Secure Forward Aggregation for Vertical Federated Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Jun 28, 2022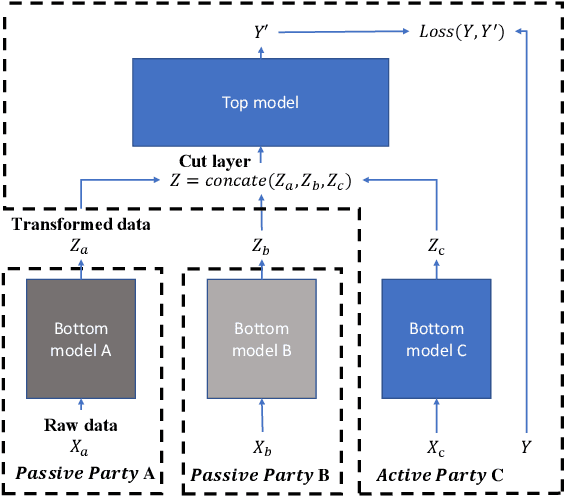

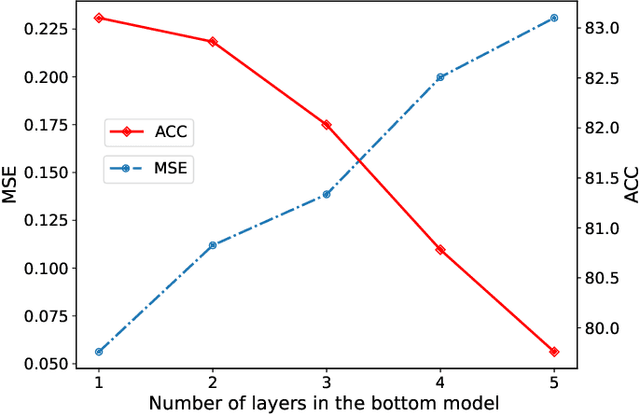
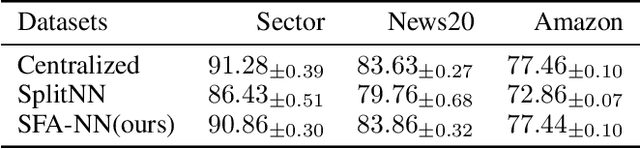
Vertical federated learning (VFL) is attracting much attention because it enables cross-silo data cooperation in a privacy-preserving manner. While most research works in VFL focus on linear and tree models, deep models (e.g., neural networks) are not well studied in VFL. In this paper, we focus on SplitNN, a well-known neural network framework in VFL, and identify a trade-off between data security and model performance in SplitNN. Briefly, SplitNN trains the model by exchanging gradients and transformed data. On the one hand, SplitNN suffers from the loss of model performance since multiply parties jointly train the model using transformed data instead of raw data, and a large amount of low-level feature information is discarded. On the other hand, a naive solution of increasing the model performance through aggregating at lower layers in SplitNN (i.e., the data is less transformed and more low-level feature is preserved) makes raw data vulnerable to inference attacks. To mitigate the above trade-off, we propose a new neural network protocol in VFL called Security Forward Aggregation (SFA). It changes the way of aggregating the transformed data and adopts removable masks to protect the raw data. Experiment results show that networks with SFA achieve both data security and high model performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge