White Matter Geometry-Guided Score-Based Diffusion Model for Tissue Microstructure Imputation in Tractography Imaging
Paper and Code
Jul 28, 2024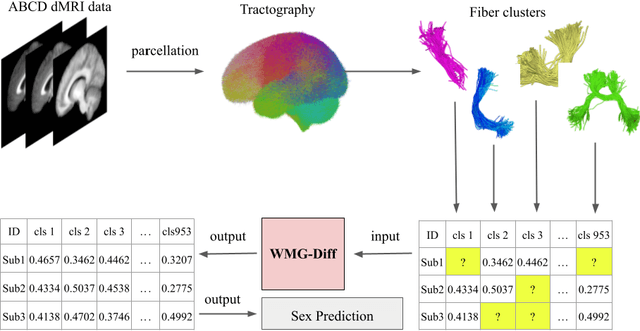
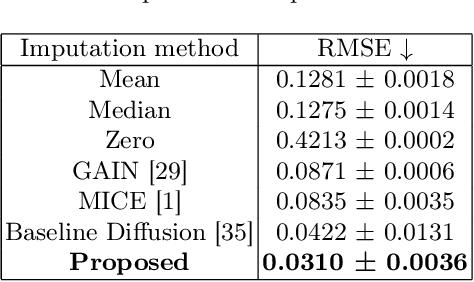
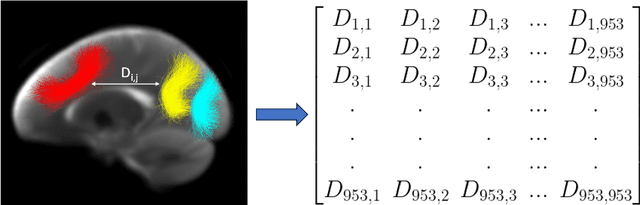
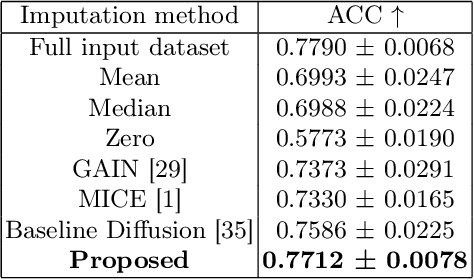
Parcellation of white matter tractography provides anatomical features for disease prediction, anatomical tract segmentation, surgical brain mapping, and non-imaging phenotype classifications. However, parcellation does not always reach 100% accuracy due to various factors, including inter-individual anatomical variability and the quality of neuroimaging scan data. The failure to identify parcels causes a problem of missing microstructure data values, which is especially challenging for downstream tasks that analyze large brain datasets. In this work, we propose a novel deep-learning model to impute tissue microstructure: the White Matter Geometry-guided Diffusion (WMG-Diff) model. Specifically, we first propose a deep score-based guided diffusion model to impute tissue microstructure for diffusion magnetic resonance imaging (dMRI) tractography fiber clusters. Second, we propose a white matter atlas geometric relationship-guided denoising function to guide the reverse denoising process at the subject-specific level. Third, we train and evaluate our model on a large dataset with 9342 subjects. Comprehensive experiments for tissue microstructure imputation and a downstream non-imaging phenotype prediction task demonstrate that our proposed WMG-Diff outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge