Zhifei Qin
IPBench: Benchmarking the Knowledge of Large Language Models in Intellectual Property
Apr 22, 2025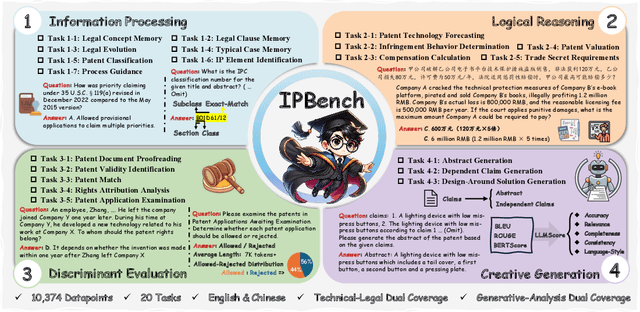
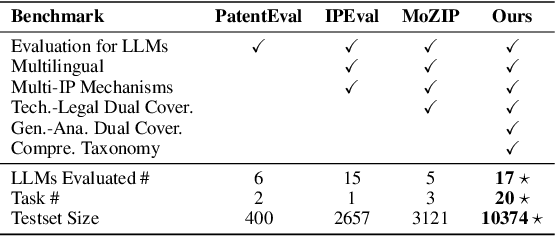
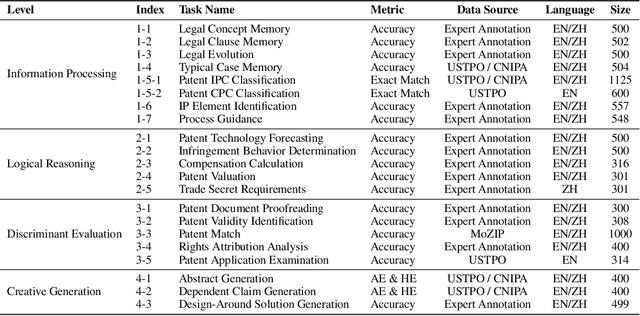
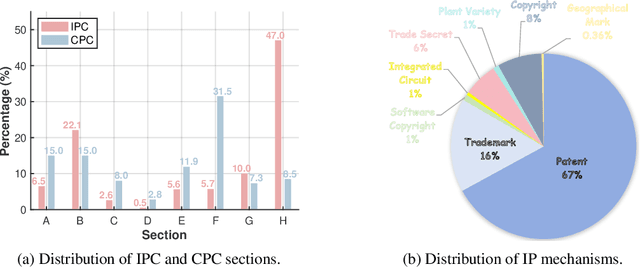
Abstract:Intellectual Property (IP) is a unique domain that integrates technical and legal knowledge, making it inherently complex and knowledge-intensive. As large language models (LLMs) continue to advance, they show great potential for processing IP tasks, enabling more efficient analysis, understanding, and generation of IP-related content. However, existing datasets and benchmarks either focus narrowly on patents or cover limited aspects of the IP field, lacking alignment with real-world scenarios. To bridge this gap, we introduce the first comprehensive IP task taxonomy and a large, diverse bilingual benchmark, IPBench, covering 8 IP mechanisms and 20 tasks. This benchmark is designed to evaluate LLMs in real-world intellectual property applications, encompassing both understanding and generation. We benchmark 16 LLMs, ranging from general-purpose to domain-specific models, and find that even the best-performing model achieves only 75.8% accuracy, revealing substantial room for improvement. Notably, open-source IP and law-oriented models lag behind closed-source general-purpose models. We publicly release all data and code of IPBench and will continue to update it with additional IP-related tasks to better reflect real-world challenges in the intellectual property domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge