Zhexiao Lin
Variance reduction combining pre-experiment and in-experiment data
Oct 11, 2024Abstract:Online controlled experiments (A/B testing) are essential in data-driven decision-making for many companies. Increasing the sensitivity of these experiments, particularly with a fixed sample size, relies on reducing the variance of the estimator for the average treatment effect (ATE). Existing methods like CUPED and CUPAC use pre-experiment data to reduce variance, but their effectiveness depends on the correlation between the pre-experiment data and the outcome. In contrast, in-experiment data is often more strongly correlated with the outcome and thus more informative. In this paper, we introduce a novel method that combines both pre-experiment and in-experiment data to achieve greater variance reduction than CUPED and CUPAC, without introducing bias or additional computation complexity. We also establish asymptotic theory and provide consistent variance estimators for our method. Applying this method to multiple online experiments at Etsy, we reach substantial variance reduction over CUPAC with the inclusion of only a few in-experiment covariates. These results highlight the potential of our approach to significantly improve experiment sensitivity and accelerate decision-making.
On the Sequence Evaluation based on Stochastic Processes
May 28, 2024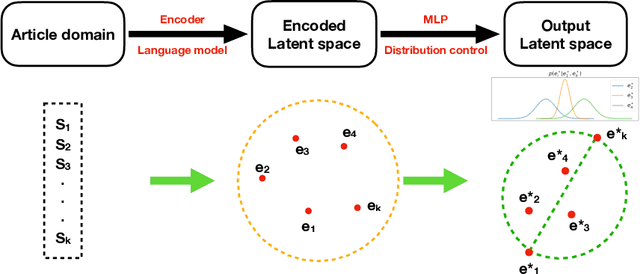
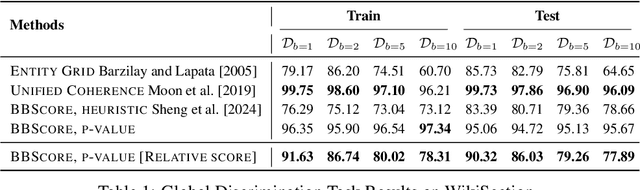

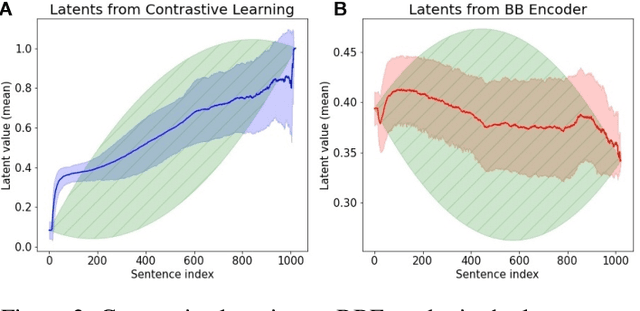
Abstract:Modeling and analyzing long sequences of text is an essential task for Natural Language Processing. Success in capturing long text dynamics using neural language models will facilitate many downstream tasks such as coherence evaluation, text generation, machine translation and so on. This paper presents a novel approach to model sequences through a stochastic process. We introduce a likelihood-based training objective for the text encoder and design a more thorough measurement (score) for long text evaluation compared to the previous approach. The proposed training objective effectively preserves the sequence coherence, while the new score comprehensively captures both temporal and spatial dependencies. Theoretical properties of our new score show its advantages in sequence evaluation. Experimental results show superior performance in various sequence evaluation tasks, including global and local discrimination within and between documents of different lengths. We also demonstrate the encoder achieves competitive results on discriminating human and AI written text.
Limit theorems of Chatterjee's rank correlation
Apr 17, 2022Abstract:Establishing limiting distributions of Chatterjee's rank correlation for a general, possibly non-independent, pair of random variables has been eagerly awaited to many. This paper shows that (a) Chatterjee's rank correlation is asymptotically normal as long as one variable is not a measurable function of the other, and (b) the corresponding asymptotic variance is uniformly bounded by 36. Similar results also hold for Azadkia-Chatterjee's graph-based correlation coefficient, a multivariate analogue of Chatterjee's original proposal. The proof is given by appealing to H\'ajek representation and Chatterjee's nearest-neighbor CLT.
Topic-aware chatbot using Recurrent Neural Networks and Nonnegative Matrix Factorization
Dec 04, 2019


Abstract:We propose a novel model for a topic-aware chatbot by combining the traditional Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) encoder-decoder model with a topic attention layer based on Nonnegative Matrix Factorization (NMF). After learning topic vectors from an auxiliary text corpus via NMF, the decoder is trained so that it is more likely to sample response words from the most correlated topic vectors. One of the main advantages in our architecture is that the user can easily switch the NMF-learned topic vectors so that the chatbot obtains desired topic-awareness. We demonstrate our model by training on a single conversational data set which is then augmented with topic matrices learned from different auxiliary data sets. We show that our topic-aware chatbot not only outperforms the non-topic counterpart, but also that each topic-aware model qualitatively and contextually gives the most relevant answer depending on the topic of question.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge