Do You Listen with One or Two Microphones? A Unified ASR Model for Single and Multi-Channel Audio
Paper and Code
Jun 28, 2021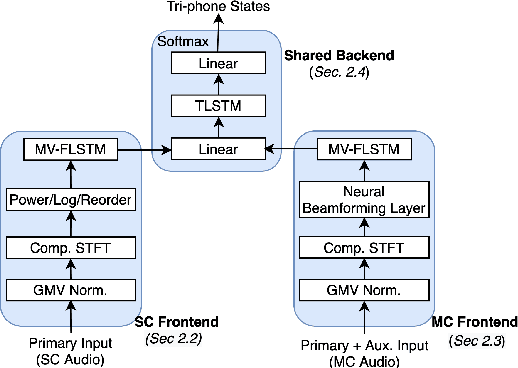
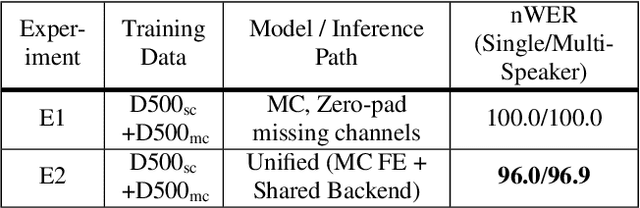
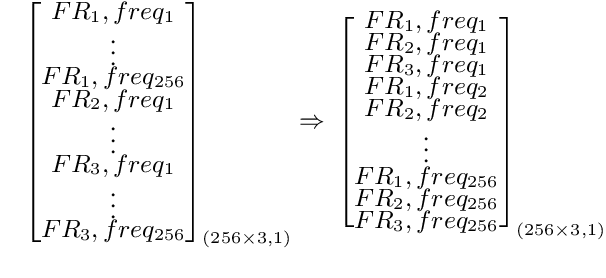
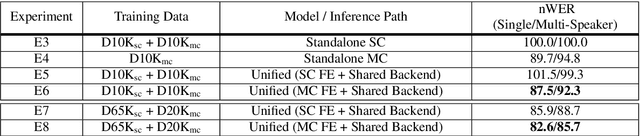
Automatic speech recognition (ASR) models are typically designed to operate on a single input data type, e.g. a single or multi-channel audio streamed from a device. This design decision assumes the primary input data source does not change and if an additional (auxiliary) data source is occasionally available, it cannot be used. An ASR model that operates on both primary and auxiliary data can achieve better accuracy compared to a primary-only solution; and a model that can serve both primary-only (PO) and primary-plus-auxiliary (PPA) modes is highly desirable. In this work, we propose a unified ASR model that can serve both modes. We demonstrate its efficacy in a realistic scenario where a set of devices typically stream a single primary audio channel, and two additional auxiliary channels only when upload bandwidth allows it. The architecture enables a unique methodology that uses both types of input audio during training time. Our proposed approach achieves up to 12.5% relative word-error-rate reduction (WERR) compared to a PO baseline, and up to 16.0% relative WERR in low-SNR conditions. The unique training methodology achieves up to 2.5% relative WERR compared to a PPA baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge