ASI++: Towards Distributionally Balanced End-to-End Generative Retrieval
Paper and Code
May 23, 2024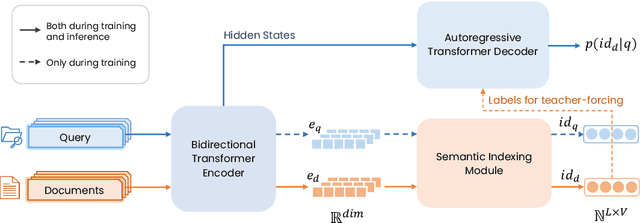



Generative retrieval, a promising new paradigm in information retrieval, employs a seq2seq model to encode document features into parameters and decode relevant document identifiers (IDs) based on search queries. Existing generative retrieval solutions typically rely on a preprocessing stage to pre-define document IDs, which can suffer from a semantic gap between these IDs and the retrieval task. However, end-to-end training for both ID assignments and retrieval tasks is challenging due to the long-tailed distribution characteristics of real-world data, resulting in inefficient and unbalanced ID space utilization. To address these issues, we propose ASI++, a novel fully end-to-end generative retrieval method that aims to simultaneously learn balanced ID assignments and improve retrieval performance. ASI++ builds on the fully end-to-end training framework of vanilla ASI and introduces several key innovations. First, a distributionally balanced criterion addresses the imbalance in ID assignments, promoting more efficient utilization of the ID space. Next, a representation bottleneck criterion enhances dense representations to alleviate bottlenecks in learning ID assignments. Finally, an information consistency criterion integrates these processes into a joint optimization framework grounded in information theory. We further explore various module structures for learning ID assignments, including neural quantization, differentiable product quantization, and residual quantization. Extensive experiments on both public and industrial datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of ASI++ in improving retrieval performance and achieving balanced ID assignments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge