deployed in agentic settings where they act as collaborators with humans. Therefore, it is increasingly important to be able to evaluate their abilities to collaborate effectively in multi-turn, multi-party tasks. In this paper, we build on the AI alignment and safe interruptability literature to offer novel theoretical insights on collaborative behavior between LLM-driven collaborator agents and an intervention agent. Our goal is to learn an ideal partner-aware collaborator that increases the group's common-ground (CG)-alignment on task-relevant propositions-by intelligently collecting information provided in interventions by a partner agent.We show how LLM agents trained using standard RLHF and related approaches are naturally inclined to ignore possibly well-meaning interventions, which makes increasing group common ground non-trivial in this setting. We employ a two-player Modified-Action MDP to examine this suboptimal behavior of standard AI agents, and propose Interruptible Collaborative Roleplayer (ICR)-a novel partner-aware learning algorithm to train CG-optimal collaborators. Experiments on multiple collaborative task environments show that ICR, on average, is more capable of promoting successful CG convergence and exploring more diverse solutions in such tasks.
Dynamic Epistemic Friction in Dialogue
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Recent developments in aligning Large Language Models (LLMs) with human preferences have significantly enhanced their utility in human-AI collaborative scenarios. However, such approaches often neglect the critical role of "epistemic friction," or the inherent resistance encountered when updating beliefs in response to new, conflicting, or ambiguous information. In this paper, we define dynamic epistemic friction as the resistance to epistemic integration, characterized by the misalignment between an agent's current belief state and new propositions supported by external evidence. We position this within the framework of Dynamic Epistemic Logic (Van Benthem and Pacuit, 2011), where friction emerges as nontrivial belief-revision during the interaction. We then present analyses from a situated collaborative task that demonstrate how this model of epistemic friction can effectively predict belief updates in dialogues, and we subsequently discuss how the model of belief alignment as a measure of epistemic resistance or friction can naturally be made more sophisticated to accommodate the complexities of real-world dialogue scenarios.
Frictional Agent Alignment Framework: Slow Down and Don't Break Things
May 26, 2025Abstract:AI support of collaborative interactions entails mediating potential misalignment between interlocutor beliefs. Common preference alignment methods like DPO excel in static settings, but struggle in dynamic collaborative tasks where the explicit signals of interlocutor beliefs are sparse and skewed. We propose the Frictional Agent Alignment Framework (FAAF), to generate precise, context-aware "friction" that prompts for deliberation and re-examination of existing evidence. FAAF's two-player objective decouples from data skew: a frictive-state policy identifies belief misalignments, while an intervention policy crafts collaborator-preferred responses. We derive an analytical solution to this objective, enabling training a single policy via a simple supervised loss. Experiments on three benchmarks show FAAF outperforms competitors in producing concise, interpretable friction and in OOD generalization. By aligning LLMs to act as adaptive "thought partners" -- not passive responders -- FAAF advances scalable, dynamic human-AI collaboration. Our code and data can be found at https://github.com/csu-signal/FAAF_ACL.
Any Other Thoughts, Hedgehog? Linking Deliberation Chains in Collaborative Dialogues
Oct 25, 2024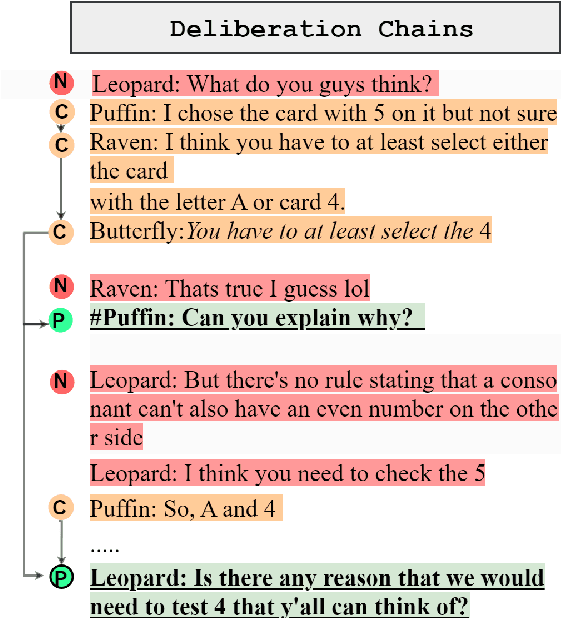
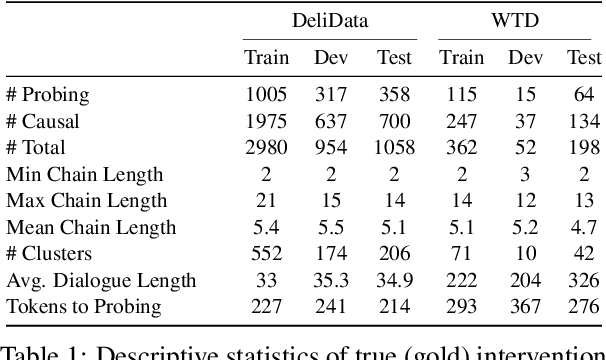

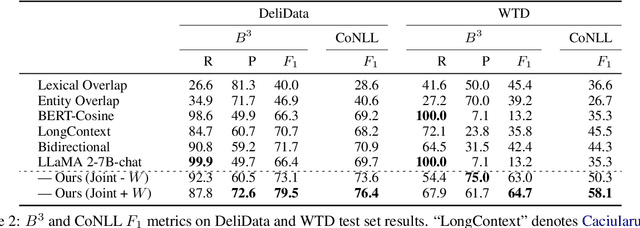
Abstract:Question-asking in collaborative dialogue has long been established as key to knowledge construction, both in internal and collaborative problem solving. In this work, we examine probing questions in collaborative dialogues: questions that explicitly elicit responses from the speaker's interlocutors. Specifically, we focus on modeling the causal relations that lead directly from utterances earlier in the dialogue to the emergence of the probing question. We model these relations using a novel graph-based framework of deliberation chains, and reframe the problem of constructing such chains as a coreference-style clustering problem. Our framework jointly models probing and causal utterances and the links between them, and we evaluate on two challenging collaborative task datasets: the Weights Task and DeliData. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of our theoretically-grounded approach compared to both baselines and stronger coreference approaches, and establish a standard of performance in this novel task.
Simultaneous Reward Distillation and Preference Learning: Get You a Language Model Who Can Do Both
Oct 11, 2024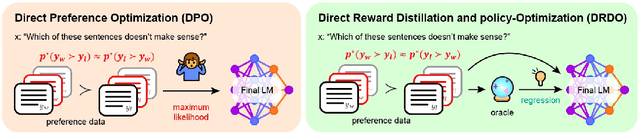
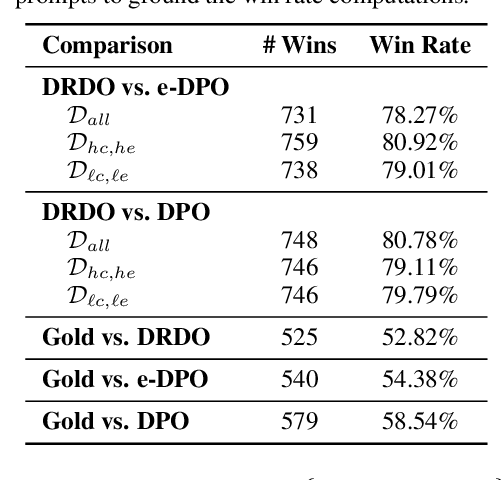
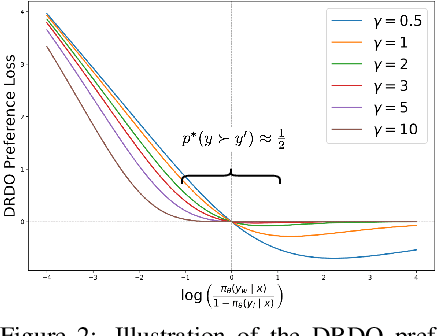
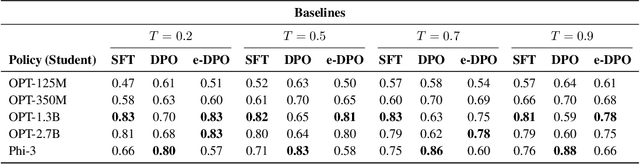
Abstract:Reward modeling of human preferences is one of the cornerstones of building usable generative large language models (LLMs). While traditional RLHF-based alignment methods explicitly maximize the expected rewards from a separate reward model, more recent supervised alignment methods like Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) circumvent this phase to avoid problems including model drift and reward overfitting. Although popular due to its simplicity, DPO and similar direct alignment methods can still lead to degenerate policies, and rely heavily on the Bradley-Terry-based preference formulation to model reward differences between pairs of candidate outputs. This formulation is challenged by non-deterministic or noisy preference labels, for example human scoring of two candidate outputs is of low confidence. In this paper, we introduce DRDO (Direct Reward Distillation and policy-Optimization), a supervised knowledge distillation-based preference alignment method that simultaneously models rewards and preferences to avoid such degeneracy. DRDO directly mimics rewards assigned by an oracle while learning human preferences from a novel preference likelihood formulation. Our experimental results on the Ultrafeedback and TL;DR datasets demonstrate that policies trained using DRDO surpass previous methods such as DPO and e-DPO in terms of expected rewards and are more robust, on average, to noisy preference signals as well as out-of-distribution (OOD) settings.
Multimodal Cross-Document Event Coreference Resolution Using Linear Semantic Transfer and Mixed-Modality Ensembles
Apr 13, 2024



Abstract:Event coreference resolution (ECR) is the task of determining whether distinct mentions of events within a multi-document corpus are actually linked to the same underlying occurrence. Images of the events can help facilitate resolution when language is ambiguous. Here, we propose a multimodal cross-document event coreference resolution method that integrates visual and textual cues with a simple linear map between vision and language models. As existing ECR benchmark datasets rarely provide images for all event mentions, we augment the popular ECB+ dataset with event-centric images scraped from the internet and generated using image diffusion models. We establish three methods that incorporate images and text for coreference: 1) a standard fused model with finetuning, 2) a novel linear mapping method without finetuning and 3) an ensembling approach based on splitting mention pairs by semantic and discourse-level difficulty. We evaluate on 2 datasets: the augmented ECB+, and AIDA Phase 1. Our ensemble systems using cross-modal linear mapping establish an upper limit (91.9 CoNLL F1) on ECB+ ECR performance given the preprocessing assumptions used, and establish a novel baseline on AIDA Phase 1. Our results demonstrate the utility of multimodal information in ECR for certain challenging coreference problems, and highlight a need for more multimodal resources in the coreference resolution space.
Okay, Let's Do This! Modeling Event Coreference with Generated Rationales and Knowledge Distillation
Apr 04, 2024


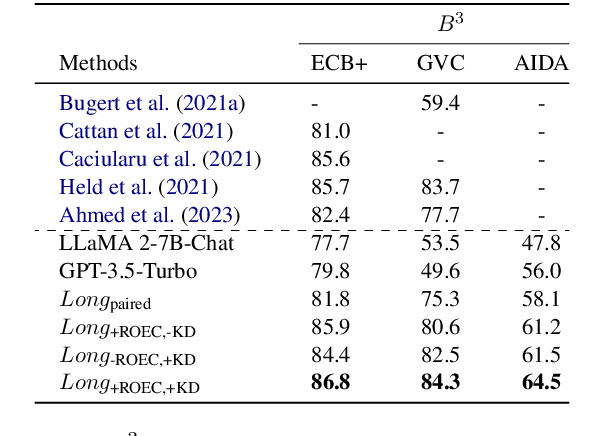
Abstract:In NLP, Event Coreference Resolution (ECR) is the task of connecting event clusters that refer to the same underlying real-life event, usually via neural systems. In this work, we investigate using abductive free-text rationales (FTRs) generated by modern autoregressive LLMs as distant supervision of smaller student models for cross-document coreference (CDCR) of events. We implement novel rationale-oriented event clustering and knowledge distillation methods for event coreference scoring that leverage enriched information from the FTRs for improved CDCR without additional annotation or expensive document clustering. Our model using coreference specific knowledge distillation achieves SOTA B3 F1 on the ECB+ and GVC corpora and we establish a new baseline on the AIDA Phase 1 corpus. Our code can be found at https://github.com/csu-signal/llama_cdcr
How Good is the Model in Model-in-the-loop Event Coreference Resolution Annotation?
Jun 06, 2023Abstract:Annotating cross-document event coreference links is a time-consuming and cognitively demanding task that can compromise annotation quality and efficiency. To address this, we propose a model-in-the-loop annotation approach for event coreference resolution, where a machine learning model suggests likely corefering event pairs only. We evaluate the effectiveness of this approach by first simulating the annotation process and then, using a novel annotator-centric Recall-Annotation effort trade-off metric, we compare the results of various underlying models and datasets. We finally present a method for obtaining 97\% recall while substantially reducing the workload required by a fully manual annotation process. Code and data can be found at https://github.com/ahmeshaf/model_in_coref
AxomiyaBERTa: A Phonologically-aware Transformer Model for Assamese
May 23, 2023Abstract:Despite their successes in NLP, Transformer-based language models still require extensive computing resources and suffer in low-resource or low-compute settings. In this paper, we present AxomiyaBERTa, a novel BERT model for Assamese, a morphologically-rich low-resource language (LRL) of Eastern India. AxomiyaBERTa is trained only on the masked language modeling (MLM) task, without the typical additional next sentence prediction (NSP) objective, and our results show that in resource-scarce settings for very low-resource languages like Assamese, MLM alone can be successfully leveraged for a range of tasks. AxomiyaBERTa achieves SOTA on token-level tasks like Named Entity Recognition and also performs well on "longer-context" tasks like Cloze-style QA and Wiki Title Prediction, with the assistance of a novel embedding disperser and phonological signals respectively. Moreover, we show that AxomiyaBERTa can leverage phonological signals for even more challenging tasks, such as a novel cross-document coreference task on a translated version of the ECB+ corpus, where we present a new SOTA result for an LRL. Our source code and evaluation scripts may be found at https://github.com/csu-signal/axomiyaberta.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge