Zhi-xin Yang
GaussianPretrain: A Simple Unified 3D Gaussian Representation for Visual Pre-training in Autonomous Driving
Nov 19, 2024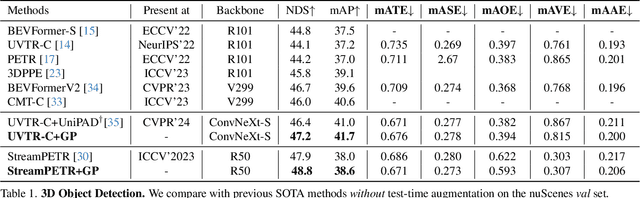
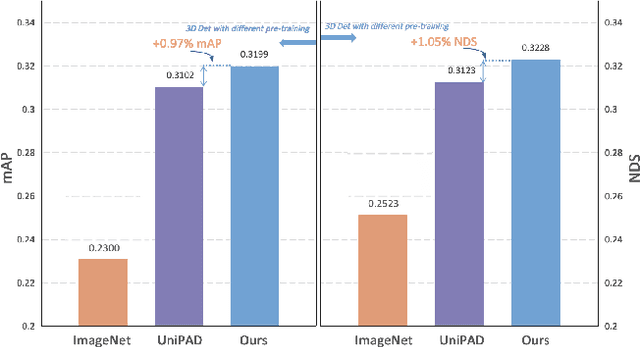
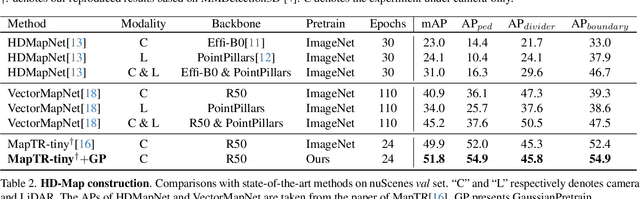
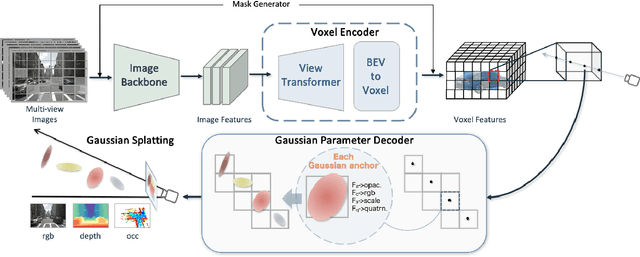
Abstract:Self-supervised learning has made substantial strides in image processing, while visual pre-training for autonomous driving is still in its infancy. Existing methods often focus on learning geometric scene information while neglecting texture or treating both aspects separately, hindering comprehensive scene understanding. In this context, we are excited to introduce GaussianPretrain, a novel pre-training paradigm that achieves a holistic understanding of the scene by uniformly integrating geometric and texture representations. Conceptualizing 3D Gaussian anchors as volumetric LiDAR points, our method learns a deepened understanding of scenes to enhance pre-training performance with detailed spatial structure and texture, achieving that 40.6% faster than NeRF-based method UniPAD with 70% GPU memory only. We demonstrate the effectiveness of GaussianPretrain across multiple 3D perception tasks, showing significant performance improvements, such as a 7.05% increase in NDS for 3D object detection, boosts mAP by 1.9% in HD map construction and 0.8% improvement on Occupancy prediction. These significant gains highlight GaussianPretrain's theoretical innovation and strong practical potential, promoting visual pre-training development for autonomous driving. Source code will be available at https://github.com/Public-BOTs/GaussianPretrain
Robust and Efficient Memory Network for Video Object Segmentation
Apr 24, 2023Abstract:This paper proposes a Robust and Efficient Memory Network, referred to as REMN, for studying semi-supervised video object segmentation (VOS). Memory-based methods have recently achieved outstanding VOS performance by performing non-local pixel-wise matching between the query and memory. However, these methods have two limitations. 1) Non-local matching could cause distractor objects in the background to be incorrectly segmented. 2) Memory features with high temporal redundancy consume significant computing resources. For limitation 1, we introduce a local attention mechanism that tackles the background distraction by enhancing the features of foreground objects with the previous mask. For limitation 2, we first adaptively decide whether to update the memory features depending on the variation of foreground objects to reduce temporal redundancy. Second, we employ a dynamic memory bank, which uses a lightweight and differentiable soft modulation gate to decide how many memory features need to be removed in the temporal dimension. Experiments demonstrate that our REMN achieves state-of-the-art results on DAVIS 2017, with a $\mathcal{J\&F}$ score of 86.3% and on YouTube-VOS 2018, with a $\mathcal{G}$ over mean of 85.5%. Furthermore, our network shows a high inference speed of 25+ FPS and uses relatively few computing resources.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge