Zitong Chao
UGMathBench: A Diverse and Dynamic Benchmark for Undergraduate-Level Mathematical Reasoning with Large Language Models
Jan 23, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have made significant strides in mathematical reasoning, underscoring the need for a comprehensive and fair evaluation of their capabilities. However, existing benchmarks often fall short, either lacking extensive coverage of undergraduate-level mathematical problems or probably suffering from test-set contamination. To address these issues, we introduce UGMathBench, a diverse and dynamic benchmark specifically designed for evaluating undergraduate-level mathematical reasoning with LLMs. UGMathBench comprises 5,062 problems across 16 subjects and 111 topics, featuring 10 distinct answer types. Each problem includes three randomized versions, with additional versions planned for release as leading open-source LLMs become saturated in UGMathBench. Furthermore, we propose two key metrics: effective accuracy (EAcc), which measures the percentage of correctly solved problems across all three versions, and reasoning gap ($\Delta$), which assesses reasoning robustness by calculating the difference between the average accuracy across all versions and EAcc. Our extensive evaluation of 23 leading LLMs reveals that the highest EAcc achieved is 56.3\% by OpenAI-o1-mini, with large $\Delta$ values observed across different models. This highlights the need for future research aimed at developing "large reasoning models" with high EAcc and $\Delta = 0$. We anticipate that the release of UGMathBench, along with its detailed evaluation codes, will serve as a valuable resource to advance the development of LLMs in solving mathematical problems.
* Accepted to ICLR 2025
Can LLMs Solve longer Math Word Problems Better?
May 23, 2024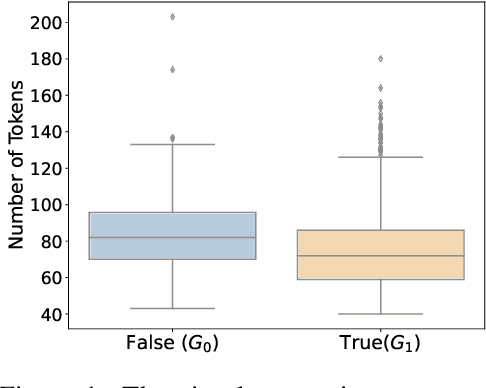
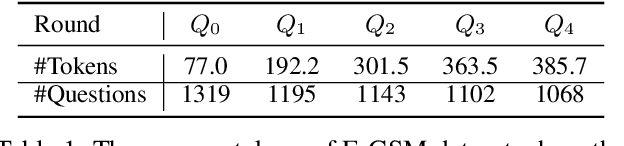
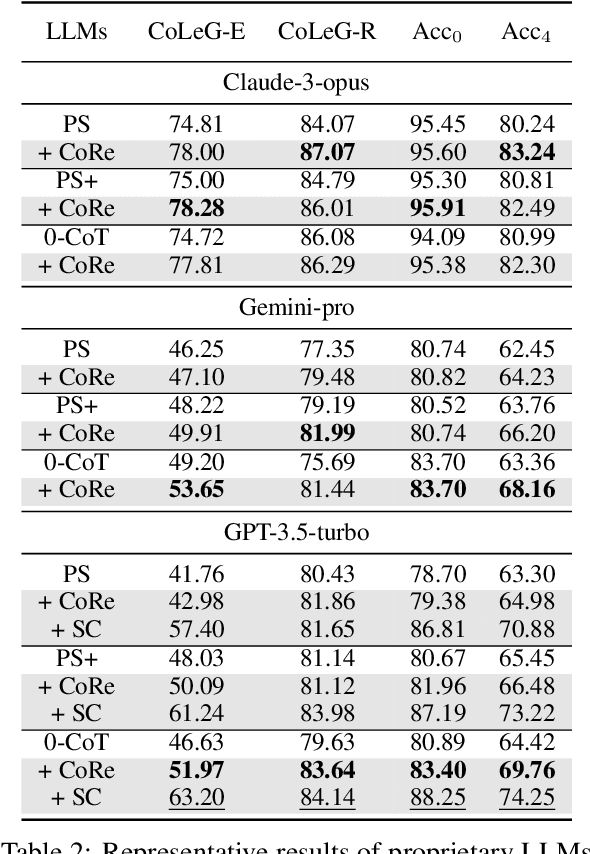
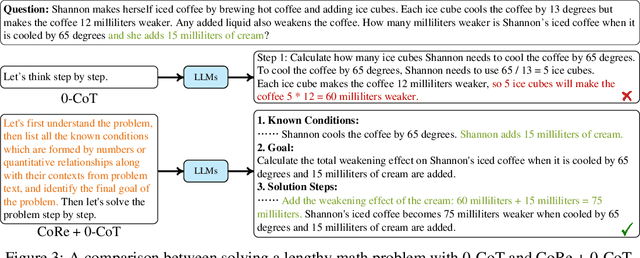
Abstract:Math Word Problems (MWPs) are crucial for evaluating the capability of Large Language Models (LLMs), with current research primarily focusing on questions with concise contexts. However, as real-world math problems often involve complex circumstances, LLMs' ability to solve long MWPs is vital for their applications in these scenarios, yet remains under-explored. This study pioneers the exploration of Context Length Generalizability (CoLeG), the ability of LLMs to solve long MWPs. We introduce Extended Grade-School Math (E-GSM), a collection of MWPs with lengthy narratives. Two novel metrics are proposed to assess the efficacy and resilience of LLMs in solving these problems. Our examination of existing zero-shot prompting techniques and both proprietary and open-source LLMs reveals a general deficiency in CoLeG. To alleviate these challenges, we propose distinct approaches for different categories of LLMs. For proprietary LLMs, a new instructional prompt is proposed to mitigate the influence of long context. For open-source LLMs, a new data augmentation task is developed to improve CoLeG. Our comprehensive results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed methods, showing not only improved performance on E-GSM but also generalizability across several other MWP benchmarks. Our findings pave the way for future research in employing LLMs for complex, real-world applications, offering practical solutions to current limitations and opening avenues for further exploration of model generalizability and training methodologies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge