Mining Latent Relationships among Clients: Peer-to-peer Federated Learning with Adaptive Neighbor Matching
Paper and Code
Mar 23, 2022

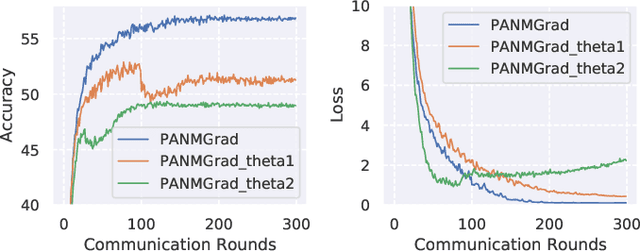

In federated learning (FL), clients may have diverse objectives, merging all clients' knowledge into one global model will cause negative transfers to local performance. Thus, clustered FL is proposed to group similar clients into clusters and maintain several global models. Nevertheless, current clustered FL algorithms require the assumption of the number of clusters, they are not effective enough to explore the latent relationships among clients. However, we take advantage of peer-to-peer (P2P) FL, where clients communicate with neighbors without a central server and propose an algorithm that enables clients to form an effective communication topology in a decentralized manner without assuming the number of clusters. Additionally, the P2P setting will release the concerns caused by the central server in centralized FL, such as reliability and communication bandwidth problems. In our method, 1) we present two novel metrics for measuring client similarity, applicable under P2P protocols; 2) we devise a two-stage algorithm, in the first stage, an efficient method to enable clients to match same-cluster neighbors with high confidence is proposed; 3) then in the second stage, a heuristic method based on Expectation Maximization under the Gaussian Mixture Model assumption of similarities is used for clients to discover more neighbors with similar objectives. We make a theoretical analysis of how our work is superior to the P2P FL counterpart and extensive experiments show that our method outperforms all P2P FL baselines and has comparable or even superior performance to centralized cluster FL. Moreover, results show that our method is much effective in mining latent cluster relationships under various heterogeneity without assuming the number of clusters and it is effective even under low communication budgets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge