Zonghan Li
RflyUT-Sim: A Simulation Platform for Development and Testing of Complex Low-Altitude Traffic Control
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Significant challenges are posed by simulation and testing in the field of low-altitude unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) traffic due to the high costs associated with large-scale UAV testing and the complexity of establishing low-altitude traffic test scenarios. Stringent safety requirements make high fidelity one of the key metrics for simulation platforms. Despite advancements in simulation platforms for low-altitude UAVs, there is still a shortage of platforms that feature rich traffic scenarios, high-precision UAV and scenario simulators, and comprehensive testing capabilities for low-altitude traffic. Therefore, this paper introduces an integrated high-fidelity simulation platform for low-altitude UAV traffic. This platform simulates all components of the UAV traffic network, including the control system, the traffic management system, the UAV system, the communication network , the anomaly and fault modules, etc. Furthermore, it integrates RflySim/AirSim and Unreal Engine 5 to develop full-state models of UAVs and 3D maps that model the real world using the oblique photogrammetry technique. Additionally, the platform offers a wide range of interfaces, and all models and scenarios can be customized with a high degree of flexibility. The platform's source code has been released, making it easier to conduct research related to low-altitude traffic.
Potential of large language model-powered nudges for promoting daily water and energy conservation
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:The increasing amount of pressure related to water and energy shortages has increased the urgency of cultivating individual conservation behaviors. While the concept of nudging, i.e., providing usage-based feedback, has shown promise in encouraging conservation behaviors, its efficacy is often constrained by the lack of targeted and actionable content. This study investigates the impact of the use of large language models (LLMs) to provide tailored conservation suggestions for conservation intentions and their rationale. Through a survey experiment with 1,515 university participants, we compare three virtual nudging scenarios: no nudging, traditional nudging with usage statistics, and LLM-powered nudging with usage statistics and personalized conservation suggestions. The results of statistical analyses and causal forest modeling reveal that nudging led to an increase in conservation intentions among 86.9%-98.0% of the participants. LLM-powered nudging achieved a maximum increase of 18.0% in conservation intentions, surpassing traditional nudging by 88.6%. Furthermore, structural equation modeling results reveal that exposure to LLM-powered nudges enhances self-efficacy and outcome expectations while diminishing dependence on social norms, thereby increasing intrinsic motivation to conserve. These findings highlight the transformative potential of LLMs in promoting individual water and energy conservation, representing a new frontier in the design of sustainable behavioral interventions and resource management.
Improving Drumming Robot Via Attention Transformer Network
Oct 04, 2023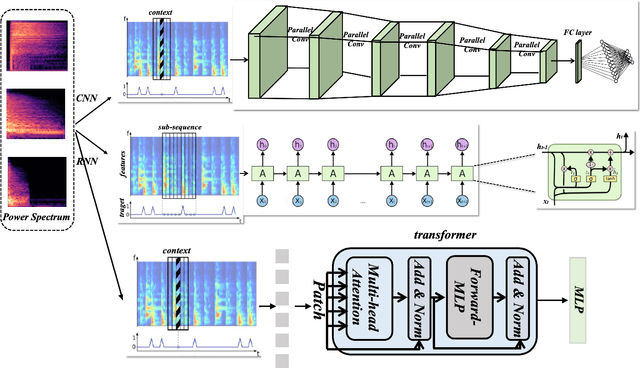
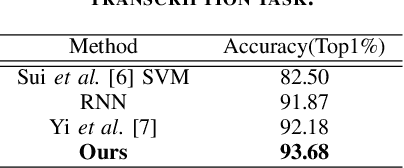
Abstract:Robotic technology has been widely used in nowadays society, which has made great progress in various fields such as agriculture, manufacturing and entertainment. In this paper, we focus on the topic of drumming robots in entertainment. To this end, we introduce an improving drumming robot that can automatically complete music transcription based on the popular vision transformer network based on the attention mechanism. Equipped with the attention transformer network, our method can efficiently handle the sequential audio embedding input and model their global long-range dependencies. Massive experimental results demonstrate that the improving algorithm can help the drumming robot promote drum classification performance, which can also help the robot to enjoy a variety of smart applications and services.
Dual-Augmented Transformer Network for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Sep 30, 2023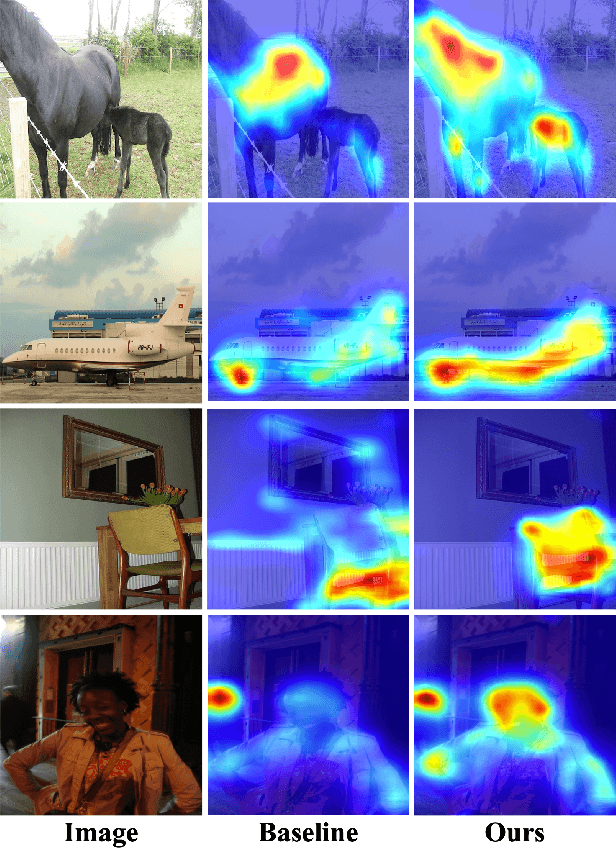
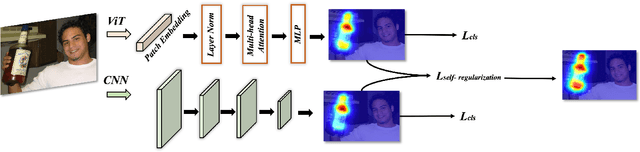

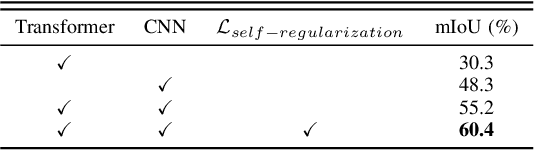
Abstract:Weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS), a fundamental computer vision task, which aims to segment out the object within only class-level labels. The traditional methods adopt the CNN-based network and utilize the class activation map (CAM) strategy to discover the object regions. However, such methods only focus on the most discriminative region of the object, resulting in incomplete segmentation. An alternative is to explore vision transformers (ViT) to encode the image to acquire the global semantic information. Yet, the lack of transductive bias to objects is a flaw of ViT. In this paper, we explore the dual-augmented transformer network with self-regularization constraints for WSSS. Specifically, we propose a dual network with both CNN-based and transformer networks for mutually complementary learning, where both networks augment the final output for enhancement. Massive systemic evaluations on the challenging PASCAL VOC 2012 benchmark demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, outperforming previous state-of-the-art methods.
COMNet: Co-Occurrent Matching for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Sep 29, 2023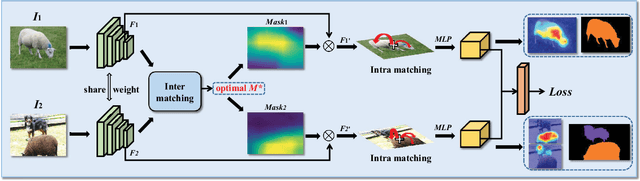
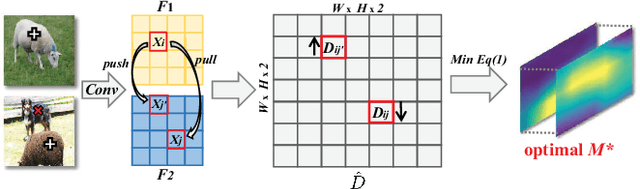
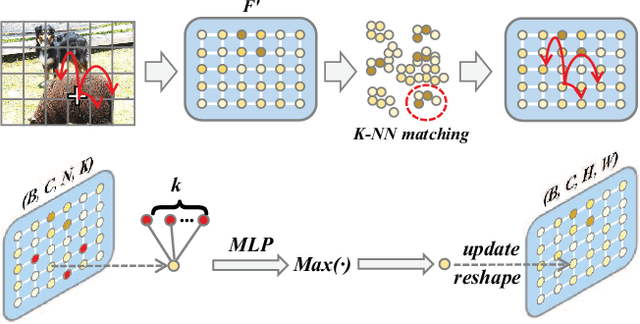
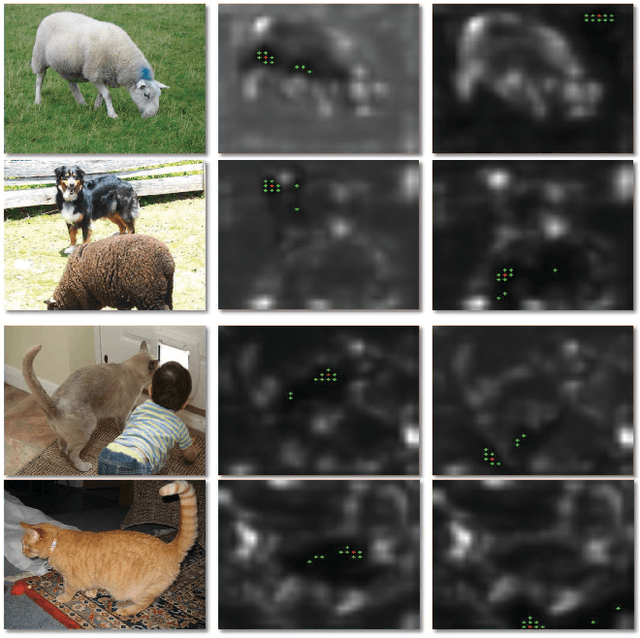
Abstract:Image-level weakly supervised semantic segmentation is a challenging task that has been deeply studied in recent years. Most of the common solutions exploit class activation map (CAM) to locate object regions. However, such response maps generated by the classification network usually focus on discriminative object parts. In this paper, we propose a novel Co-Occurrent Matching Network (COMNet), which can promote the quality of the CAMs and enforce the network to pay attention to the entire parts of objects. Specifically, we perform inter-matching on paired images that contain common classes to enhance the corresponded areas, and construct intra-matching on a single image to propagate the semantic features across the object regions. The experiments on the Pascal VOC 2012 and MS-COCO datasets show that our network can effectively boost the performance of the baseline model and achieve new state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge