What Hinders Perceptual Quality of PSNR-oriented Methods?
Paper and Code
Jan 04, 2022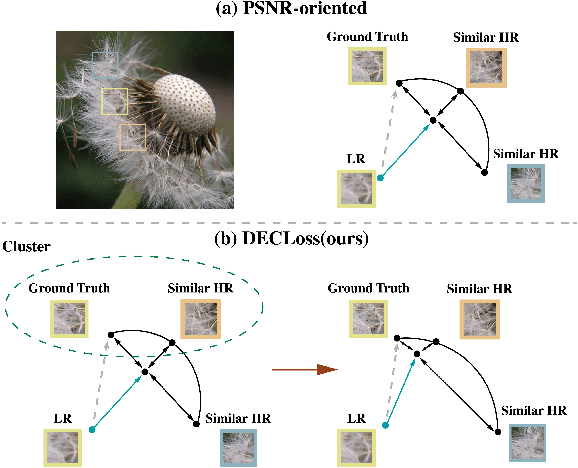
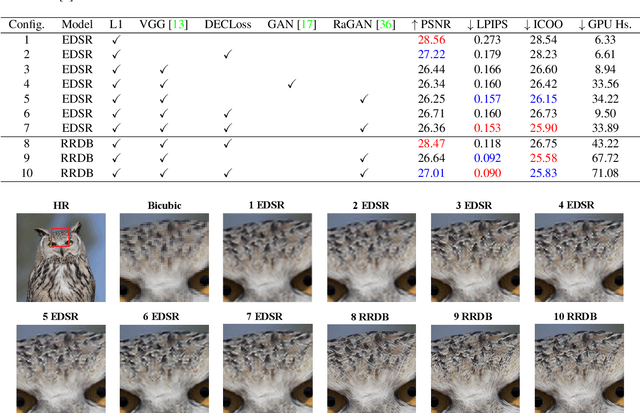
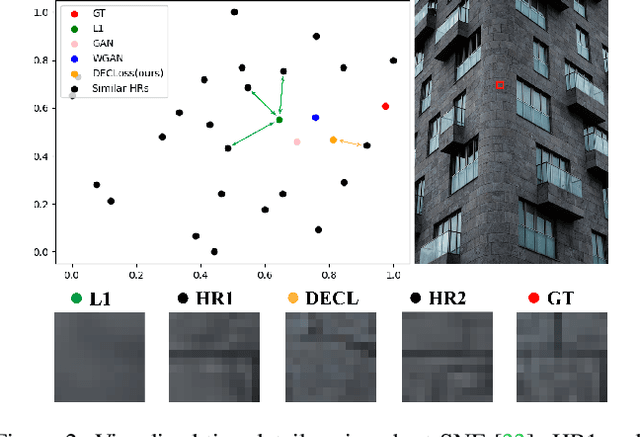
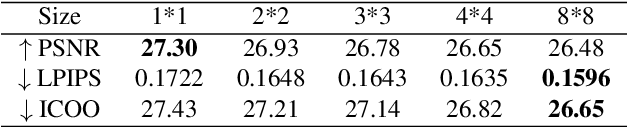
In this paper, we discover two factors that inhibit POMs from achieving high perceptual quality: 1) center-oriented optimization (COO) problem and 2) model's low-frequency tendency. First, POMs tend to generate an SR image whose position in the feature space is closest to the distribution center of all potential high-resolution (HR) images, resulting in such POMs losing high-frequency details. Second, $90\%$ area of an image consists of low-frequency signals; in contrast, human perception relies on an image's high-frequency details. However, POMs apply the same calculation to process different-frequency areas, so that POMs tend to restore the low-frequency regions. Based on these two factors, we propose a Detail Enhanced Contrastive Loss (DECLoss), by combining a high-frequency enhancement module and spatial contrastive learning module, to reduce the influence of the COO problem and low-Frequency tendency. Experimental results show the efficiency and effectiveness when applying DECLoss on several regular SR models. E.g, in EDSR, our proposed method achieves 3.60$\times$ faster learning speed compared to a GAN-based method with a subtle degradation in visual quality. In addition, our final results show that an SR network equipped with our DECLoss generates more realistic and visually pleasing textures compared to state-of-the-art methods. %The source code of the proposed method is included in the supplementary material and will be made publicly available in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge