The ARRT of Language-Models-as-a-Service: Overview of a New Paradigm and its Challenges
Paper and Code
Sep 28, 2023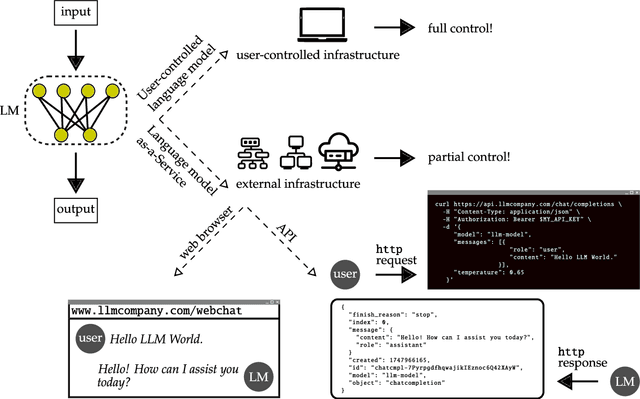

Some of the most powerful language models currently are proprietary systems, accessible only via (typically restrictive) web or software programming interfaces. This is the Language-Models-as-a-Service (LMaaS) paradigm. Contrasting with scenarios where full model access is available, as in the case of open-source models, such closed-off language models create specific challenges for evaluating, benchmarking, and testing them. This paper has two goals: on the one hand, we delineate how the aforementioned challenges act as impediments to the accessibility, replicability, reliability, and trustworthiness (ARRT) of LMaaS. We systematically examine the issues that arise from a lack of information about language models for each of these four aspects. We shed light on current solutions, provide some recommendations, and highlight the directions for future advancements. On the other hand, it serves as a one-stop-shop for the extant knowledge about current, major LMaaS, offering a synthesized overview of the licences and capabilities their interfaces offer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge