Revisiting the Message Passing in Heterophilous Graph Neural Networks
Paper and Code
May 28, 2024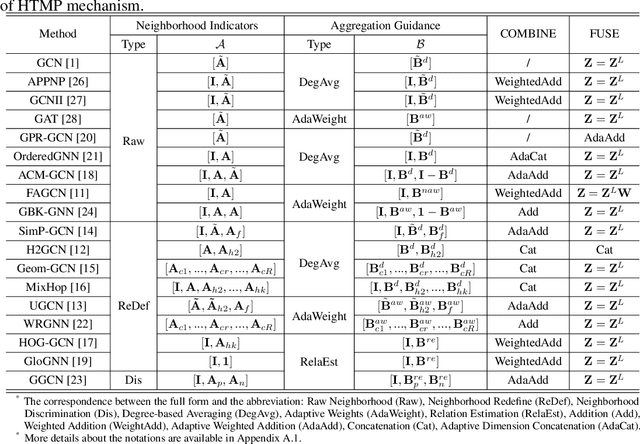
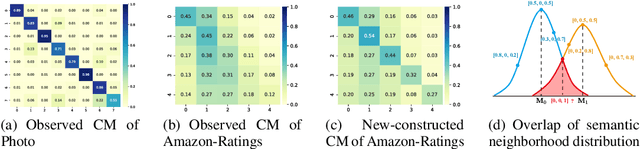
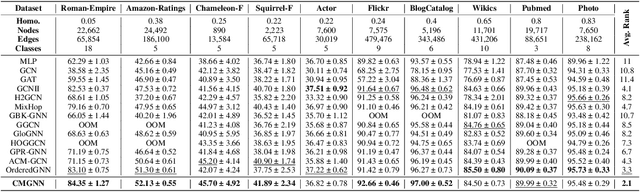
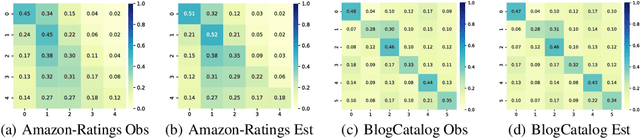
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have demonstrated strong performance in graph mining tasks due to their message-passing mechanism, which is aligned with the homophily assumption that adjacent nodes exhibit similar behaviors. However, in many real-world graphs, connected nodes may display contrasting behaviors, termed as heterophilous patterns, which has attracted increased interest in heterophilous GNNs (HTGNNs). Although the message-passing mechanism seems unsuitable for heterophilous graphs due to the propagation of class-irrelevant information, it is still widely used in many existing HTGNNs and consistently achieves notable success. This raises the question: why does message passing remain effective on heterophilous graphs? To answer this question, in this paper, we revisit the message-passing mechanisms in heterophilous graph neural networks and reformulate them into a unified heterophilious message-passing (HTMP) mechanism. Based on HTMP and empirical analysis, we reveal that the success of message passing in existing HTGNNs is attributed to implicitly enhancing the compatibility matrix among classes. Moreover, we argue that the full potential of the compatibility matrix is not completely achieved due to the existence of incomplete and noisy semantic neighborhoods in real-world heterophilous graphs. To bridge this gap, we introduce a new approach named CMGNN, which operates within the HTMP mechanism to explicitly leverage and improve the compatibility matrix. A thorough evaluation involving 10 benchmark datasets and comparative analysis against 13 well-established baselines highlights the superior performance of the HTMP mechanism and CMGNN method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge