Reinforcement Learning-based Black-Box Evasion Attacks to Link Prediction in Dynamic Graphs
Paper and Code
Sep 12, 2020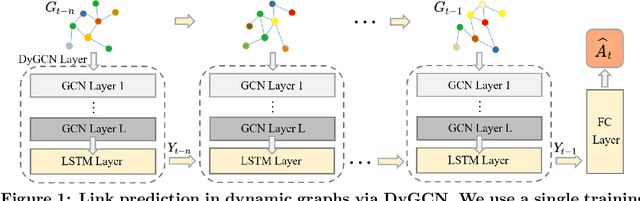
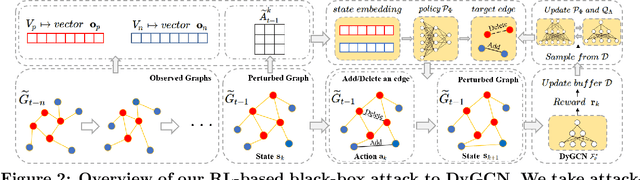
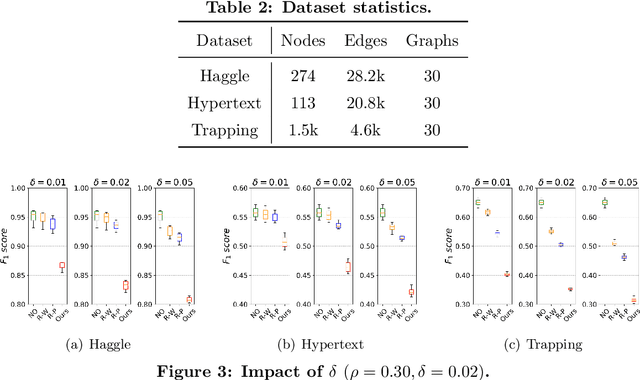
Link prediction in dynamic graphs (LPDG) is an important research problem that has diverse applications such as online recommendations, studies on disease contagion, organizational studies, etc. Various LPDG methods based on graph embedding and graph neural networks have been recently proposed and achieved state-of-the-art performance. In this paper, we study the vulnerability of LPDG methods and propose the first practical black-box evasion attack. Specifically, given a trained LPDG model, our attack aims to perturb the graph structure, without knowing to model parameters, model architecture, etc., such that the LPDG model makes as many wrong predicted links as possible. We design our attack based on a stochastic policy-based RL algorithm. Moreover, we evaluate our attack on three real-world graph datasets from different application domains. Experimental results show that our attack is both effective and efficient.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge