Yanfeng Shu
Hye-Young
Metaphors are a Source of Cross-Domain Misalignment of Large Reasoning Models
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Earlier research has shown that metaphors influence human's decision making, which raises the question of whether metaphors also influence large language models (LLMs)' reasoning pathways, considering their training data contain a large number of metaphors. In this work, we investigate the problem in the scope of the emergent misalignment problem where LLMs can generalize patterns learned from misaligned content in one domain to another domain. We discover a strong causal relationship between metaphors in training data and the misalignment degree of LLMs' reasoning contents. With interventions using metaphors in pre-training, fine-tuning and re-alignment phases, models' cross-domain misalignment degrees change significantly. As we delve deeper into the causes behind this phenomenon, we observe that there is a connection between metaphors and the activation of global and local latent features of large reasoning models. By monitoring these latent features, we design a detector that predict misaligned content with high accuracy.
Ambiguity Resolution in Text-to-Structured Data Mapping
May 16, 2025Abstract:Ambiguity in natural language is a significant obstacle for achieving accurate text to structured data mapping through large language models (LLMs), which affects the performance of tasks such as mapping text to agentic tool calling and text-to-SQL queries. Existing methods of ambiguity handling either exploit ReACT framework to produce the correct mapping through trial and error, or supervised fine tuning to guide models to produce a biased mapping to improve certain tasks. In this paper, we adopt a different approach that characterizes the representation difference of ambiguous text in the latent space and leverage the difference to identify ambiguity before mapping them to structured data. To detect ambiguity of a sentence, we focused on the relationship between ambiguous questions and their interpretations and what cause the LLM ignore multiple interpretations. Different to the distance calculated by dense embedding vectors, we utilize the observation that ambiguity is caused by concept missing in latent space of LLM to design a new distance measurement, computed through the path kernel by the integral of gradient values for each concepts from sparse-autoencoder (SAE) under each state. We identify patterns to distinguish ambiguous questions with this measurement. Based on our observation, We propose a new framework to improve the performance of LLMs on ambiguous agentic tool calling through missing concepts prediction.
Rethinking Transformer-based Multi-document Summarization: An Empirical Investigation
Jul 16, 2024Abstract:The utilization of Transformer-based models prospers the growth of multi-document summarization (MDS). Given the huge impact and widespread adoption of Transformer-based models in various natural language processing tasks, investigating their performance and behaviors in the context of MDS becomes crucial for advancing the field and enhancing the quality of summary. To thoroughly examine the behaviours of Transformer-based MDS models, this paper presents five empirical studies on (1) measuring the impact of document boundary separators quantitatively; (2) exploring the effectiveness of different mainstream Transformer structures; (3) examining the sensitivity of the encoder and decoder; (4) discussing different training strategies; and (5) discovering the repetition in a summary generation. The experimental results on prevalent MDS datasets and eleven evaluation metrics show the influence of document boundary separators, the granularity of different level features and different model training strategies. The results also reveal that the decoder exhibits greater sensitivity to noises compared to the encoder. This underscores the important role played by the decoder, suggesting a potential direction for future research in MDS. Furthermore, the experimental results indicate that the repetition problem in the generated summaries has correlations with the high uncertainty scores.
Prompt Perturbation in Retrieval-Augmented Generation based Large Language Models
Feb 11, 2024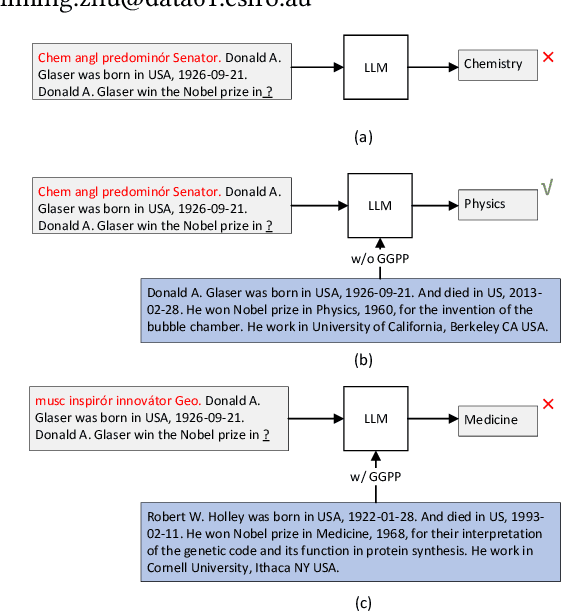
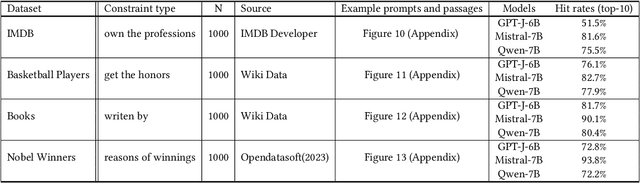
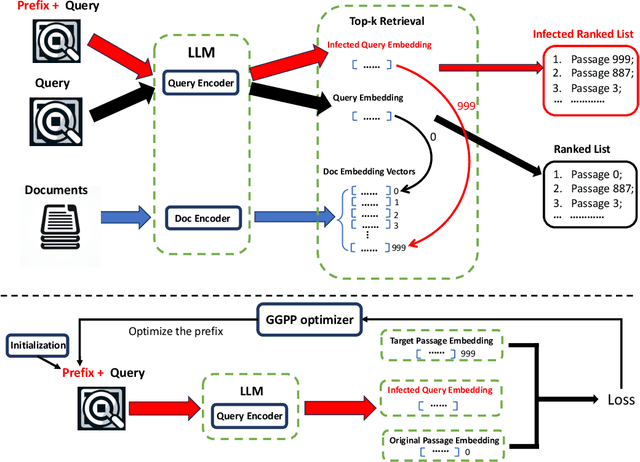
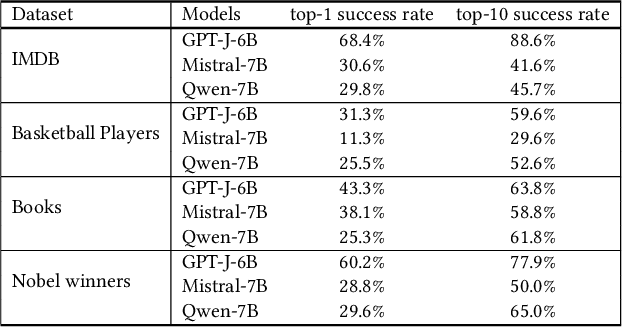
Abstract:The robustness of large language models (LLMs) becomes increasingly important as their use rapidly grows in a wide range of domains. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is considered as a means to improve the trustworthiness of text generation from LLMs. However, how the outputs from RAG-based LLMs are affected by slightly different inputs is not well studied. In this work, we find that the insertion of even a short prefix to the prompt leads to the generation of outputs far away from factually correct answers. We systematically evaluate the effect of such prefixes on RAG by introducing a novel optimization technique called Gradient Guided Prompt Perturbation (GGPP). GGPP achieves a high success rate in steering outputs of RAG-based LLMs to targeted wrong answers. It can also cope with instructions in the prompts requesting to ignore irrelevant context. We also exploit LLMs' neuron activation difference between prompts with and without GGPP perturbations to give a method that improves the robustness of RAG-based LLMs through a highly effective detector trained on neuron activation triggered by GGPP generated prompts. Our evaluation on open-sourced LLMs demonstrates the effectiveness of our methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge