Zhongyuan Ruan
A Multi-View Framework for BGP Anomaly Detection via Graph Attention Network
Dec 23, 2021



Abstract:As the default protocol for exchanging routing reachability information on the Internet, the abnormal behavior in traffic of Border Gateway Protocols (BGP) is closely related to Internet anomaly events. The BGP anomalous detection model ensures stable routing services on the Internet through its real-time monitoring and alerting capabilities. Previous studies either focused on the feature selection problem or the memory characteristic in data, while ignoring the relationship between features and the precise time correlation in feature (whether it's long or short term dependence). In this paper, we propose a multi-view model for capturing anomalous behaviors from BGP update traffic, in which Seasonal and Trend decomposition using Loess (STL) method is used to reduce the noise in the original time-series data, and Graph Attention Network (GAT) is used to discover feature relationships and time correlations in feature, respectively. Our results outperform the state-of-the-art methods at the anomaly detection task, with the average F1 score up to 96.3% and 93.2% on the balanced and imbalanced datasets respectively. Meanwhile, our model can be extended to classify multiple anomalous and to detect unknown events.
Subgraph Networks with Application to Structural Feature Space Expansion
Apr 01, 2019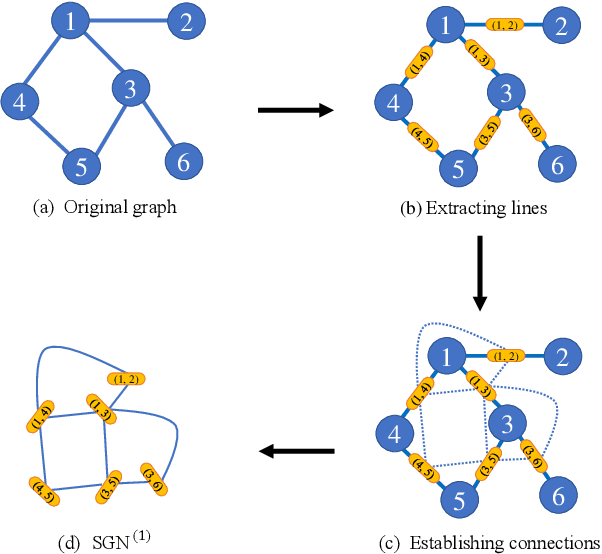
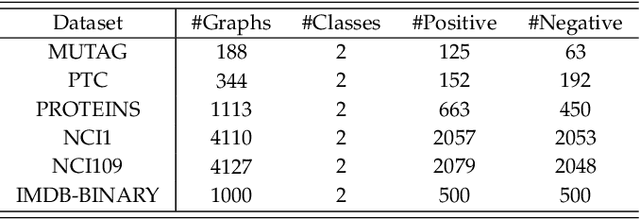
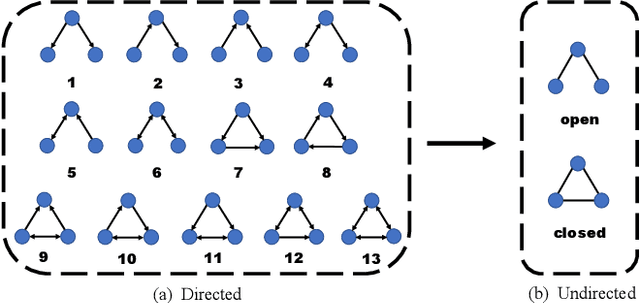
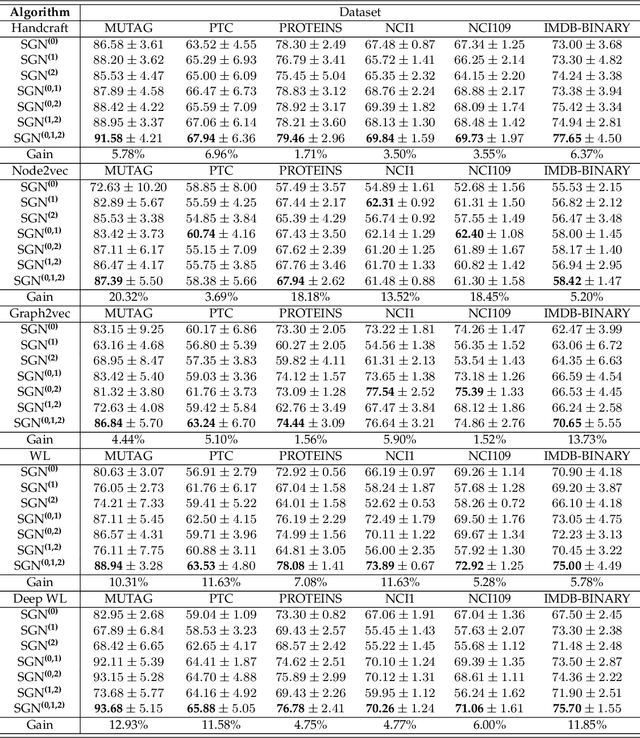
Abstract:In this paper, the concept of subgraph network (SGN) is introduced and then applied to network models, with algorithms designed for constructing the 1st-order and 2nd-order SGNs, which can be easily extended to build higher-order ones. Furthermore, these SGNs are used to expand the structural feature space of the underlying network, beneficial for network classification. Numerical experiments demonstrate that the network classification model based on the structural features of the original network together with the 1st-order and 2nd-order SGNs always performs the best as compared to the models based only on one or two of such networks. In other words, the structural features of SGNs can complement that of the original network for better network classification, regardless of the feature extraction method used, such as the handcrafted, network embedding and kernel-based methods. More interestingly, it is found that the model based on the handcrafted feature performs even better than those based on automatically generated features, at least for most datasets tested in the present investigation. This indicates that, in general, properly chosen structural features are not only more interpretable due to their clear physical meanings, but also effective in designing structure-based algorithms for network classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge