Zhiyue Liu
Target-oriented Multimodal Sentiment Classification with Counterfactual-enhanced Debiasing
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Target-oriented multimodal sentiment classification seeks to predict sentiment polarity for specific targets from image-text pairs. While existing works achieve competitive performance, they often over-rely on textual content and fail to consider dataset biases, in particular word-level contextual biases. This leads to spurious correlations between text features and output labels, impairing classification accuracy. In this paper, we introduce a novel counterfactual-enhanced debiasing framework to reduce such spurious correlations. Our framework incorporates a counterfactual data augmentation strategy that minimally alters sentiment-related causal features, generating detail-matched image-text samples to guide the model's attention toward content tied to sentiment. Furthermore, for learning robust features from counterfactual data and prompting model decisions, we introduce an adaptive debiasing contrastive learning mechanism, which effectively mitigates the influence of biased words. Experimental results on several benchmark datasets show that our proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art baselines.
A Knowledge Noise Mitigation Framework for Knowledge-based Visual Question Answering
Sep 11, 2025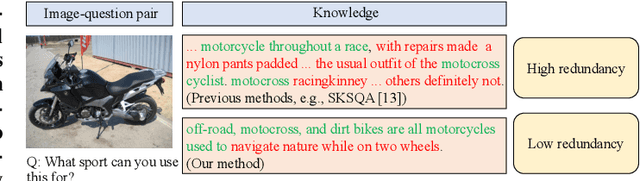
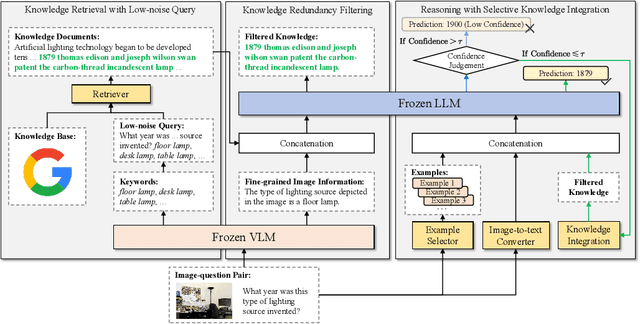
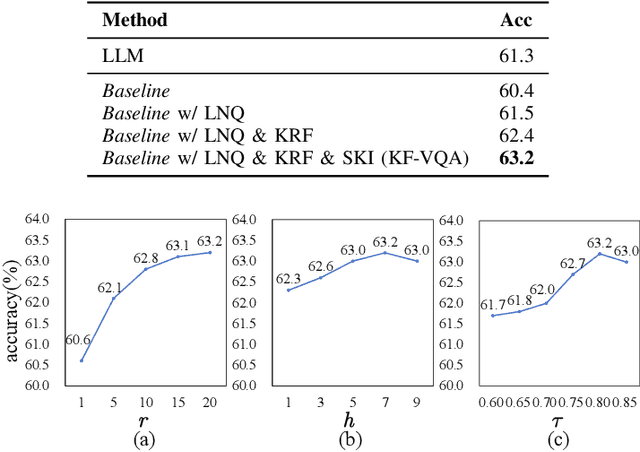
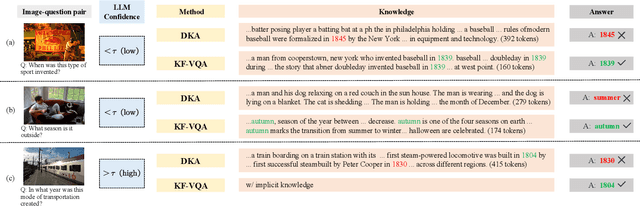
Abstract:Knowledge-based visual question answering (KB-VQA) requires a model to understand images and utilize external knowledge to provide accurate answers. Existing approaches often directly augment models with retrieved information from knowledge sources while ignoring substantial knowledge redundancy, which introduces noise into the answering process. To address this, we propose a training-free framework with knowledge focusing for KB-VQA, that mitigates the impact of noise by enhancing knowledge relevance and reducing redundancy. First, for knowledge retrieval, our framework concludes essential parts from the image-question pairs, creating low-noise queries that enhance the retrieval of highly relevant knowledge. Considering that redundancy still persists in the retrieved knowledge, we then prompt large models to identify and extract answer-beneficial segments from knowledge. In addition, we introduce a selective knowledge integration strategy, allowing the model to incorporate knowledge only when it lacks confidence in answering the question, thereby mitigating the influence of redundant information. Our framework enables the acquisition of accurate and critical knowledge, and extensive experiments demonstrate that it outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
Improving Cross-modal Alignment with Synthetic Pairs for Text-only Image Captioning
Dec 14, 2023Abstract:Although image captioning models have made significant advancements in recent years, the majority of them heavily depend on high-quality datasets containing paired images and texts which are costly to acquire. Previous works leverage the CLIP's cross-modal association ability for image captioning, relying solely on textual information under unsupervised settings. However, not only does a modality gap exist between CLIP text and image features, but a discrepancy also arises between training and inference due to the unavailability of real-world images, which hinders the cross-modal alignment in text-only captioning. This paper proposes a novel method to address these issues by incorporating synthetic image-text pairs. A pre-trained text-to-image model is deployed to obtain images that correspond to textual data, and the pseudo features of generated images are optimized toward the real ones in the CLIP embedding space. Furthermore, textual information is gathered to represent image features, resulting in the image features with various semantics and the bridged modality gap. To unify training and inference, synthetic image features would serve as the training prefix for the language decoder, while real images are used for inference. Additionally, salient objects in images are detected as assistance to enhance the learning of modality alignment. Experimental results demonstrate that our method obtains the state-of-the-art performance on benchmark datasets.
Deep Learning-Based Knowledge Injection for Metaphor Detection: A Comprehensive Review
Aug 15, 2023


Abstract:The history of metaphor research also marks the evolution of knowledge infusion research. With the continued advancement of deep learning techniques in recent years, the natural language processing community has shown great interest in applying knowledge to successful results in metaphor recognition tasks. Although there has been a gradual increase in the number of approaches involving knowledge injection in the field of metaphor recognition, there is a lack of a complete review article on knowledge injection based approaches. Therefore, the goal of this paper is to provide a comprehensive review of research advances in the application of deep learning for knowledge injection in metaphor recognition tasks. In this paper, we systematically summarize and generalize the mainstream knowledge and knowledge injection principles, as well as review the datasets, evaluation metrics, and benchmark models used in metaphor recognition tasks. Finally, we explore the current issues facing knowledge injection methods and provide an outlook on future research directions.
Topic-to-Essay Generation with Comprehensive Knowledge Enhancement
Jun 29, 2021



Abstract:Generating high-quality and diverse essays with a set of topics is a challenging task in natural language generation. Since several given topics only provide limited source information, utilizing various topic-related knowledge is essential for improving essay generation performance. However, previous works cannot sufficiently use that knowledge to facilitate the generation procedure. This paper aims to improve essay generation by extracting information from both internal and external knowledge. Thus, a topic-to-essay generation model with comprehensive knowledge enhancement, named TEGKE, is proposed. For internal knowledge enhancement, both topics and related essays are fed to a teacher network as source information. Then, informative features would be obtained from the teacher network and transferred to a student network which only takes topics as input but provides comparable information compared with the teacher network. For external knowledge enhancement, a topic knowledge graph encoder is proposed. Unlike the previous works only using the nearest neighbors of topics in the commonsense base, our topic knowledge graph encoder could exploit more structural and semantic information of the commonsense knowledge graph to facilitate essay generation. Moreover, the adversarial training based on the Wasserstein distance is proposed to improve generation quality. Experimental results demonstrate that TEGKE could achieve state-of-the-art performance on both automatic and human evaluation.
Utilizing BERT Intermediate Layers for Aspect Based Sentiment Analysis and Natural Language Inference
Feb 12, 2020



Abstract:Aspect based sentiment analysis aims to identify the sentimental tendency towards a given aspect in text. Fine-tuning of pretrained BERT performs excellent on this task and achieves state-of-the-art performances. Existing BERT-based works only utilize the last output layer of BERT and ignore the semantic knowledge in the intermediate layers. This paper explores the potential of utilizing BERT intermediate layers to enhance the performance of fine-tuning of BERT. To the best of our knowledge, no existing work has been done on this research. To show the generality, we also apply this approach to a natural language inference task. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness and generality of the proposed approach.
CatGAN: Category-aware Generative Adversarial Networks with Hierarchical Evolutionary Learning for Category Text Generation
Nov 20, 2019



Abstract:Generating multiple categories of texts is a challenging task and draws more and more attention. Since generative adversarial nets (GANs) have shown competitive results on general text generation, they are extended for category text generation in some previous works. However, the complicated model structures and learning strategies limit their performance and exacerbate the training instability. This paper proposes a category-aware GAN (CatGAN) which consists of an efficient category-aware model for category text generation and a hierarchical evolutionary learning algorithm for training our model. The category-aware model directly measures the gap between real samples and generated samples on each category, then reducing this gap will guide the model to generate high-quality category samples. The Gumbel-Softmax relaxation further frees our model from complicated learning strategies for updating CatGAN on discrete data. Moreover, only focusing on the sample quality normally leads the mode collapse problem, thus a hierarchical evolutionary learning algorithm is introduced to stabilize the training procedure and obtain the trade-off between quality and diversity while training CatGAN. Experimental results demonstrate that CatGAN outperforms most of the existing state-of-the-art methods.
Attentional Encoder Network for Targeted Sentiment Classification
Apr 01, 2019
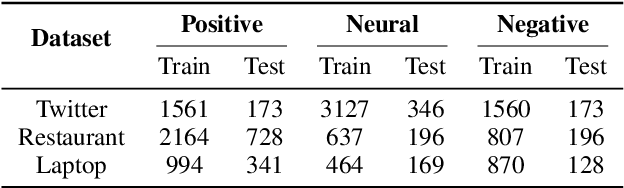
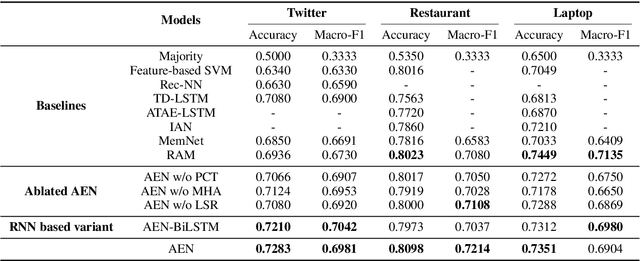
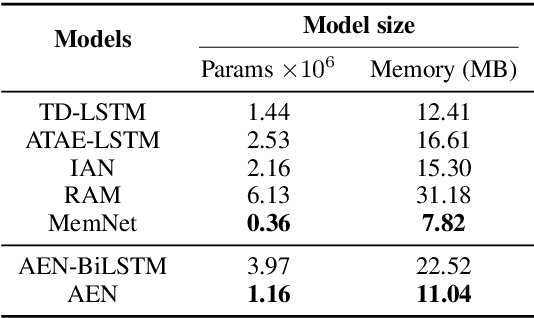
Abstract:Targeted sentiment classification aims at determining the sentimental tendency towards specific targets. Most of the previous approaches model context and target words with RNN and attention. However, RNNs are difficult to parallelize and truncated backpropagation through time brings difficulty in remembering long-term patterns. To address this issue, this paper proposes an Attentional Encoder Network (AEN) which eschews recurrence and employs attention based encoders for the modeling between context and target. We raise the label unreliability issue and introduce label smoothing regularization. We also apply pre-trained BERT to this task and obtain new state-of-the-art results. Experiments and analysis demonstrate the effectiveness and lightweight of our model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge