Abdulmajid Murad
Learning to Land Anywhere: Transferable Generative Models for Aircraft Trajectories
Nov 06, 2025



Abstract:Access to trajectory data is a key requirement for developing and validating Air Traffic Management (ATM) solutions, yet many secondary and regional airports face severe data scarcity. This limits the applicability of machine learning methods and the ability to perform large-scale simulations or "what-if" analyses. In this paper, we investigate whether generative models trained on data-rich airports can be efficiently adapted to data-scarce airports using transfer learning. We adapt state-of-the-art diffusion- and flow-matching-based architectures to the aviation domain and evaluate their transferability between Zurich (source) and Dublin (target) landing trajectory datasets. Models are pretrained on Zurich and fine-tuned on Dublin with varying amounts of local data, ranging from 0% to 100%. Results show that diffusion-based models achieve competitive performance with as little as 5% of the Dublin data and reach baseline-level performance around 20%, consistently outperforming models trained from scratch across metrics and visual inspections. Latent flow matching and latent diffusion models also benefit from pretraining, though with more variable gains, while flow matching models show weaker generalization. Despite challenges in capturing rare trajectory patterns, these findings demonstrate the potential of transfer learning to substantially reduce data requirements for trajectory generation in ATM, enabling realistic synthetic data generation even in environments with limited historical records.
PIGPVAE: Physics-Informed Gaussian Process Variational Autoencoders
May 25, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in generative AI offer promising solutions for synthetic data generation but often rely on large datasets for effective training. To address this limitation, we propose a novel generative model that learns from limited data by incorporating physical constraints to enhance performance. Specifically, we extend the VAE architecture by incorporating physical models in the generative process, enabling it to capture underlying dynamics more effectively. While physical models provide valuable insights, they struggle to capture complex temporal dependencies present in real-world data. To bridge this gap, we introduce a discrepancy term to account for unmodeled dynamics, represented within a latent Gaussian Process VAE (GPVAE). Furthermore, we apply regularization to ensure the generated data aligns closely with observed data, enhancing both the diversity and accuracy of the synthetic samples. The proposed method is applied to indoor temperature data, achieving state-of-the-art performance. Additionally, we demonstrate that PIGPVAE can produce realistic samples beyond the observed distribution, highlighting its robustness and usefulness under distribution shifts.
Synthetic Aircraft Trajectory Generation Using Time-Based VQ-VAE
Apr 12, 2025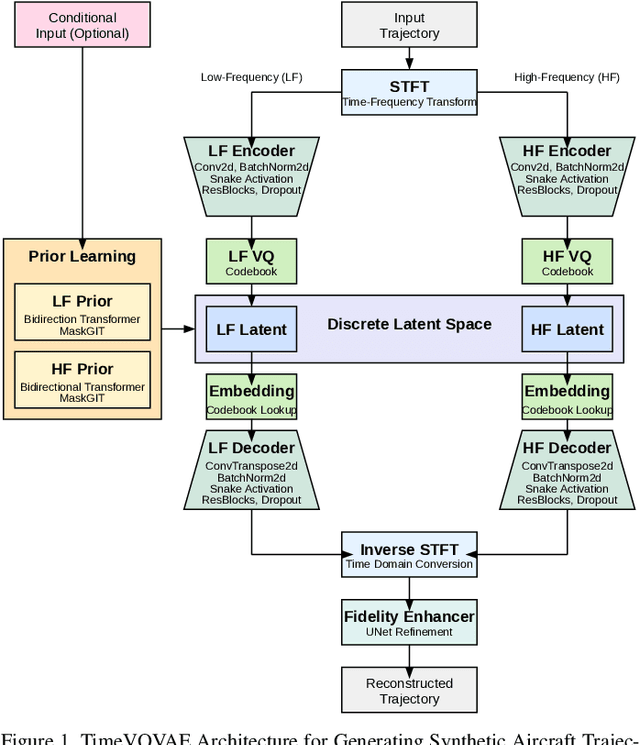
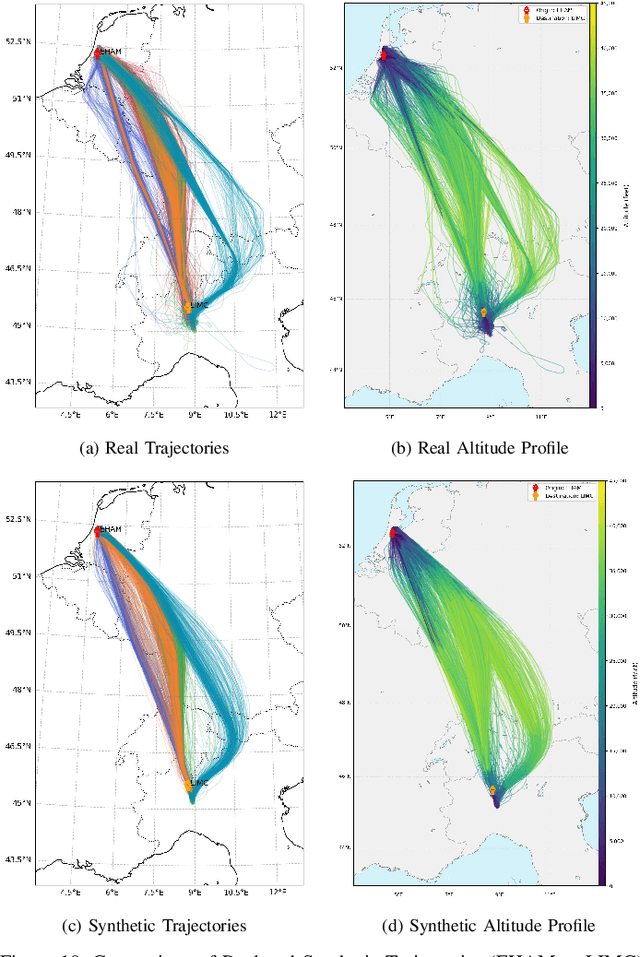
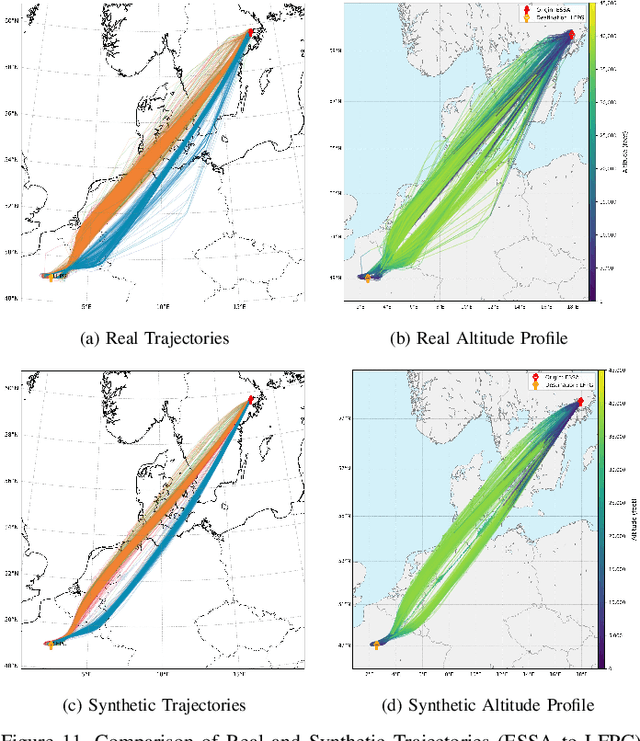
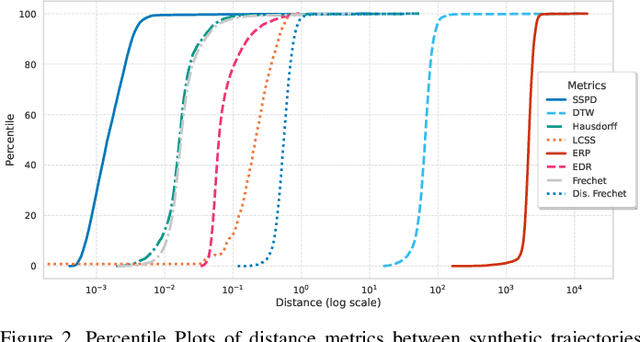
Abstract:In modern air traffic management, generating synthetic flight trajectories has emerged as a promising solution for addressing data scarcity, protecting sensitive information, and supporting large-scale analyses. In this paper, we propose a novel method for trajectory synthesis by adapting the Time-Based Vector Quantized Variational Autoencoder (TimeVQVAE). Our approach leverages time-frequency domain processing, vector quantization, and transformer-based priors to capture both global and local dynamics in flight data. By discretizing the latent space and integrating transformer priors, the model learns long-range spatiotemporal dependencies and preserves coherence across entire flight paths. We evaluate the adapted TimeVQVAE using an extensive suite of quality, statistical, and distributional metrics, as well as a flyability assessment conducted in an open-source air traffic simulator. Results indicate that TimeVQVAE outperforms a temporal convolutional VAE baseline, generating synthetic trajectories that mirror real flight data in terms of spatial accuracy, temporal consistency, and statistical properties. Furthermore, the simulator-based assessment shows that most generated trajectories maintain operational feasibility, although occasional outliers underscore the potential need for additional domain-specific constraints. Overall, our findings underscore the importance of multi-scale representation learning for capturing complex flight behaviors and demonstrate the promise of TimeVQVAE in producing representative synthetic trajectories for downstream tasks such as model training, airspace design, and air traffic forecasting.
Probabilistic Deep Learning to Quantify Uncertainty in Air Quality Forecasting
Dec 05, 2021
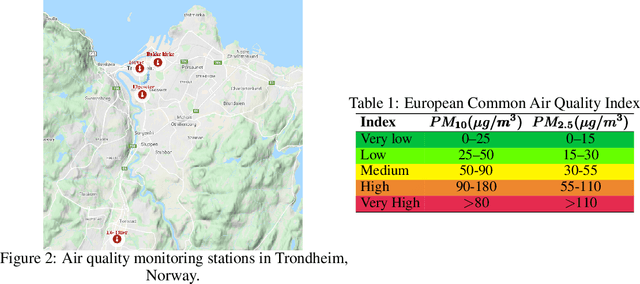
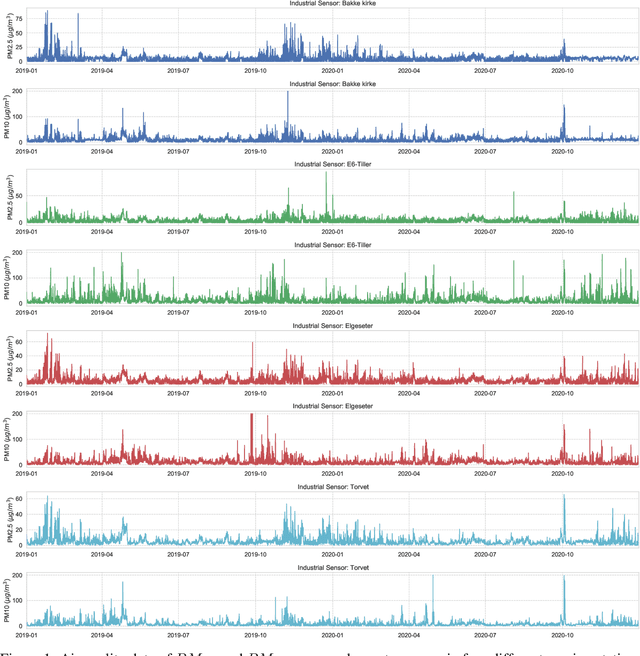
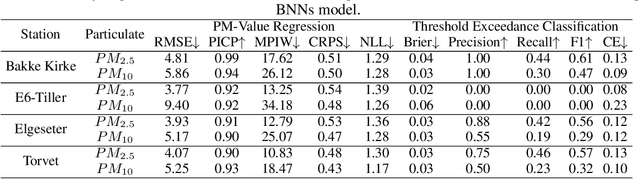
Abstract:Data-driven forecasts of air quality have recently achieved more accurate short-term predictions. Despite their success, most of the current data-driven solutions lack proper quantifications of model uncertainty that communicate how much to trust the forecasts. Recently, several practical tools to estimate uncertainty have been developed in probabilistic deep learning. However, there have not been empirical applications and extensive comparisons of these tools in the domain of air quality forecasts. Therefore, this work applies state-of-the-art techniques of uncertainty quantification in a real-world setting of air quality forecasts. Through extensive experiments, we describe training probabilistic models and evaluate their predictive uncertainties based on empirical performance, reliability of confidence estimate, and practical applicability. We also propose improving these models using "free" adversarial training and exploiting temporal and spatial correlation inherent in air quality data. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed models perform better than previous works in quantifying uncertainty in data-driven air quality forecasts. Overall, Bayesian neural networks provide a more reliable uncertainty estimate but can be challenging to implement and scale. Other scalable methods, such as deep ensemble, Monte Carlo (MC) dropout, and stochastic weight averaging-Gaussian (SWAG), can perform well if applied correctly but with different tradeoffs and slight variations in performance metrics. Finally, our results show the practical impact of uncertainty estimation and demonstrate that, indeed, probabilistic models are more suitable for making informed decisions. Code and dataset are available at \url{https://github.com/Abdulmajid-Murad/deep_probabilistic_forecast}
Learning Task Agnostic Skills with Data-driven Guidance
Aug 04, 2021



Abstract:To increase autonomy in reinforcement learning, agents need to learn useful behaviours without reliance on manually designed reward functions. To that end, skill discovery methods have been used to learn the intrinsic options available to an agent using task-agnostic objectives. However, without the guidance of task-specific rewards, emergent behaviours are generally useless due to the under-constrained problem of skill discovery in complex and high-dimensional spaces. This paper proposes a framework for guiding the skill discovery towards the subset of expert-visited states using a learned state projection. We apply our method in various reinforcement learning (RL) tasks and show that such a projection results in more useful behaviours.
Information-Driven Adaptive Sensing Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning
Oct 08, 2020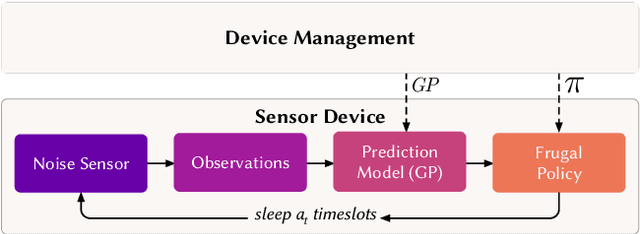
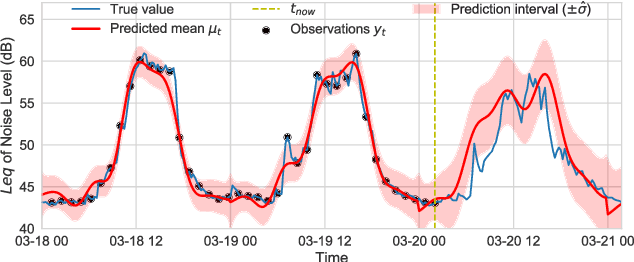
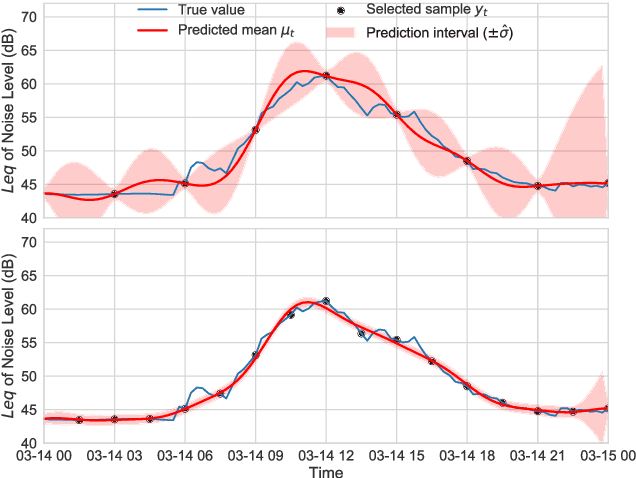
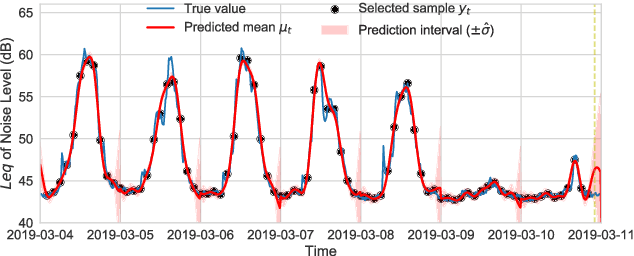
Abstract:In order to make better use of deep reinforcement learning in the creation of sensing policies for resource-constrained IoT devices, we present and study a novel reward function based on the Fisher information value. This reward function enables IoT sensor devices to learn to spend available energy on measurements at otherwise unpredictable moments, while conserving energy at times when measurements would provide little new information. This is a highly general approach, which allows for a wide range of use cases without significant human design effort or hyper-parameter tuning. We illustrate the approach in a scenario of workplace noise monitoring, where results show that the learned behavior outperforms a uniform sampling strategy and comes close to a near-optimal oracle solution.
* 8 pages, 8 figures
Autonomous Management of Energy-Harvesting IoT Nodes Using Deep Reinforcement Learning
May 10, 2019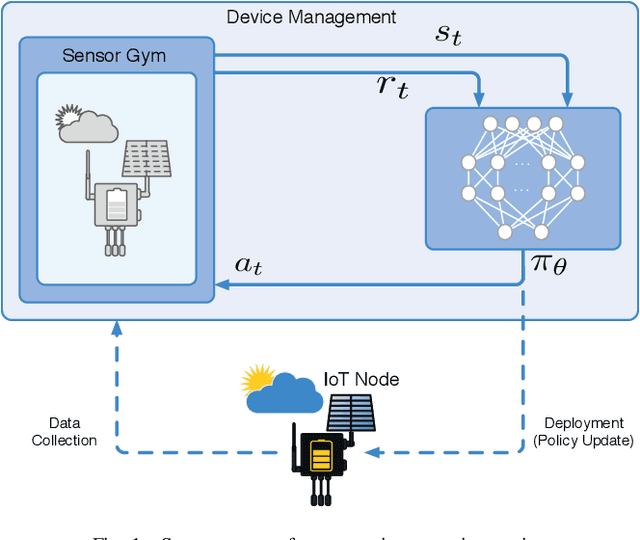
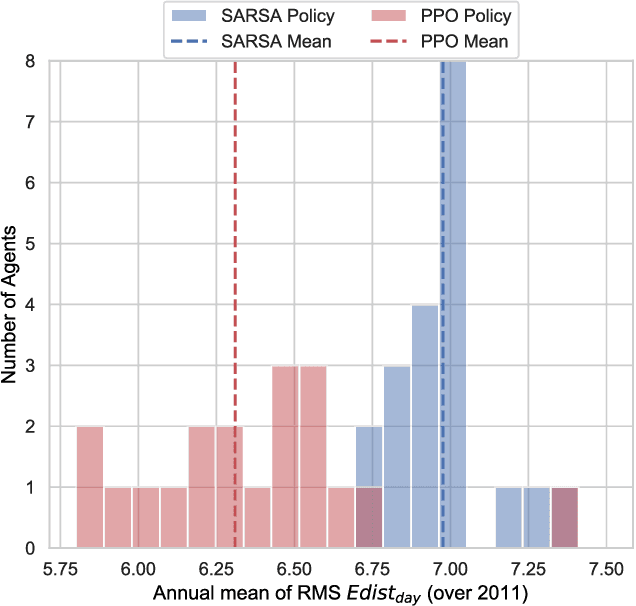
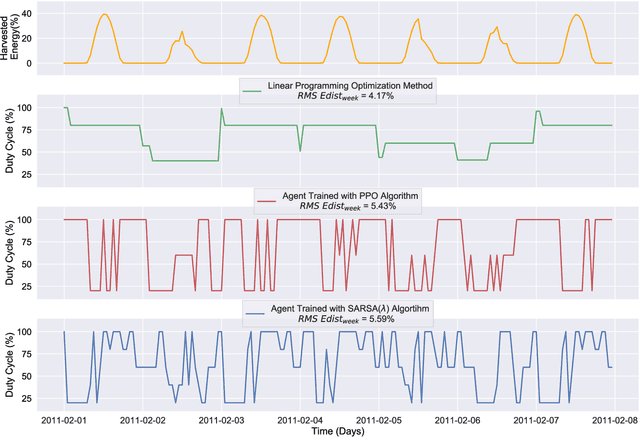
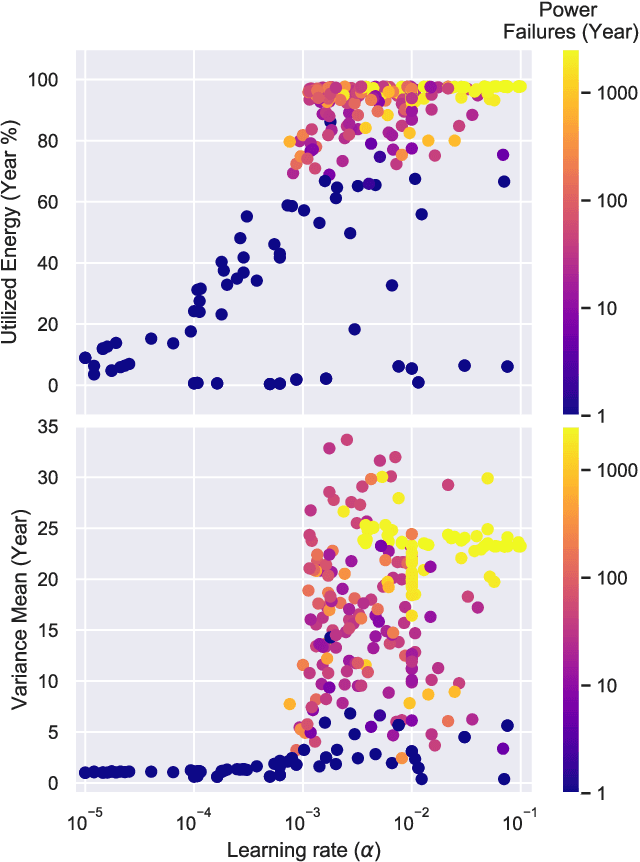
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) is capable of managing wireless, energy-harvesting IoT nodes by solving the problem of autonomous management in non-stationary, resource-constrained settings. We show that the state-of-the-art policy-gradient approaches to RL are appropriate for the IoT domain and that they outperform previous approaches. Due to the ability to model continuous observation and action spaces, as well as improved function approximation capability, the new approaches are able to solve harder problems, permitting reward functions that are better aligned with the actual application goals. We show such a reward function and use policy-gradient approaches to learn capable policies, leading to behavior more appropriate for IoT nodes with less manual design effort, increasing the level of autonomy in IoT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge