Zhi-Hao Tan
Learnware of Language Models: Specialized Small Language Models Can Do Big
May 19, 2025Abstract:The learnware paradigm offers a novel approach to machine learning by enabling users to reuse a set of well-trained models for tasks beyond the models' original purposes. It eliminates the need to build models from scratch, instead relying on specifications (representations of a model's capabilities) to identify and leverage the most suitable models for new tasks. While learnware has proven effective in many scenarios, its application to language models has remained largely unexplored. At the same time, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable universal question-answering abilities, yet they face challenges in specialized scenarios due to data scarcity, privacy concerns, and high computational costs, thus more and more specialized small language models (SLMs) are being trained for specific domains. To address these limitations systematically, the learnware paradigm provides a promising solution by enabling maximum utilization of specialized SLMs, and allowing users to identify and reuse them in a collaborative and privacy-preserving manner. This paper presents a preliminary attempt to apply the learnware paradigm to language models. We simulated a learnware system comprising approximately 100 learnwares of specialized SLMs with 8B parameters, fine-tuned across finance, healthcare, and mathematics domains. Each learnware contains an SLM and a specification, which enables users to identify the most relevant models without exposing their own data. Experimental results demonstrate promising performance: by selecting one suitable learnware for each task-specific inference, the system outperforms the base SLMs on all benchmarks. Compared to LLMs, the system outperforms Qwen1.5-110B, Qwen2.5-72B, and Llama3.1-70B-Instruct by at least 14% in finance domain tasks, and surpasses Flan-PaLM-540B (ranked 7th on the Open Medical LLM Leaderboard) in medical domain tasks.
Beimingwu: A Learnware Dock System
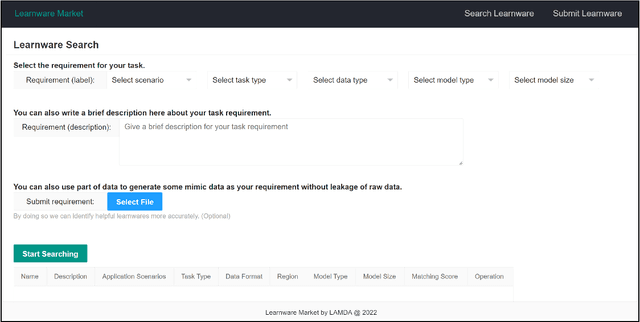
Jan 24, 2024Abstract:The learnware paradigm proposed by Zhou [2016] aims to enable users to reuse numerous existing well-trained models instead of building machine learning models from scratch, with the hope of solving new user tasks even beyond models' original purposes. In this paradigm, developers worldwide can submit their high-performing models spontaneously to the learnware dock system (formerly known as learnware market) without revealing their training data. Once the dock system accepts the model, it assigns a specification and accommodates the model. This specification allows the model to be adequately identified and assembled to reuse according to future users' needs, even if they have no prior knowledge of the model. This paradigm greatly differs from the current big model direction and it is expected that a learnware dock system housing millions or more high-performing models could offer excellent capabilities for both planned tasks where big models are applicable; and unplanned, specialized, data-sensitive scenarios where big models are not present or applicable. This paper describes Beimingwu, the first open-source learnware dock system providing foundational support for future research of learnware paradigm.The system significantly streamlines the model development for new user tasks, thanks to its integrated architecture and engine design, extensive engineering implementations and optimizations, and the integration of various algorithms for learnware identification and reuse. Notably, this is possible even for users with limited data and minimal expertise in machine learning, without compromising the raw data's security. Beimingwu supports the entire process of learnware paradigm. The system lays the foundation for future research in learnware-related algorithms and systems, and prepares the ground for hosting a vast array of learnwares and establishing a learnware ecosystem.
Learnware: Small Models Do Big
Oct 07, 2022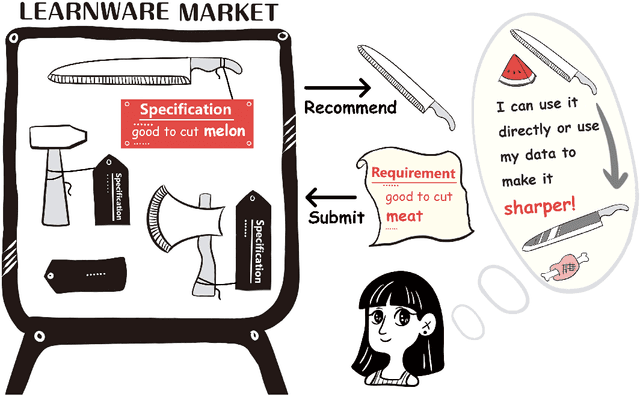
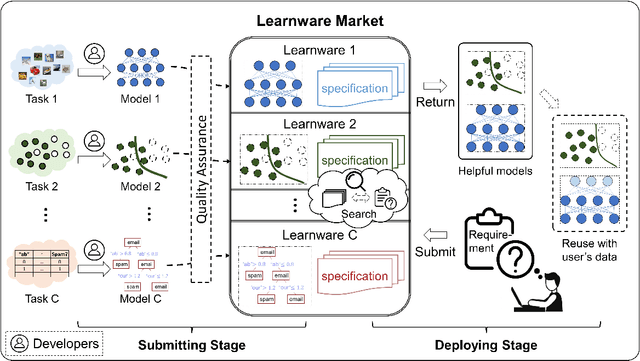
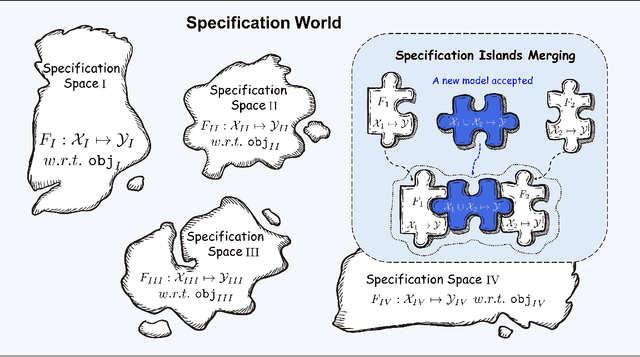
Abstract:There are complaints about current machine learning techniques such as the requirement of a huge amount of training data and proficient training skills, the difficulty of continual learning, the risk of catastrophic forgetting, the leaking of data privacy/proprietary, etc. Most research efforts have been focusing on one of those concerned issues separately, paying less attention to the fact that most issues are entangled in practice. The prevailing big model paradigm, which has achieved impressive results in natural language processing and computer vision applications, has not yet addressed those issues, whereas becoming a serious source of carbon emissions. This article offers an overview of the learnware paradigm, which attempts to enable users not need to build machine learning models from scratch, with the hope of reusing small models to do things even beyond their original purposes, where the key ingredient is the specification which enables a trained model to be adequately identified to reuse according to the requirement of future users who know nothing about the model in advance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge