Self-Supervised Learning of Dynamic Planar Manipulation of Free-End Cables
Paper and Code
May 15, 2024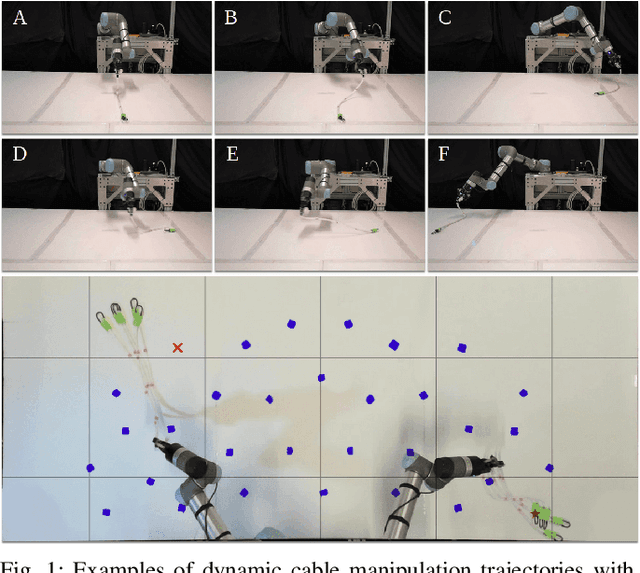

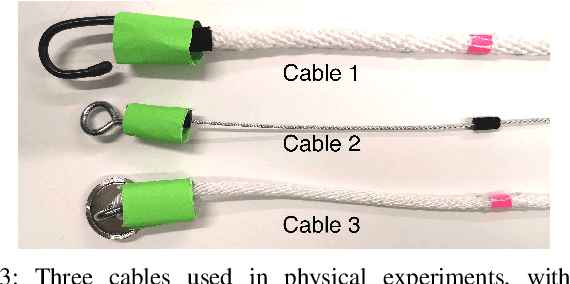
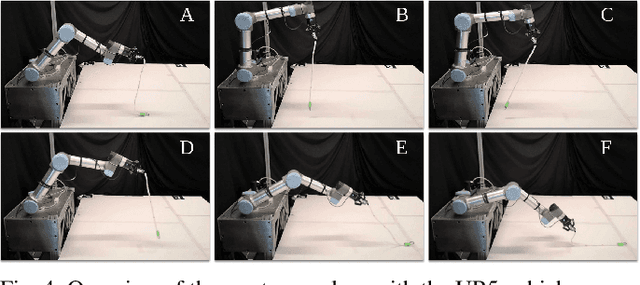
Dynamic manipulation of free-end cables has applications for cable management in homes, warehouses and manufacturing plants. We present a supervised learning approach for dynamic manipulation of free-end cables, focusing on the problem of getting the cable endpoint to a designated target position, which may lie outside the reachable workspace of the robot end effector. We present a simulator, tune it to closely match experiments with physical cables, and then collect training data for learning dynamic cable manipulation. We evaluate with 3 cables and a physical UR5 robot. Results over 32x5 trials on 3 cables suggest that a physical UR5 robot can attain a median error distance ranging from 22% to 35% of the cable length among cables, outperforming an analytic baseline by 21% and a Gaussian Process baseline by 7% with lower interquartile range (IQR).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge