What Was Written vs. Who Read It: News Media Profiling Using Text Analysis and Social Media Context
Paper and Code
May 09, 2020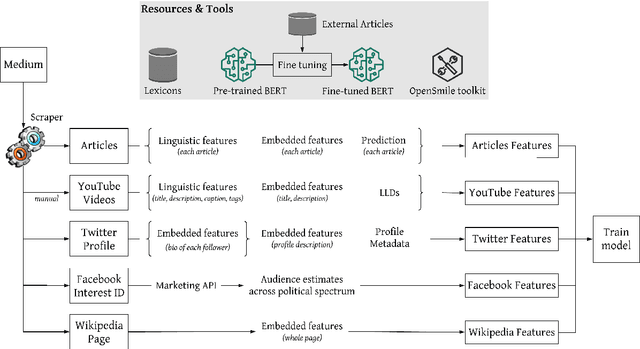
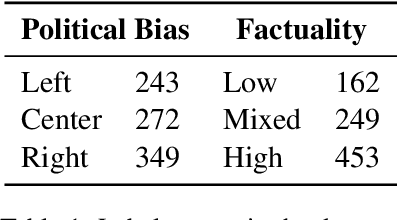
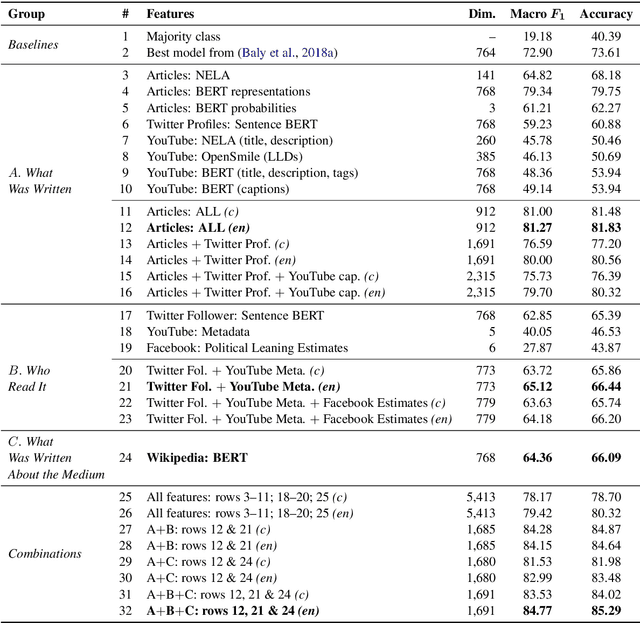
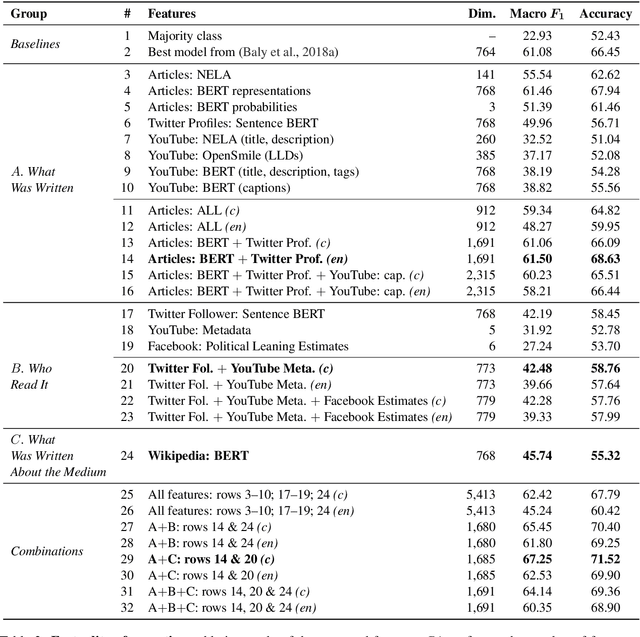
Predicting the political bias and the factuality of reporting of entire news outlets are critical elements of media profiling, which is an understudied but an increasingly important research direction. The present level of proliferation of fake, biased, and propagandistic content online, has made it impossible to fact-check every single suspicious claim, either manually or automatically. Alternatively, we can profile entire news outlets and look for those that are likely to publish fake or biased content. This approach makes it possible to detect likely "fake news" the moment they are published, by simply checking the reliability of their source. From a practical perspective, political bias and factuality of reporting have a linguistic aspect but also a social context. Here, we study the impact of both, namely (i) what was written (i.e., what was published by the target medium, and how it describes itself on Twitter) vs. (ii) who read it (i.e., analyzing the readers of the target medium on Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube). We further study (iii) what was written about the target medium on Wikipedia. The evaluation results show that what was written matters most, and that putting all information sources together yields huge improvements over the current state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge