A Comparative Study on Early Detection of COVID-19 from Chest X-Ray Images
Paper and Code
Jun 07, 2020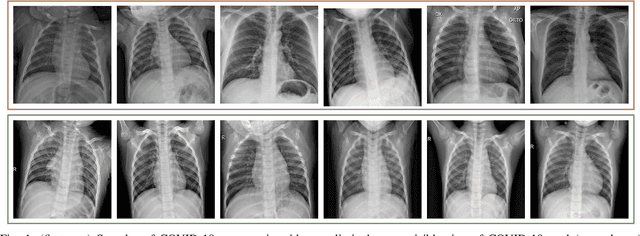
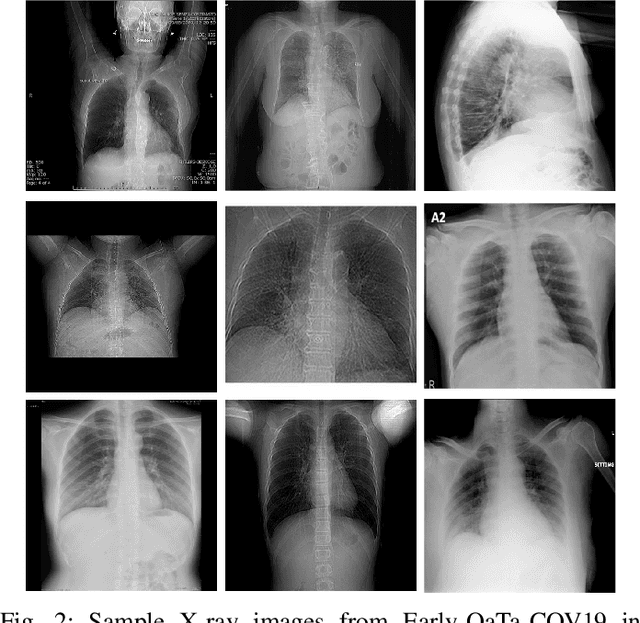
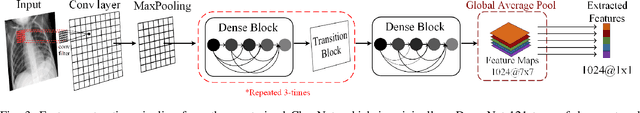
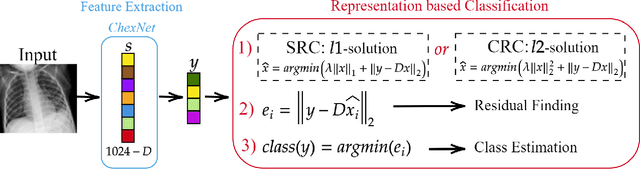
In this study, our first aim is to evaluate the ability of recent state-of-the-art Machine Learning techniques to early detect COVID-19 from plain chest X-ray images. Both compact classifiers and deep learning approaches are considered in this study. Furthermore, we propose a recent compact classifier, Convolutional Support Estimator Network (CSEN) approach for this purpose since it is well-suited for a scarce-data classification task. Finally, this study introduces a new benchmark dataset called Early-QaTa-COV19, which consists of 175 early-stage COVID-19 Pneumonia samples (very limited or no infection signs) labelled by the medical doctors and 1579 samples for control (normal) class. A detailed set of experiments show that the CSEN achieves the top (over 98.5%) sensitivity with over 96% specificity. Moreover, transfer learning over the deep CheXNet fine-tuned with the augmented data produces the leading performance among other deep networks with 97.14% sensitivity and 99.49% specificity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge