Zoltan Gorocs
An insertable glucose sensor using a compact and cost-effective phosphorescence lifetime imager and machine learning
Jun 12, 2024Abstract:Optical continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems are emerging for personalized glucose management owing to their lower cost and prolonged durability compared to conventional electrochemical CGMs. Here, we report a computational CGM system, which integrates a biocompatible phosphorescence-based insertable biosensor and a custom-designed phosphorescence lifetime imager (PLI). This compact and cost-effective PLI is designed to capture phosphorescence lifetime images of an insertable sensor through the skin, where the lifetime of the emitted phosphorescence signal is modulated by the local concentration of glucose. Because this phosphorescence signal has a very long lifetime compared to tissue autofluorescence or excitation leakage processes, it completely bypasses these noise sources by measuring the sensor emission over several tens of microseconds after the excitation light is turned off. The lifetime images acquired through the skin are processed by neural network-based models for misalignment-tolerant inference of glucose levels, accurately revealing normal, low (hypoglycemia) and high (hyperglycemia) concentration ranges. Using a 1-mm thick skin phantom mimicking the optical properties of human skin, we performed in vitro testing of the PLI using glucose-spiked samples, yielding 88.8% inference accuracy, also showing resilience to random and unknown misalignments within a lateral distance of ~4.7 mm with respect to the position of the insertable sensor underneath the skin phantom. Furthermore, the PLI accurately identified larger lateral misalignments beyond 5 mm, prompting user intervention for re-alignment. The misalignment-resilient glucose concentration inference capability of this compact and cost-effective phosphorescence lifetime imager makes it an appealing wearable diagnostics tool for real-time tracking of glucose and other biomarkers.
Deep learning enhanced mobile-phone microscopy
Dec 12, 2017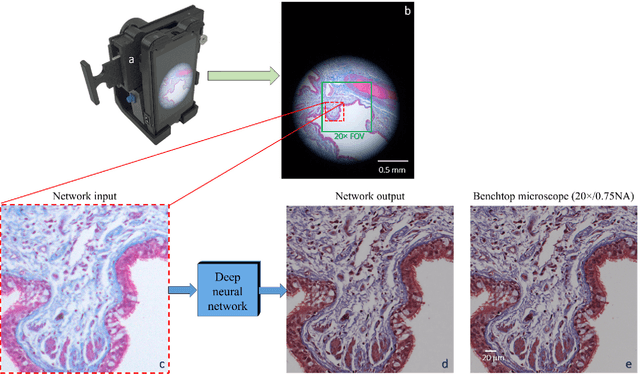
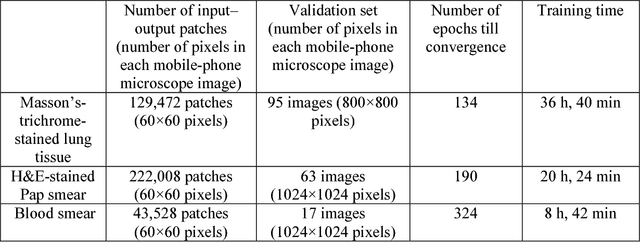
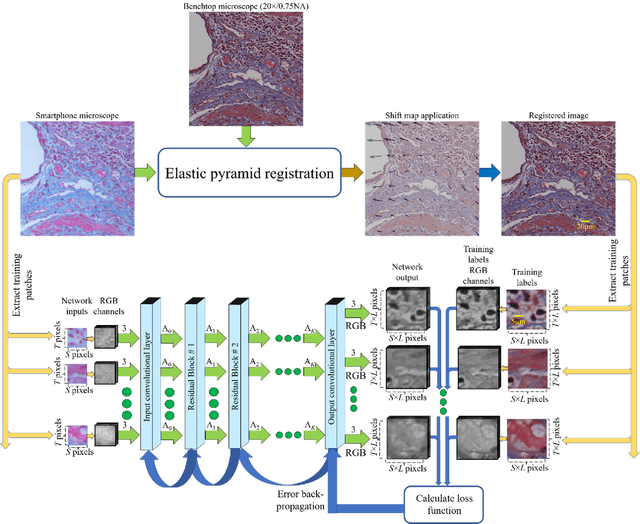
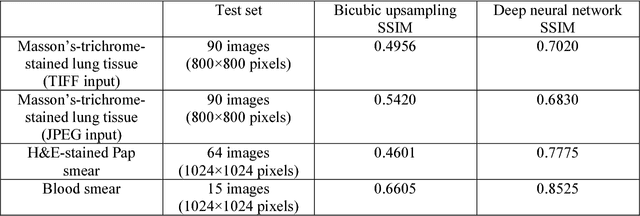
Abstract:Mobile-phones have facilitated the creation of field-portable, cost-effective imaging and sensing technologies that approach laboratory-grade instrument performance. However, the optical imaging interfaces of mobile-phones are not designed for microscopy and produce spatial and spectral distortions in imaging microscopic specimens. Here, we report on the use of deep learning to correct such distortions introduced by mobile-phone-based microscopes, facilitating the production of high-resolution, denoised and colour-corrected images, matching the performance of benchtop microscopes with high-end objective lenses, also extending their limited depth-of-field. After training a convolutional neural network, we successfully imaged various samples, including blood smears, histopathology tissue sections, and parasites, where the recorded images were highly compressed to ease storage and transmission for telemedicine applications. This method is applicable to other low-cost, aberrated imaging systems, and could offer alternatives for costly and bulky microscopes, while also providing a framework for standardization of optical images for clinical and biomedical applications.
Deep Learning Microscopy
May 12, 2017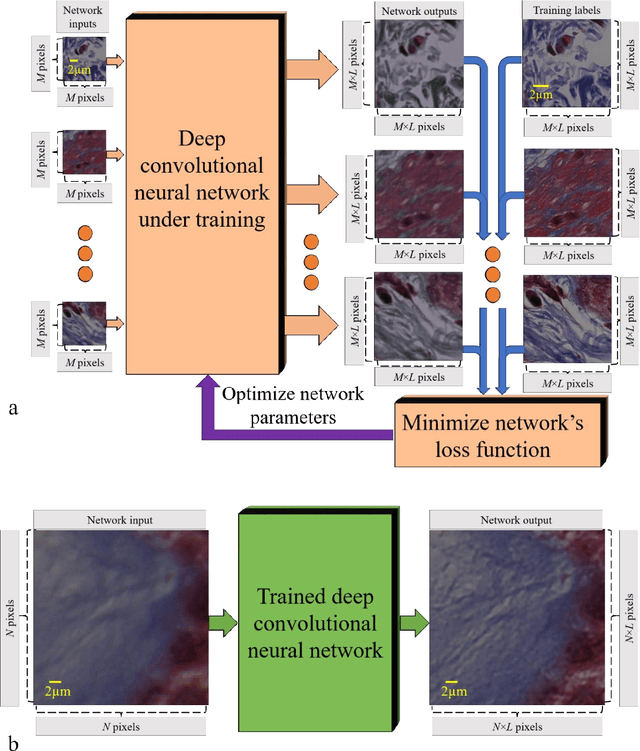
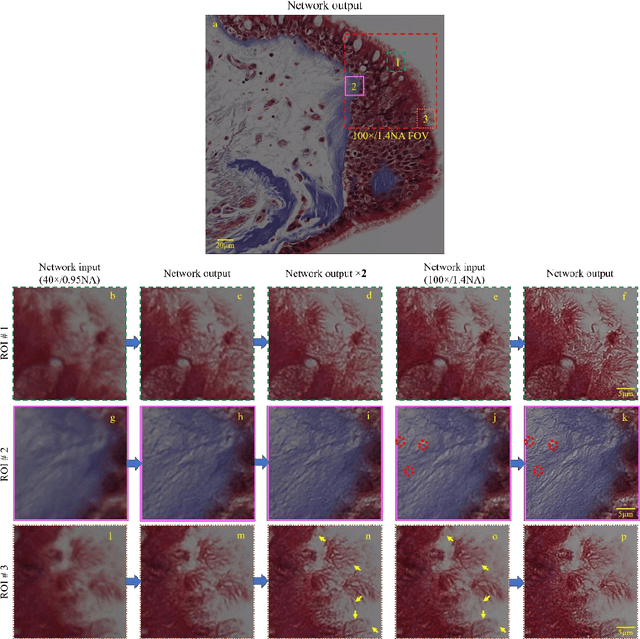
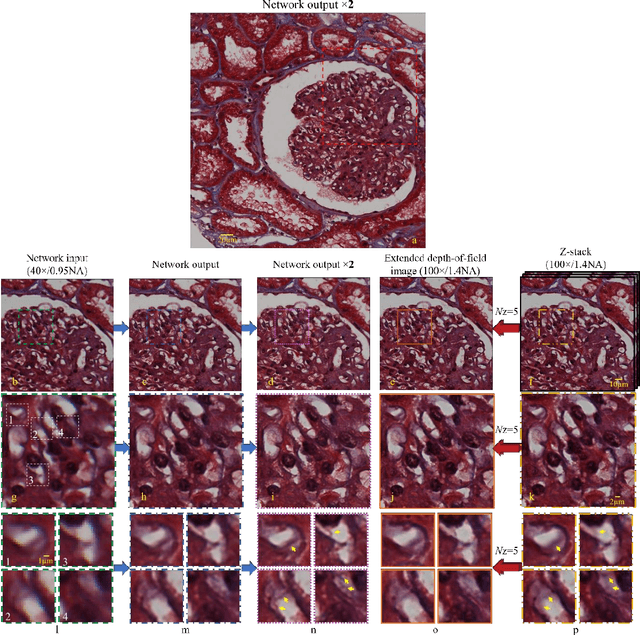
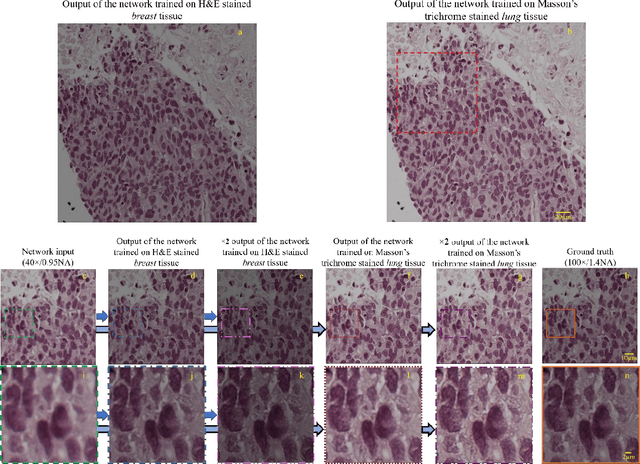
Abstract:We demonstrate that a deep neural network can significantly improve optical microscopy, enhancing its spatial resolution over a large field-of-view and depth-of-field. After its training, the only input to this network is an image acquired using a regular optical microscope, without any changes to its design. We blindly tested this deep learning approach using various tissue samples that are imaged with low-resolution and wide-field systems, where the network rapidly outputs an image with remarkably better resolution, matching the performance of higher numerical aperture lenses, also significantly surpassing their limited field-of-view and depth-of-field. These results are transformative for various fields that use microscopy tools, including e.g., life sciences, where optical microscopy is considered as one of the most widely used and deployed techniques. Beyond such applications, our presented approach is broadly applicable to other imaging modalities, also spanning different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, and can be used to design computational imagers that get better and better as they continue to image specimen and establish new transformations among different modes of imaging.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge