Željko Agić
Do End-to-End Speech Recognition Models Care About Context?
Feb 17, 2021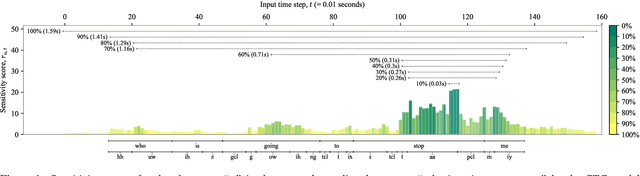
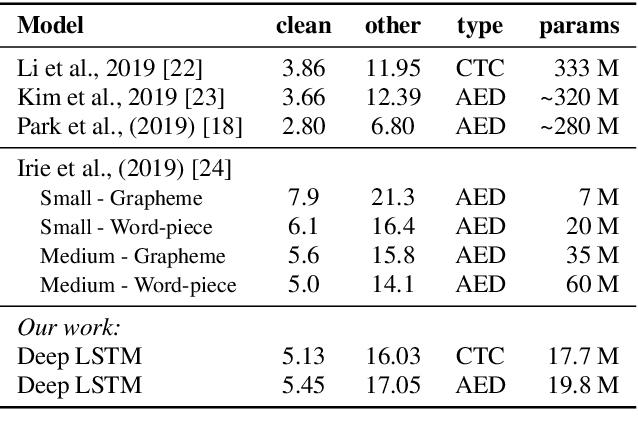
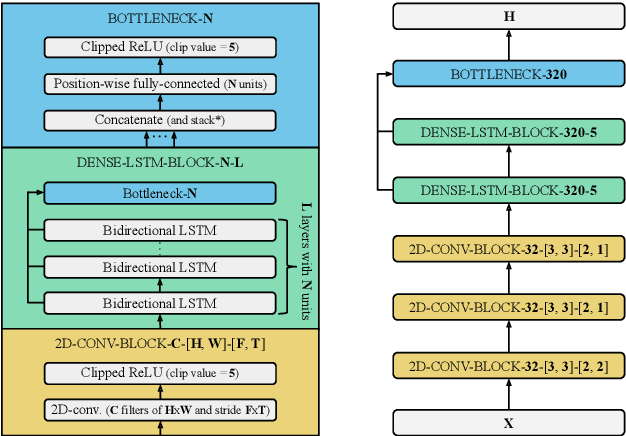
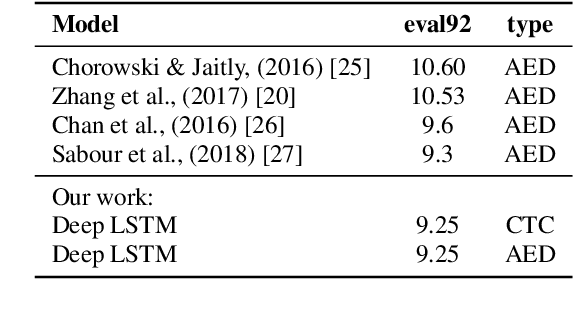
Abstract:The two most common paradigms for end-to-end speech recognition are connectionist temporal classification (CTC) and attention-based encoder-decoder (AED) models. It has been argued that the latter is better suited for learning an implicit language model. We test this hypothesis by measuring temporal context sensitivity and evaluate how the models perform when we constrain the amount of contextual information in the audio input. We find that the AED model is indeed more context sensitive, but that the gap can be closed by adding self-attention to the CTC model. Furthermore, the two models perform similarly when contextual information is constrained. Finally, in contrast to previous research, our results show that the CTC model is highly competitive on WSJ and LibriSpeech without the help of an external language model.
MultiQT: Multimodal Learning for Real-Time Question Tracking in Speech
May 12, 2020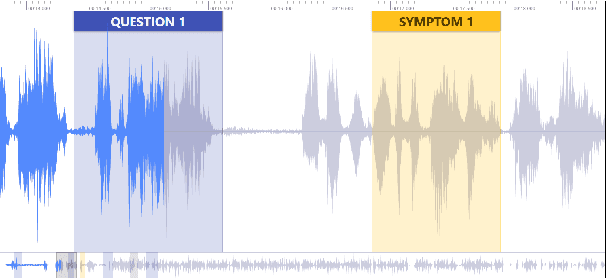

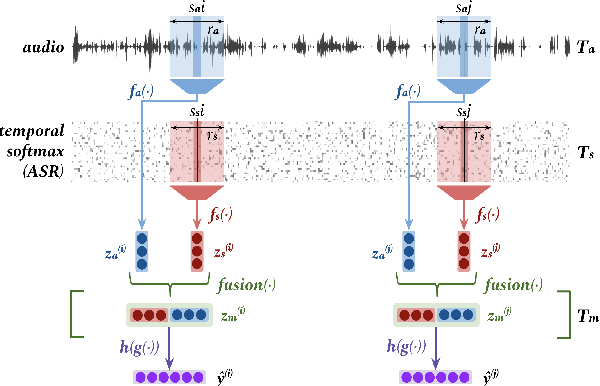
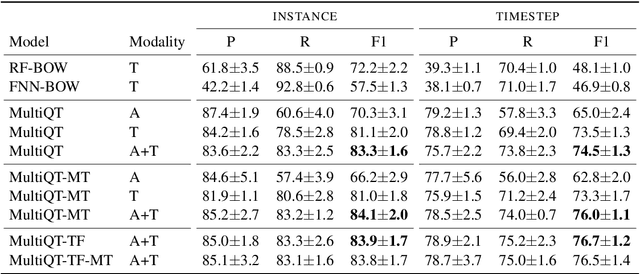
Abstract:We address a challenging and practical task of labeling questions in speech in real time during telephone calls to emergency medical services in English, which embeds within a broader decision support system for emergency call-takers. We propose a novel multimodal approach to real-time sequence labeling in speech. Our model treats speech and its own textual representation as two separate modalities or views, as it jointly learns from streamed audio and its noisy transcription into text via automatic speech recognition. Our results show significant gains of jointly learning from the two modalities when compared to text or audio only, under adverse noise and limited volume of training data. The results generalize to medical symptoms detection where we observe a similar pattern of improvements with multimodal learning.
Towards Instance-Level Parser Selection for Cross-Lingual Transfer of Dependency Parsers
Apr 16, 2020



Abstract:Current methods of cross-lingual parser transfer focus on predicting the best parser for a low-resource target language globally, that is, "at treebank level". In this work, we propose and argue for a novel cross-lingual transfer paradigm: instance-level parser selection (ILPS), and present a proof-of-concept study focused on instance-level selection in the framework of delexicalized parser transfer. We start from an empirical observation that different source parsers are the best choice for different Universal POS sequences in the target language. We then propose to predict the best parser at the instance level. To this end, we train a supervised regression model, based on the Transformer architecture, to predict parser accuracies for individual POS-sequences. We compare ILPS against two strong single-best parser selection baselines (SBPS): (1) a model that compares POS n-gram distributions between the source and target languages (KL) and (2) a model that selects the source based on the similarity between manually created language vectors encoding syntactic properties of languages (L2V). The results from our extensive evaluation, coupling 42 source parsers and 20 diverse low-resource test languages, show that ILPS outperforms KL and L2V on 13/20 and 14/20 test languages, respectively. Further, we show that by predicting the best parser "at the treebank level" (SBPS), using the aggregation of predictions from our instance-level model, we outperform the same baselines on 17/20 and 16/20 test languages.
Distant Supervision from Disparate Sources for Low-Resource Part-of-Speech Tagging
Aug 29, 2018



Abstract:We introduce DsDs: a cross-lingual neural part-of-speech tagger that learns from disparate sources of distant supervision, and realistically scales to hundreds of low-resource languages. The model exploits annotation projection, instance selection, tag dictionaries, morphological lexicons, and distributed representations, all in a uniform framework. The approach is simple, yet surprisingly effective, resulting in a new state of the art without access to any gold annotated data.
Baselines and test data for cross-lingual inference
Mar 02, 2018
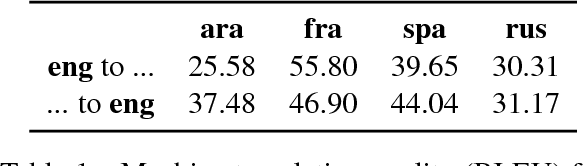
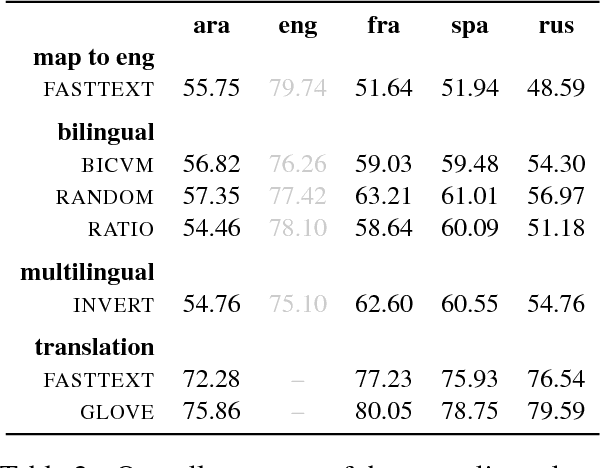
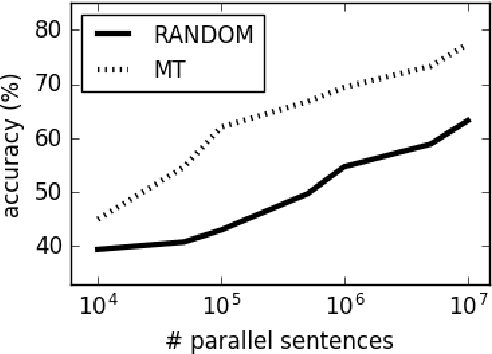
Abstract:The recent years have seen a revival of interest in textual entailment, sparked by i) the emergence of powerful deep neural network learners for natural language processing and ii) the timely development of large-scale evaluation datasets such as SNLI. Recast as natural language inference, the problem now amounts to detecting the relation between pairs of statements: they either contradict or entail one another, or they are mutually neutral. Current research in natural language inference is effectively exclusive to English. In this paper, we propose to advance the research in SNLI-style natural language inference toward multilingual evaluation. To that end, we provide test data for four major languages: Arabic, French, Spanish, and Russian. We experiment with a set of baselines. Our systems are based on cross-lingual word embeddings and machine translation. While our best system scores an average accuracy of just over 75%, we focus largely on enabling further research in multilingual inference.
Parsing Universal Dependencies without training
Jan 11, 2017



Abstract:We propose UDP, the first training-free parser for Universal Dependencies (UD). Our algorithm is based on PageRank and a small set of head attachment rules. It features two-step decoding to guarantee that function words are attached as leaf nodes. The parser requires no training, and it is competitive with a delexicalized transfer system. UDP offers a linguistically sound unsupervised alternative to cross-lingual parsing for UD, which can be used as a baseline for such systems. The parser has very few parameters and is distinctly robust to domain change across languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge