Zhenqi Jia
Towards Authentic Movie Dubbing with Retrieve-Augmented Director-Actor Interaction Learning
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:The automatic movie dubbing model generates vivid speech from given scripts, replicating a speaker's timbre from a brief timbre prompt while ensuring lip-sync with the silent video. Existing approaches simulate a simplified workflow where actors dub directly without preparation, overlooking the critical director-actor interaction. In contrast, authentic workflows involve a dynamic collaboration: directors actively engage with actors, guiding them to internalize the context cues, specifically emotion, before performance. To address this issue, we propose a new Retrieve-Augmented Director-Actor Interaction Learning scheme to achieve authentic movie dubbing, termed Authentic-Dubber, which contains three novel mechanisms: (1) We construct a multimodal Reference Footage library to simulate the learning footage provided by directors. Note that we integrate Large Language Models (LLMs) to achieve deep comprehension of emotional representations across multimodal signals. (2) To emulate how actors efficiently and comprehensively internalize director-provided footage during dubbing, we propose an Emotion-Similarity-based Retrieval-Augmentation strategy. This strategy retrieves the most relevant multimodal information that aligns with the target silent video. (3) We develop a Progressive Graph-based speech generation approach that incrementally incorporates the retrieved multimodal emotional knowledge, thereby simulating the actor's final dubbing process. The above mechanisms enable the Authentic-Dubber to faithfully replicate the authentic dubbing workflow, achieving comprehensive improvements in emotional expressiveness. Both subjective and objective evaluations on the V2C Animation benchmark dataset validate the effectiveness. The code and demos are available at https://github.com/AI-S2-Lab/Authentic-Dubber.
Retrieval-Augmented Dialogue Knowledge Aggregation for Expressive Conversational Speech Synthesis
Jan 11, 2025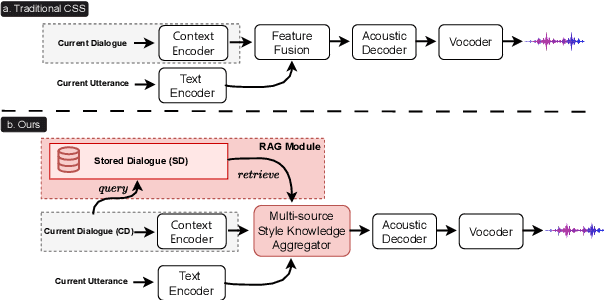
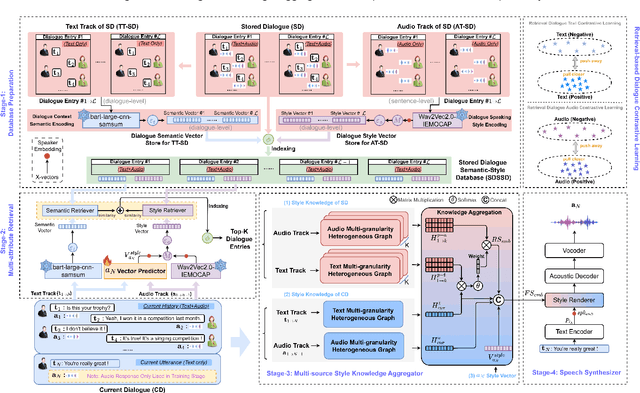
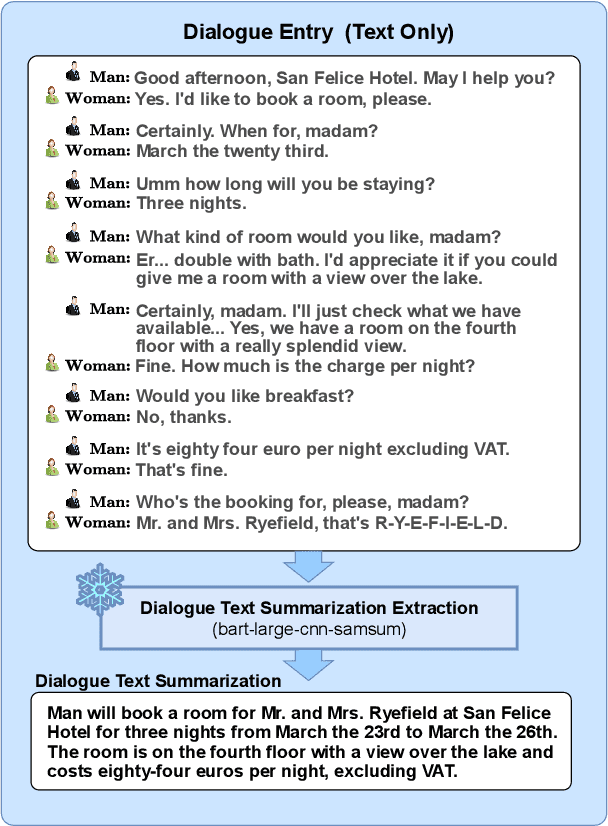
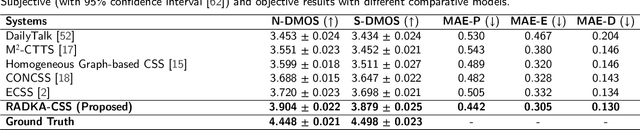
Abstract:Conversational speech synthesis (CSS) aims to take the current dialogue (CD) history as a reference to synthesize expressive speech that aligns with the conversational style. Unlike CD, stored dialogue (SD) contains preserved dialogue fragments from earlier stages of user-agent interaction, which include style expression knowledge relevant to scenarios similar to those in CD. Note that this knowledge plays a significant role in enabling the agent to synthesize expressive conversational speech that generates empathetic feedback. However, prior research has overlooked this aspect. To address this issue, we propose a novel Retrieval-Augmented Dialogue Knowledge Aggregation scheme for expressive CSS, termed RADKA-CSS, which includes three main components: 1) To effectively retrieve dialogues from SD that are similar to CD in terms of both semantic and style. First, we build a stored dialogue semantic-style database (SDSSD) which includes the text and audio samples. Then, we design a multi-attribute retrieval scheme to match the dialogue semantic and style vectors of the CD with the stored dialogue semantic and style vectors in the SDSSD, retrieving the most similar dialogues. 2) To effectively utilize the style knowledge from CD and SD, we propose adopting the multi-granularity graph structure to encode the dialogue and introducing a multi-source style knowledge aggregation mechanism. 3) Finally, the aggregated style knowledge are fed into the speech synthesizer to help the agent synthesize expressive speech that aligns with the conversational style. We conducted a comprehensive and in-depth experiment based on the DailyTalk dataset, which is a benchmarking dataset for the CSS task. Both objective and subjective evaluations demonstrate that RADKA-CSS outperforms baseline models in expressiveness rendering. Code and audio samples can be found at: https://github.com/Coder-jzq/RADKA-CSS.
Intra- and Inter-modal Context Interaction Modeling for Conversational Speech Synthesis
Dec 25, 2024Abstract:Conversational Speech Synthesis (CSS) aims to effectively take the multimodal dialogue history (MDH) to generate speech with appropriate conversational prosody for target utterance. The key challenge of CSS is to model the interaction between the MDH and the target utterance. Note that text and speech modalities in MDH have their own unique influences, and they complement each other to produce a comprehensive impact on the target utterance. Previous works did not explicitly model such intra-modal and inter-modal interactions. To address this issue, we propose a new intra-modal and inter-modal context interaction scheme-based CSS system, termed III-CSS. Specifically, in the training phase, we combine the MDH with the text and speech modalities in the target utterance to obtain four modal combinations, including Historical Text-Next Text, Historical Speech-Next Speech, Historical Text-Next Speech, and Historical Speech-Next Text. Then, we design two contrastive learning-based intra-modal and two inter-modal interaction modules to deeply learn the intra-modal and inter-modal context interaction. In the inference phase, we take MDH and adopt trained interaction modules to fully infer the speech prosody of the target utterance's text content. Subjective and objective experiments on the DailyTalk dataset show that III-CSS outperforms the advanced baselines in terms of prosody expressiveness. Code and speech samples are available at https://github.com/AI-S2-Lab/I3CSS.
Emphasis Rendering for Conversational Text-to-Speech with Multi-modal Multi-scale Context Modeling
Oct 12, 2024



Abstract:Conversational Text-to-Speech (CTTS) aims to accurately express an utterance with the appropriate style within a conversational setting, which attracts more attention nowadays. While recognizing the significance of the CTTS task, prior studies have not thoroughly investigated speech emphasis expression, which is essential for conveying the underlying intention and attitude in human-machine interaction scenarios, due to the scarcity of conversational emphasis datasets and the difficulty in context understanding. In this paper, we propose a novel Emphasis Rendering scheme for the CTTS model, termed ER-CTTS, that includes two main components: 1) we simultaneously take into account textual and acoustic contexts, with both global and local semantic modeling to understand the conversation context comprehensively; 2) we deeply integrate multi-modal and multi-scale context to learn the influence of context on the emphasis expression of the current utterance. Finally, the inferred emphasis feature is fed into the neural speech synthesizer to generate conversational speech. To address data scarcity, we create emphasis intensity annotations on the existing conversational dataset (DailyTalk). Both objective and subjective evaluations suggest that our model outperforms the baseline models in emphasis rendering within a conversational setting. The code and audio samples are available at https://github.com/CodeStoreTTS/ER-CTTS.
MCDubber: Multimodal Context-Aware Expressive Video Dubbing
Aug 21, 2024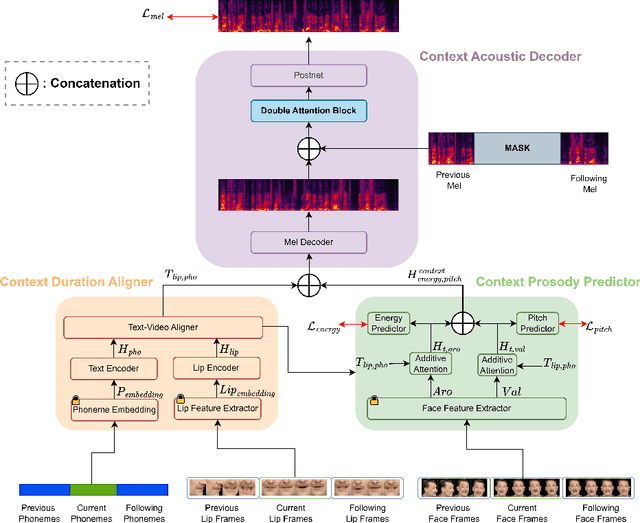
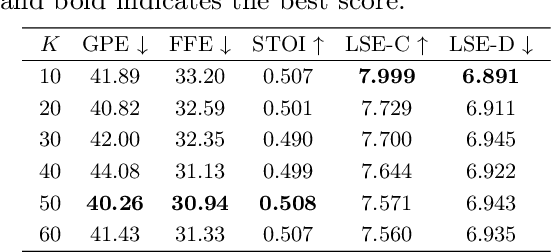
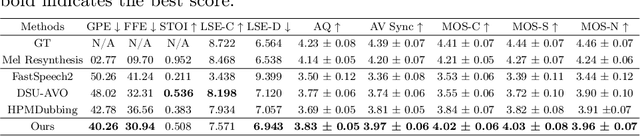
Abstract:Automatic Video Dubbing (AVD) aims to take the given script and generate speech that aligns with lip motion and prosody expressiveness. Current AVD models mainly utilize visual information of the current sentence to enhance the prosody of synthesized speech. However, it is crucial to consider whether the prosody of the generated dubbing aligns with the multimodal context, as the dubbing will be combined with the original context in the final video. This aspect has been overlooked in previous studies. To address this issue, we propose a Multimodal Context-aware video Dubbing model, termed \textbf{MCDubber}, to convert the modeling object from a single sentence to a longer sequence with context information to ensure the consistency of the global context prosody. MCDubber comprises three main components: (1) A context duration aligner aims to learn the context-aware alignment between the text and lip frames; (2) A context prosody predictor seeks to read the global context visual sequence and predict the context-aware global energy and pitch; (3) A context acoustic decoder ultimately predicts the global context mel-spectrogram with the assistance of adjacent ground-truth mel-spectrograms of the target sentence. Through this process, MCDubber fully considers the influence of multimodal context on the prosody expressiveness of the current sentence when dubbing. The extracted mel-spectrogram belonging to the target sentence from the output context mel-spectrograms is the final required dubbing audio. Extensive experiments on the Chem benchmark dataset demonstrate that our MCDubber significantly improves dubbing expressiveness compared to all advanced baselines. The code and demos are available at https://github.com/XiaoYuanJun-zy/MCDubber.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge