Summaries as Captions: Generating Figure Captions for Scientific Documents with Automated Text Summarization
Paper and Code
Feb 23, 2023
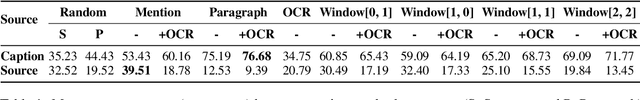
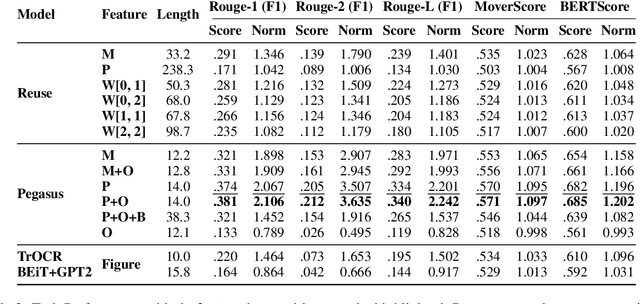
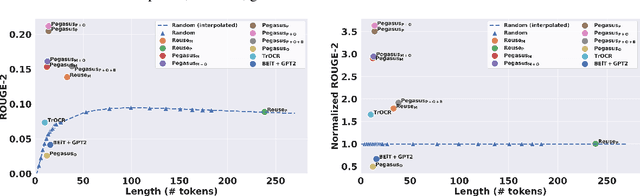
Effective figure captions are crucial for clear comprehension of scientific figures, yet poor caption writing remains a common issue in scientific articles. Our study of arXiv cs.CL papers found that 53.88% of captions were rated as unhelpful or worse by domain experts, showing the need for better caption generation. Previous efforts in figure caption generation treated it as a vision task, aimed at creating a model to understand visual content and complex contextual information. Our findings, however, demonstrate that over 75% of figure captions' tokens align with corresponding figure-mentioning paragraphs, indicating great potential for language technology to solve this task. In this paper, we present a novel approach for generating figure captions in scientific documents using text summarization techniques. Our approach extracts sentences referencing the target figure, then summarizes them into a concise caption. In the experiments on real-world arXiv papers (81.2% were published at academic conferences), our method, using only text data, outperformed previous approaches in both automatic and human evaluations. We further conducted data-driven investigations into the two core challenges: (i) low-quality author-written captions and (ii) the absence of a standard for good captions. We found that our models could generate improved captions for figures with original captions rated as unhelpful, and the model trained on captions with more than 30 tokens produced higher-quality captions. We also found that good captions often include the high-level takeaway of the figure. Our work proves the effectiveness of text summarization in generating figure captions for scholarly articles, outperforming prior vision-based approaches. Our findings have practical implications for future figure captioning systems, improving scientific communication clarity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge