Zining Chen
Data-Efficient Generalization for Zero-shot Composed Image Retrieval
Mar 07, 2025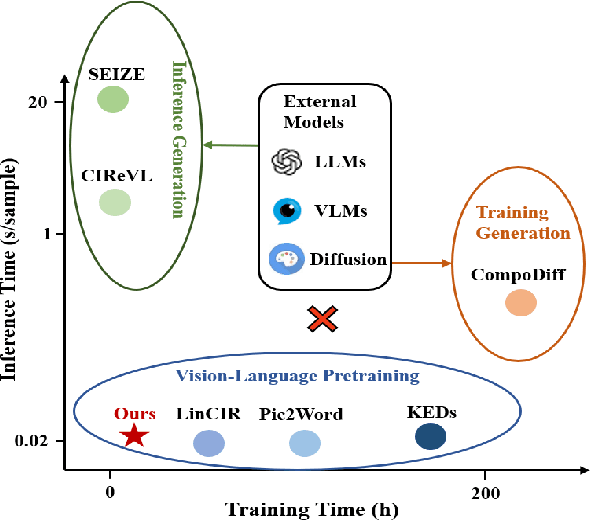
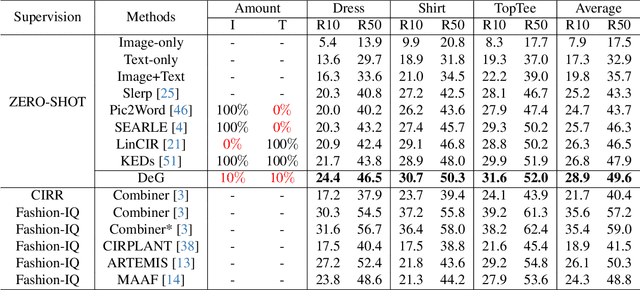
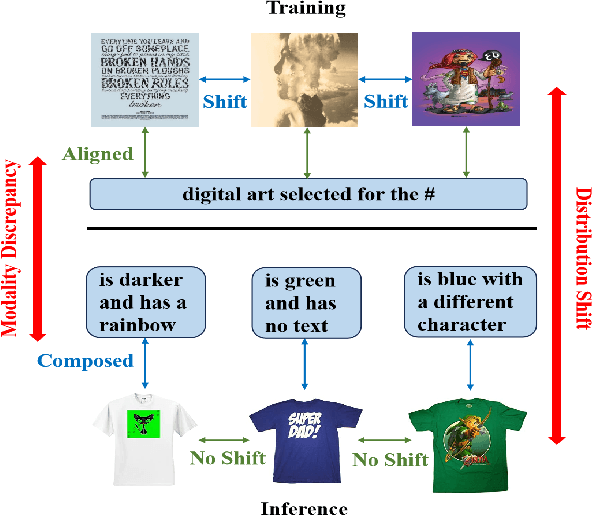
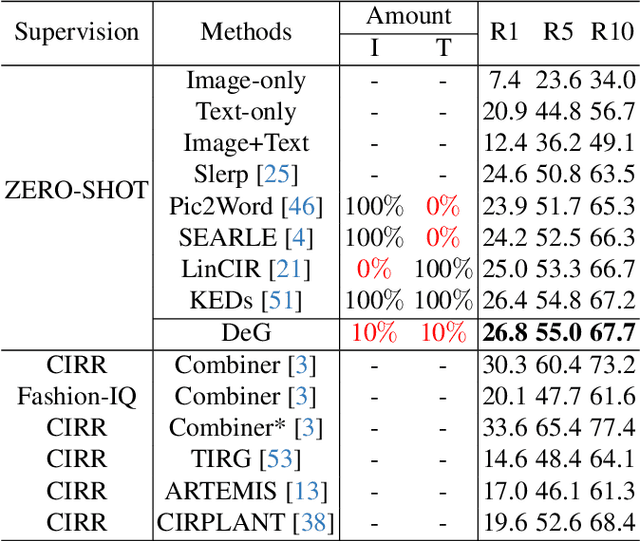
Abstract:Zero-shot Composed Image Retrieval (ZS-CIR) aims to retrieve the target image based on a reference image and a text description without requiring in-distribution triplets for training. One prevalent approach follows the vision-language pretraining paradigm that employs a mapping network to transfer the image embedding to a pseudo-word token in the text embedding space. However, this approach tends to impede network generalization due to modality discrepancy and distribution shift between training and inference. To this end, we propose a Data-efficient Generalization (DeG) framework, including two novel designs, namely, Textual Supplement (TS) module and Semantic-Set (S-Set). The TS module exploits compositional textual semantics during training, enhancing the pseudo-word token with more linguistic semantics and thus mitigating the modality discrepancy effectively. The S-Set exploits the zero-shot capability of pretrained Vision-Language Models (VLMs), alleviating the distribution shift and mitigating the overfitting issue from the redundancy of the large-scale image-text data. Extensive experiments over four ZS-CIR benchmarks show that DeG outperforms the state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods with much less training data, and saves substantial training and inference time for practical usage.
Filter or Compensate: Towards Invariant Representation from Distribution Shift for Anomaly Detection
Dec 13, 2024Abstract:Recent Anomaly Detection (AD) methods have achieved great success with In-Distribution (ID) data. However, real-world data often exhibits distribution shift, causing huge performance decay on traditional AD methods. From this perspective, few previous work has explored AD with distribution shift, and the distribution-invariant normality learning has been proposed based on the Reverse Distillation (RD) framework. However, we observe the misalignment issue between the teacher and the student network that causes detection failure, thereby propose FiCo, Filter or Compensate, to address the distribution shift issue in AD. FiCo firstly compensates the distribution-specific information to reduce the misalignment between the teacher and student network via the Distribution-Specific Compensation (DiSCo) module, and secondly filters all abnormal information to capture distribution-invariant normality with the Distribution-Invariant Filter (DiIFi) module. Extensive experiments on three different AD benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of FiCo, which outperforms all existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods, and even achieves better results on the ID scenario compared with RD-based methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/znchen666/FiCo.
PracticalDG: Perturbation Distillation on Vision-Language Models for Hybrid Domain Generalization
Apr 13, 2024



Abstract:Domain Generalization (DG) aims to resolve distribution shifts between source and target domains, and current DG methods are default to the setting that data from source and target domains share identical categories. Nevertheless, there exists unseen classes from target domains in practical scenarios. To address this issue, Open Set Domain Generalization (OSDG) has emerged and several methods have been exclusively proposed. However, most existing methods adopt complex architectures with slight improvement compared with DG methods. Recently, vision-language models (VLMs) have been introduced in DG following the fine-tuning paradigm, but consume huge training overhead with large vision models. Therefore, in this paper, we innovate to transfer knowledge from VLMs to lightweight vision models and improve the robustness by introducing Perturbation Distillation (PD) from three perspectives, including Score, Class and Instance (SCI), named SCI-PD. Moreover, previous methods are oriented by the benchmarks with identical and fixed splits, ignoring the divergence between source domains. These methods are revealed to suffer from sharp performance decay with our proposed new benchmark Hybrid Domain Generalization (HDG) and a novel metric $H^{2}$-CV, which construct various splits to comprehensively assess the robustness of algorithms. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art algorithms on multiple datasets, especially improving the robustness when confronting data scarcity.
Causality-based Dual-Contrastive Learning Framework for Domain Generalization
Jan 22, 2023Abstract:Domain Generalization (DG) is essentially a sub-branch of out-of-distribution generalization, which trains models from multiple source domains and generalizes to unseen target domains. Recently, some domain generalization algorithms have emerged, but most of them were designed with non-transferable complex architecture. Additionally, contrastive learning has become a promising solution for simplicity and efficiency in DG. However, existing contrastive learning neglected domain shifts that caused severe model confusions. In this paper, we propose a Dual-Contrastive Learning (DCL) module on feature and prototype contrast. Moreover, we design a novel Causal Fusion Attention (CFA) module to fuse diverse views of a single image to attain prototype. Furthermore, we introduce a Similarity-based Hard-pair Mining (SHM) strategy to leverage information on diversity shift. Extensive experiments show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art algorithms on three DG datasets. The proposed algorithm can also serve as a plug-and-play module without usage of domain labels.
Bag of Tricks for Out-of-Distribution Generalization
Aug 23, 2022
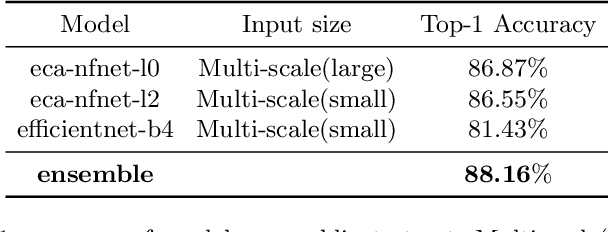
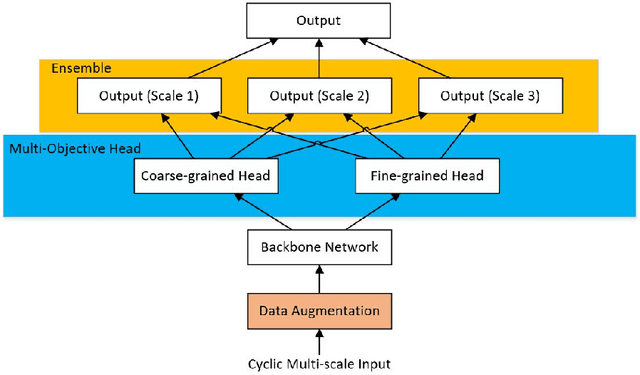
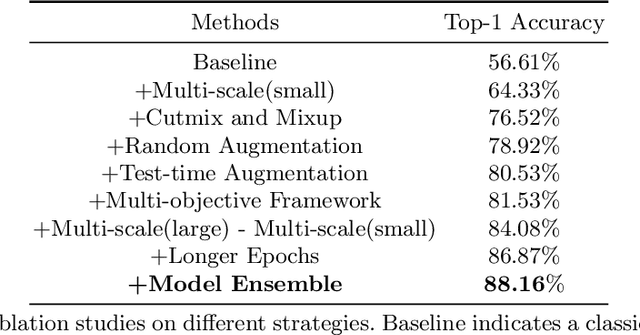
Abstract:Recently, out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization has attracted attention to the robustness and generalization ability of deep learning based models, and accordingly, many strategies have been made to address different aspects related to this issue. However, most existing algorithms for OOD generalization are complicated and specifically designed for certain dataset. To alleviate this problem, nicochallenge-2022 provides NICO++, a large-scale dataset with diverse context information. In this paper, based on systematic analysis of different schemes on NICO++ dataset, we propose a simple but effective learning framework via coupling bag of tricks, including multi-objective framework design, data augmentations, training and inference strategies. Our algorithm is memory-efficient and easily-equipped, without complicated modules and does not require for large pre-trained models. It achieves an excellent performance with Top-1 accuracy of 88.16% on public test set and 75.65% on private test set, and ranks 1st in domain generalization task of nicochallenge-2022.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge