Retrieval Augmented Classification for Long-Tail Visual Recognition
Paper and Code
Feb 22, 2022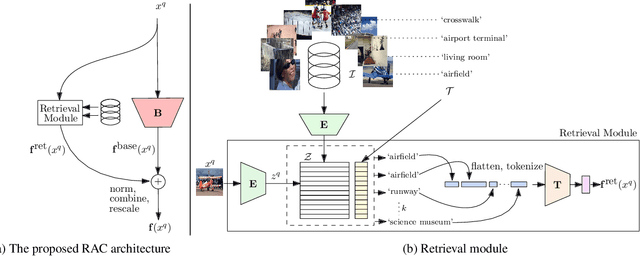
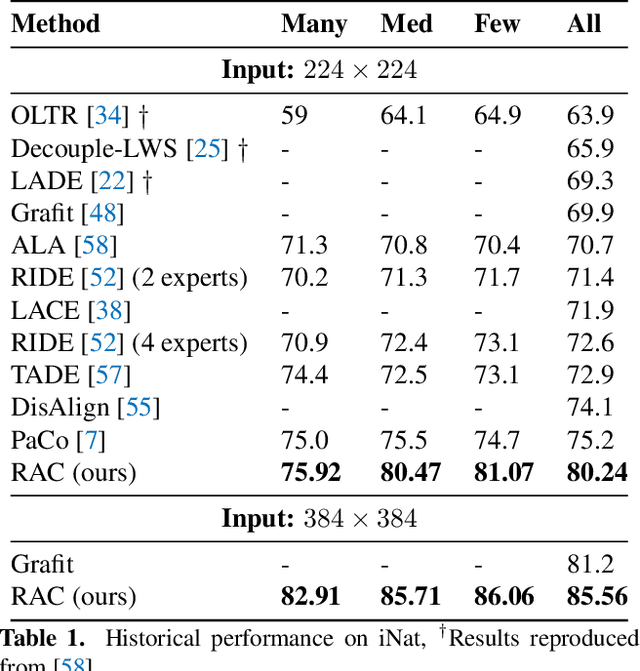
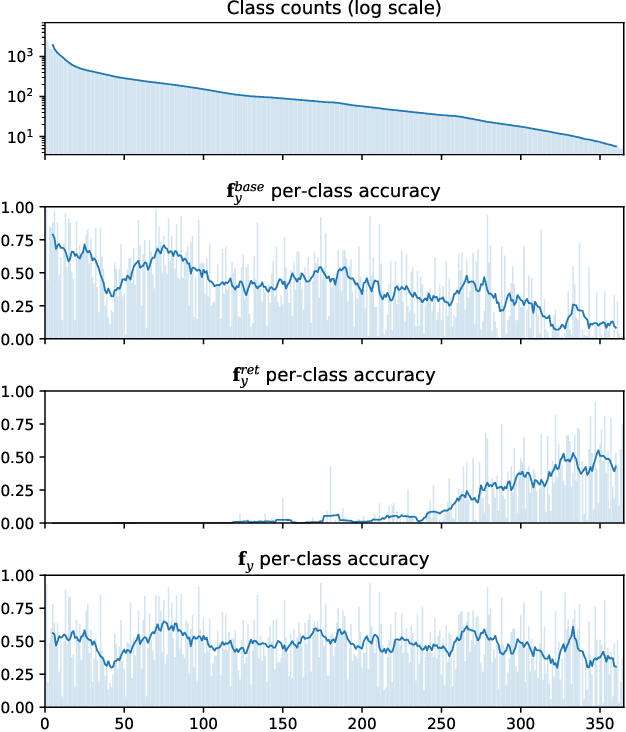
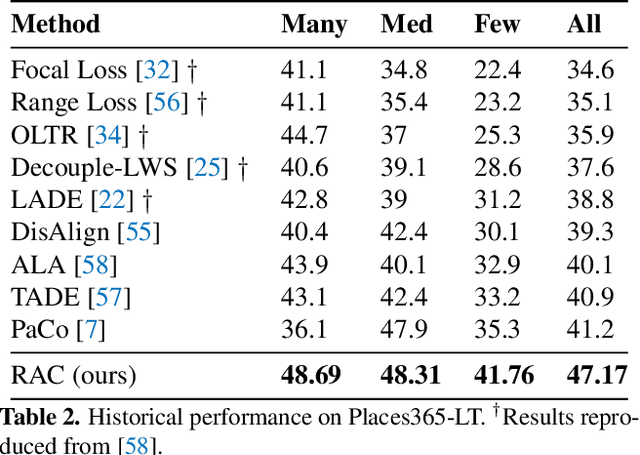
We introduce Retrieval Augmented Classification (RAC), a generic approach to augmenting standard image classification pipelines with an explicit retrieval module. RAC consists of a standard base image encoder fused with a parallel retrieval branch that queries a non-parametric external memory of pre-encoded images and associated text snippets. We apply RAC to the problem of long-tail classification and demonstrate a significant improvement over previous state-of-the-art on Places365-LT and iNaturalist-2018 (14.5% and 6.7% respectively), despite using only the training datasets themselves as the external information source. We demonstrate that RAC's retrieval module, without prompting, learns a high level of accuracy on tail classes. This, in turn, frees the base encoder to focus on common classes, and improve its performance thereon. RAC represents an alternative approach to utilizing large, pretrained models without requiring fine-tuning, as well as a first step towards more effectively making use of external memory within common computer vision architectures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge