Spatial Autoregressive Coding for Graph Neural Recommendation
Paper and Code
May 19, 2022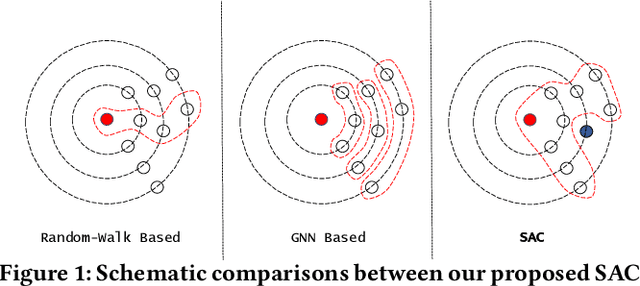
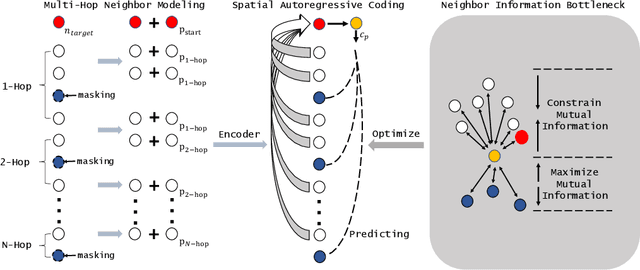
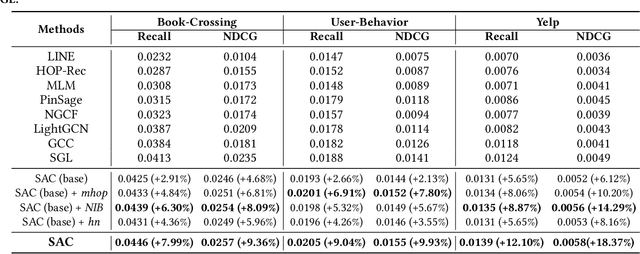
Graph embedding methods including traditional shallow models and deep Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have led to promising applications in recommendation. Nevertheless, shallow models especially random-walk-based algorithms fail to adequately exploit neighbor proximity in sampled subgraphs or sequences due to their optimization paradigm. GNN-based algorithms suffer from the insufficient utilization of high-order information and easily cause over-smoothing problems when stacking too much layers, which may deteriorate the recommendations of low-degree (long-tail) items, limiting the expressiveness and scalability. In this paper, we propose a novel framework SAC, namely Spatial Autoregressive Coding, to solve the above problems in a unified way. To adequately leverage neighbor proximity and high-order information, we design a novel spatial autoregressive paradigm. Specifically, we first randomly mask multi-hop neighbors and embed the target node by integrating all other surrounding neighbors with an explicit multi-hop attention. Then we reinforce the model to learn a neighbor-predictive coding for the target node by contrasting the coding and the masked neighbors' embedding, equipped with a new hard negative sampling strategy. To learn the minimal sufficient representation for the target-to-neighbor prediction task and remove the redundancy of neighbors, we devise Neighbor Information Bottleneck by maximizing the mutual information between target predictive coding and the masked neighbors' embedding, and simultaneously constraining those between the coding and surrounding neighbors' embedding. Experimental results on both public recommendation datasets and a real scenario web-scale dataset Douyin-Friend-Recommendation demonstrate the superiority of SAC compared with state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge