1st Place Solution to Odyssey Emotion Recognition Challenge Task1: Tackling Class Imbalance Problem
Paper and Code
May 30, 2024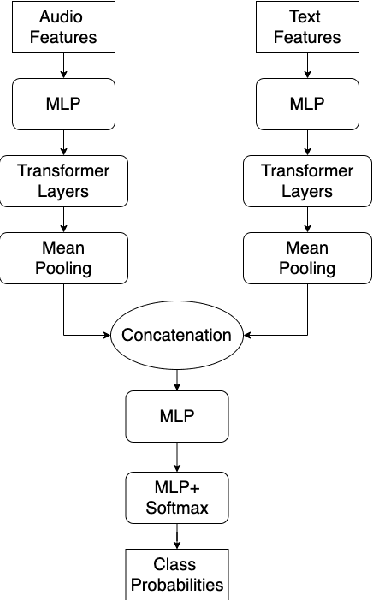



Speech emotion recognition is a challenging classification task with natural emotional speech, especially when the distribution of emotion types is imbalanced in the training and test data. In this case, it is more difficult for a model to learn to separate minority classes, resulting in those sometimes being ignored or frequently misclassified. Previous work has utilised class weighted loss for training, but problems remain as it sometimes causes over-fitting for minor classes or under-fitting for major classes. This paper presents the system developed by a multi-site team for the participation in the Odyssey 2024 Emotion Recognition Challenge Track-1. The challenge data has the aforementioned properties and therefore the presented systems aimed to tackle these issues, by introducing focal loss in optimisation when applying class weighted loss. Specifically, the focal loss is further weighted by prior-based class weights. Experimental results show that combining these two approaches brings better overall performance, by sacrificing performance on major classes. The system further employs a majority voting strategy to combine the outputs of an ensemble of 7 models. The models are trained independently, using different acoustic features and loss functions - with the aim to have different properties for different data. Hence these models show different performance preferences on major classes and minor classes. The ensemble system output obtained the best performance in the challenge, ranking top-1 among 68 submissions. It also outperformed all single models in our set. On the Odyssey 2024 Emotion Recognition Challenge Task-1 data the system obtained a Macro-F1 score of 35.69% and an accuracy of 37.32%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge