Localizing the Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve via Ultrasound with a Bayesian Shape Framework
Paper and Code
Jun 30, 2022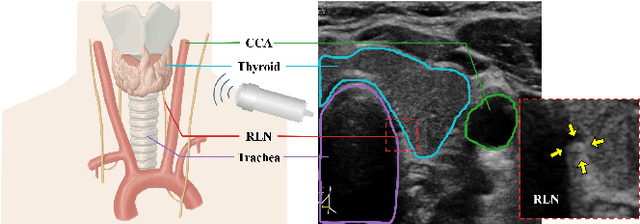
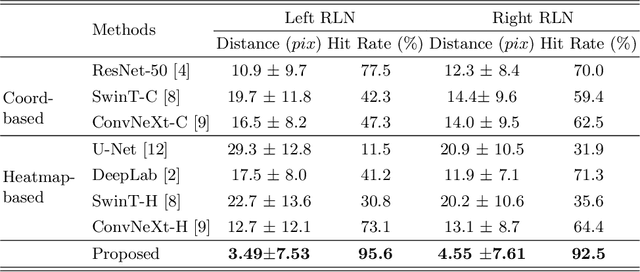
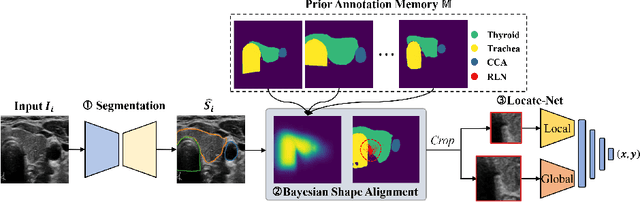
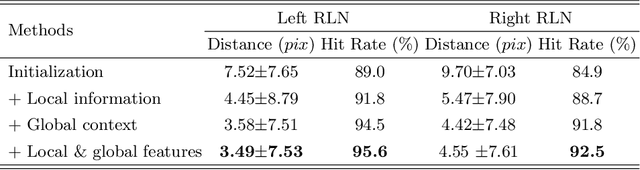
Tumor infiltration of the recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) is a contraindication for robotic thyroidectomy and can be difficult to detect via standard laryngoscopy. Ultrasound (US) is a viable alternative for RLN detection due to its safety and ability to provide real-time feedback. However, the tininess of the RLN, with a diameter typically less than 3mm, poses significant challenges to the accurate localization of the RLN. In this work, we propose a knowledge-driven framework for RLN localization, mimicking the standard approach surgeons take to identify the RLN according to its surrounding organs. We construct a prior anatomical model based on the inherent relative spatial relationships between organs. Through Bayesian shape alignment (BSA), we obtain the candidate coordinates of the center of a region of interest (ROI) that encloses the RLN. The ROI allows a decreased field of view for determining the refined centroid of the RLN using a dual-path identification network, based on multi-scale semantic information. Experimental results indicate that the proposed method achieves superior hit rates and substantially smaller distance errors compared with state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge