Forensic Analysis of Synthetically Generated Scientific Images
Paper and Code
Dec 16, 2021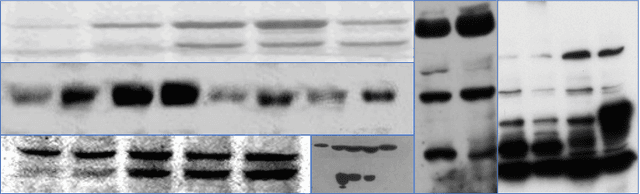
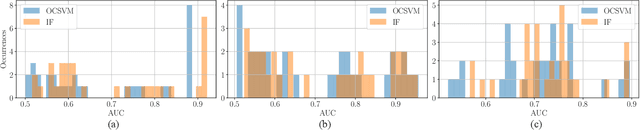
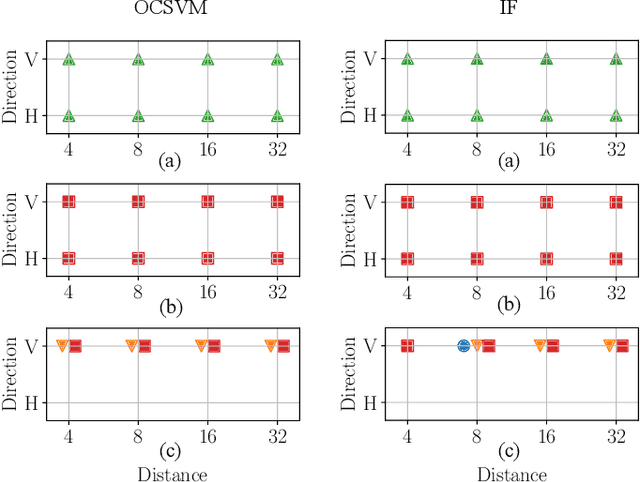

The widespread diffusion of synthetically generated content is a serious threat that needs urgent countermeasures. The generation of synthetic content is not restricted to multimedia data like videos, photographs, or audio sequences, but covers a significantly vast area that can include biological images as well, such as western-blot and microscopic images. In this paper, we focus on the detection of synthetically generated western-blot images. Western-blot images are largely explored in the biomedical literature and it has been already shown how these images can be easily counterfeited with few hope to spot manipulations by visual inspection or by standard forensics detectors. To overcome the absence of a publicly available dataset, we create a new dataset comprising more than 14K original western-blot images and 18K synthetic western-blot images, generated by three different state-of-the-art generation methods. Then, we investigate different strategies to detect synthetic western blots, exploring binary classification methods as well as one-class detectors. In both scenarios, we never exploit synthetic western-blot images at training stage. The achieved results show that synthetically generated western-blot images can be spot with good accuracy, even though the exploited detectors are not optimized over synthetic versions of these scientific images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge