A Graph is Worth 1-bit Spikes: When Graph Contrastive Learning Meets Spiking Neural Networks
Paper and Code
May 30, 2023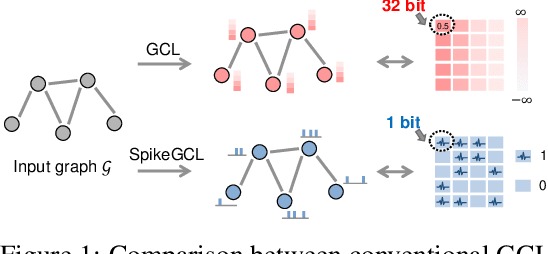

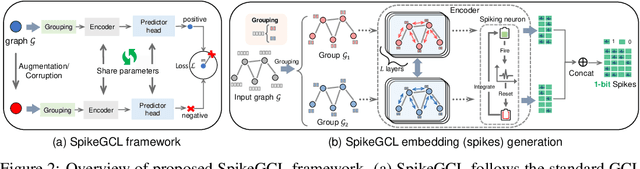
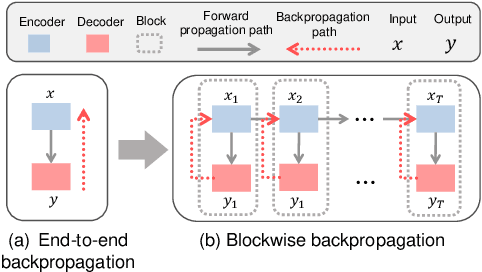
While contrastive self-supervised learning has become the de-facto learning paradigm for graph neural networks, the pursuit of high task accuracy requires a large hidden dimensionality to learn informative and discriminative full-precision representations, raising concerns about computation, memory footprint, and energy consumption burden (largely overlooked) for real-world applications. This paper explores a promising direction for graph contrastive learning (GCL) with spiking neural networks (SNNs), which leverage sparse and binary characteristics to learn more biologically plausible and compact representations. We propose SpikeGCL, a novel GCL framework to learn binarized 1-bit representations for graphs, making balanced trade-offs between efficiency and performance. We provide theoretical guarantees to demonstrate that SpikeGCL has comparable expressiveness with its full-precision counterparts. Experimental results demonstrate that, with nearly 32x representation storage compression, SpikeGCL is either comparable to or outperforms many fancy state-of-the-art supervised and self-supervised methods across several graph benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge