Rethinking the Zigzag Flattening for Image Reading
Paper and Code
Mar 15, 2022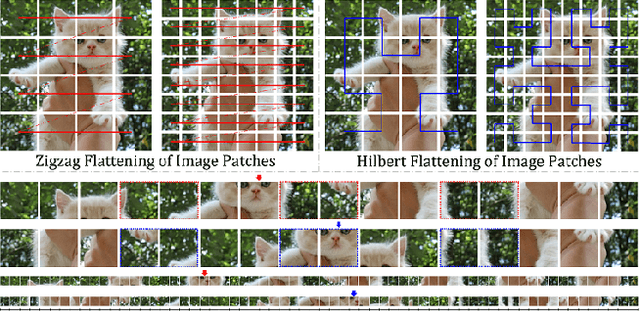
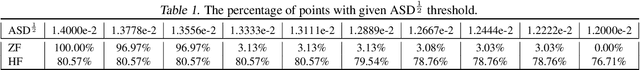
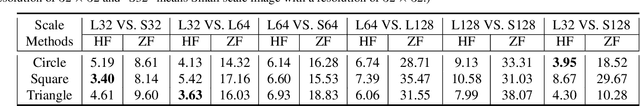
Sequence ordering of word vector matters a lot to text reading, which has been proven in natural language processing (NLP). However, the rule of different sequence ordering in computer vision (CV) was not well explored, e.g., why the "zigzag" flattening (ZF) is commonly utilized as a default option to get the image patches ordering in vision transformers (ViTs). Notably, when decomposing multi-scale images, the ZF could not maintain the invariance of feature point positions. To this end, we investigate the Hilbert fractal flattening (HF) as another method for sequence ordering in CV and contrast it against ZF. The HF has proven to be superior to other curves in maintaining spatial locality, when performing multi-scale transformations of dimensional space. And it can be easily plugged into most deep neural networks (DNNs). Extensive experiments demonstrate that it can yield consistent and significant performance boosts for a variety of architectures. Finally, we hope that our studies spark further research about the flattening strategy of image reading.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge