Zhuofan Cui
Observation Contribution Theory for Pose Estimation Accuracy
Nov 15, 2021
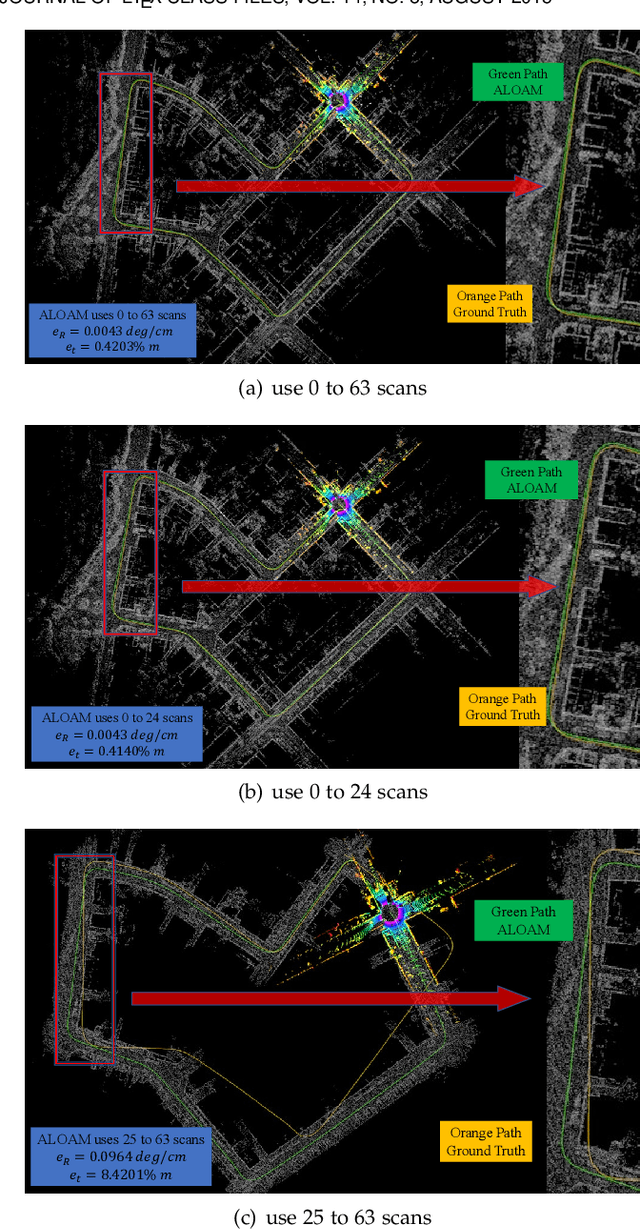
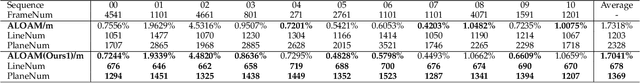
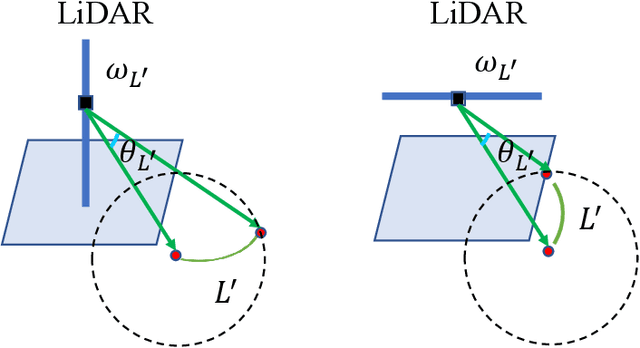
Abstract:The improvement of pose estimation accuracy is currently the fundamental problem in mobile robots. This study aims to improve the use of observations to enhance accuracy. The selection of feature points affects the accuracy of pose estimation, leading to the question of how the contribution of observation influences the system. Accordingly, the contribution of information to the pose estimation process is analyzed. Moreover, the uncertainty model, sensitivity model, and contribution theory are formulated, providing a method for calculating the contribution of every residual term. The proposed selection method has been theoretically proven capable of achieving a global statistical optimum. The proposed method is tested on artificial data simulations and compared with the KITTI benchmark. The experiments revealed superior results in contrast to ALOAM and MLOAM. The proposed algorithm is implemented in LiDAR odometry and LiDAR Inertial odometry both indoors and outdoors using diverse LiDAR sensors with different scan modes, demonstrating its effectiveness in improving pose estimation accuracy. A new configuration of two laser scan sensors is subsequently inferred. The configuration is valid for three-dimensional pose localization in a prior map and yields results at the centimeter level.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge