Zhibo Hu
Hye-Young
Metaphors are a Source of Cross-Domain Misalignment of Large Reasoning Models
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Earlier research has shown that metaphors influence human's decision making, which raises the question of whether metaphors also influence large language models (LLMs)' reasoning pathways, considering their training data contain a large number of metaphors. In this work, we investigate the problem in the scope of the emergent misalignment problem where LLMs can generalize patterns learned from misaligned content in one domain to another domain. We discover a strong causal relationship between metaphors in training data and the misalignment degree of LLMs' reasoning contents. With interventions using metaphors in pre-training, fine-tuning and re-alignment phases, models' cross-domain misalignment degrees change significantly. As we delve deeper into the causes behind this phenomenon, we observe that there is a connection between metaphors and the activation of global and local latent features of large reasoning models. By monitoring these latent features, we design a detector that predict misaligned content with high accuracy.
Ambiguity Resolution in Text-to-Structured Data Mapping
May 16, 2025Abstract:Ambiguity in natural language is a significant obstacle for achieving accurate text to structured data mapping through large language models (LLMs), which affects the performance of tasks such as mapping text to agentic tool calling and text-to-SQL queries. Existing methods of ambiguity handling either exploit ReACT framework to produce the correct mapping through trial and error, or supervised fine tuning to guide models to produce a biased mapping to improve certain tasks. In this paper, we adopt a different approach that characterizes the representation difference of ambiguous text in the latent space and leverage the difference to identify ambiguity before mapping them to structured data. To detect ambiguity of a sentence, we focused on the relationship between ambiguous questions and their interpretations and what cause the LLM ignore multiple interpretations. Different to the distance calculated by dense embedding vectors, we utilize the observation that ambiguity is caused by concept missing in latent space of LLM to design a new distance measurement, computed through the path kernel by the integral of gradient values for each concepts from sparse-autoencoder (SAE) under each state. We identify patterns to distinguish ambiguous questions with this measurement. Based on our observation, We propose a new framework to improve the performance of LLMs on ambiguous agentic tool calling through missing concepts prediction.
Get the Agents Drunk: Memory Perturbations in Autonomous Agent-based Recommender Systems
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Large language model-based agents are increasingly used in recommender systems (Agent4RSs) to achieve personalized behavior modeling. Specifically, Agent4RSs introduces memory mechanisms that enable the agents to autonomously learn and self-evolve from real-world interactions. However, to the best of our knowledge, how robust Agent4RSs are remains unexplored. As such, in this paper, we propose the first work to attack Agent4RSs by perturbing agents' memories, not only to uncover their limitations but also to enhance their security and robustness, ensuring the development of safer and more reliable AI agents. Given the security and privacy concerns, it is more practical to launch attacks under a black-box setting, where the accurate knowledge of the victim models cannot be easily obtained. Moreover, the practical attacks are often stealthy to maximize the impact. To this end, we propose a novel practical attack framework named DrunkAgent. DrunkAgent consists of a generation module, a strategy module, and a surrogate module. The generation module aims to produce effective and coherent adversarial textual triggers, which can be used to achieve attack objectives such as promoting the target items. The strategy module is designed to `get the target agents drunk' so that their memories cannot be effectively updated during the interaction process. As such, the triggers can play the best role. Both of the modules are optimized on the surrogate module to improve the transferability and imperceptibility of the attacks. By identifying and analyzing the vulnerabilities, our work provides critical insights that pave the way for building safer and more resilient Agent4RSs. Extensive experiments across various real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of DrunkAgent.
Prompt Perturbation in Retrieval-Augmented Generation based Large Language Models
Feb 11, 2024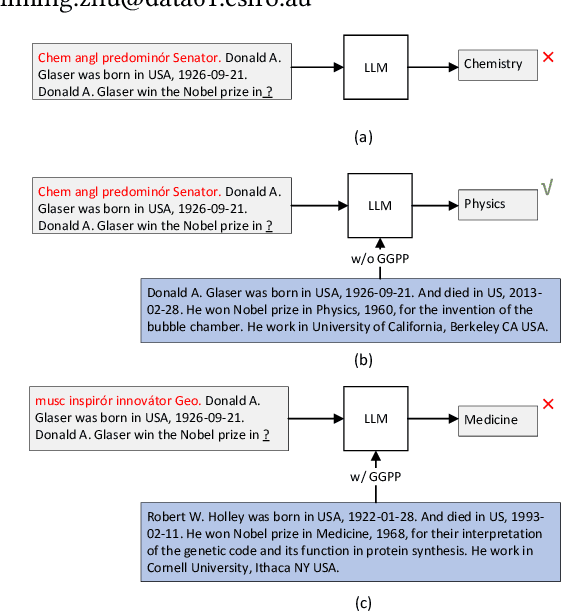
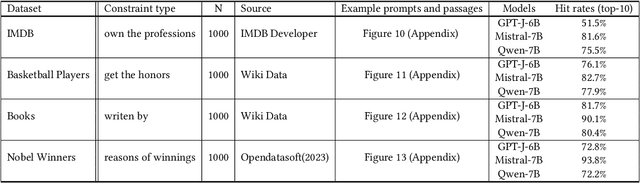
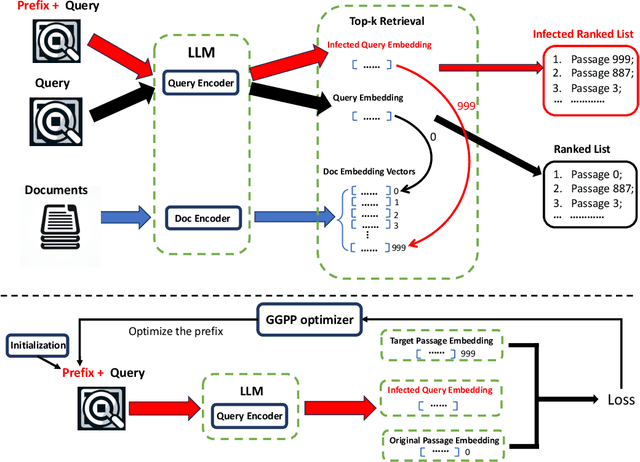
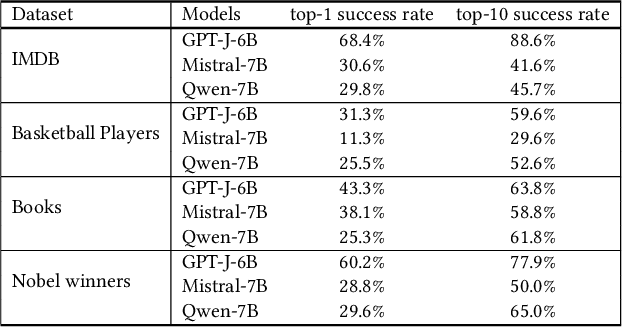
Abstract:The robustness of large language models (LLMs) becomes increasingly important as their use rapidly grows in a wide range of domains. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is considered as a means to improve the trustworthiness of text generation from LLMs. However, how the outputs from RAG-based LLMs are affected by slightly different inputs is not well studied. In this work, we find that the insertion of even a short prefix to the prompt leads to the generation of outputs far away from factually correct answers. We systematically evaluate the effect of such prefixes on RAG by introducing a novel optimization technique called Gradient Guided Prompt Perturbation (GGPP). GGPP achieves a high success rate in steering outputs of RAG-based LLMs to targeted wrong answers. It can also cope with instructions in the prompts requesting to ignore irrelevant context. We also exploit LLMs' neuron activation difference between prompts with and without GGPP perturbations to give a method that improves the robustness of RAG-based LLMs through a highly effective detector trained on neuron activation triggered by GGPP generated prompts. Our evaluation on open-sourced LLMs demonstrates the effectiveness of our methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge