Zhengjian Yao
Bridging Degradation Discrimination and Generation for Universal Image Restoration
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Universal image restoration is a critical task in low-level vision, requiring the model to remove various degradations from low-quality images to produce clean images with rich detail. The challenges lie in sampling the distribution of high-quality images and adjusting the outputs on the basis of the degradation. This paper presents a novel approach, Bridging Degradation discrimination and Generation (BDG), which aims to address these challenges concurrently. First, we propose the Multi-Angle and multi-Scale Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (MAS-GLCM) and demonstrate its effectiveness in performing fine-grained discrimination of degradation types and levels. Subsequently, we divide the diffusion training process into three distinct stages: generation, bridging, and restoration. The objective is to preserve the diffusion model's capability of restoring rich textures while simultaneously integrating the discriminative information from the MAS-GLCM into the restoration process. This enhances its proficiency in addressing multi-task and multi-degraded scenarios. Without changing the architecture, BDG achieves significant performance gains in all-in-one restoration and real-world super-resolution tasks, primarily evidenced by substantial improvements in fidelity without compromising perceptual quality. The code and pretrained models are provided in https://github.com/MILab-PKU/BDG.
Bridging Information Asymmetry: A Hierarchical Framework for Deterministic Blind Face Restoration
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Blind face restoration remains a persistent challenge due to the inherent ill-posedness of reconstructing holistic structures from severely constrained observations. Current generative approaches, while capable of synthesizing realistic textures, often suffer from information asymmetry -- the intrinsic disparity between the information-sparse low quality inputs and the information-dense high quality outputs. This imbalance leads to a one-to-many mapping, where insufficient constraints result in stochastic uncertainty and hallucinatory artifacts. To bridge this gap, we present \textbf{Pref-Restore}, a hierarchical framework that integrates discrete semantic logic with continuous texture generation to achieve deterministic, preference-aligned restoration. Our methodology fundamentally addresses this information disparity through two complementary strategies: (1) Augmenting Input Density: We employ an auto-regressive integrator to reformulate textual instructions into dense latent queries, injecting high-level semantic stability to constrain the degraded signals; (2) Pruning Output Distribution: We pioneer the integration of on-policy reinforcement learning directly into the diffusion restoration loop. By transforming human preferences into differentiable constraints, we explicitly penalize stochastic deviations, thereby sharpening the posterior distribution toward the desired high-fidelity outcomes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Pref-Restore achieves state-of-the-art performance across synthetic and real-world benchmarks. Furthermore, empirical analysis confirms that our preference-aligned strategy significantly reduces solution entropy, establishing a robust pathway toward reliable and deterministic blind restoration.
AdaTok: Adaptive Token Compression with Object-Aware Representations for Efficient Multimodal LLMs
Nov 18, 2025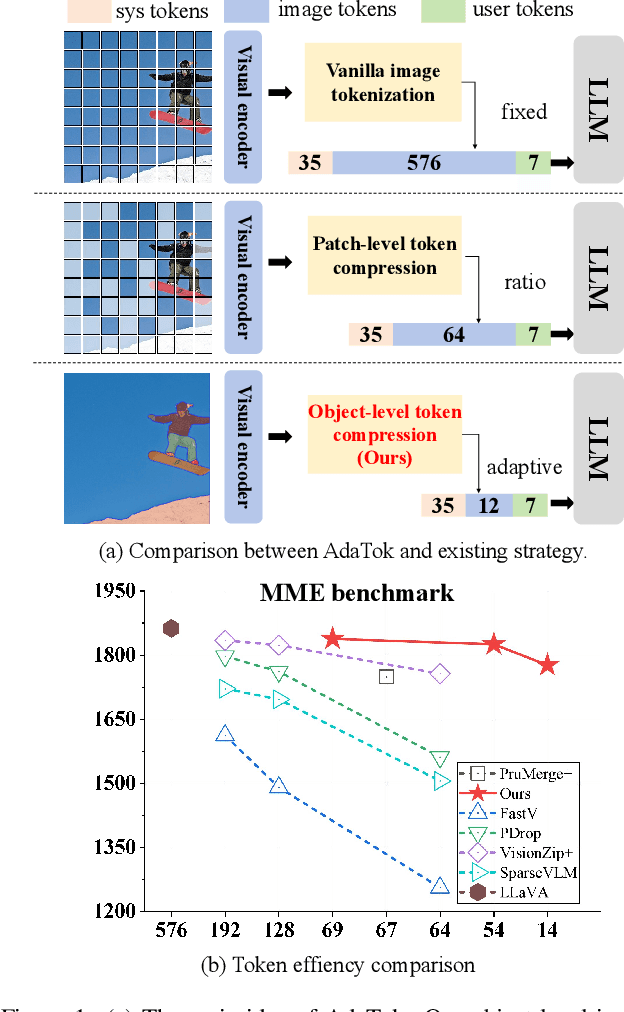
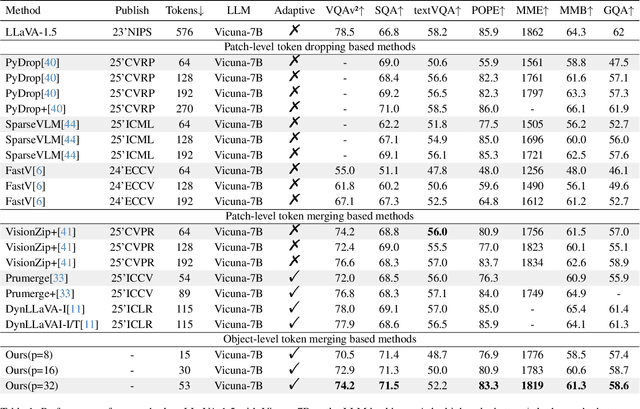
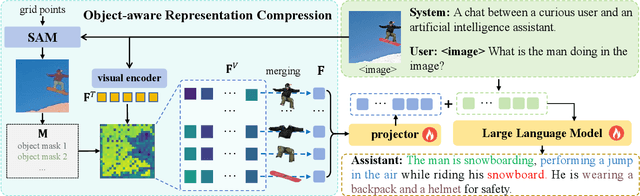
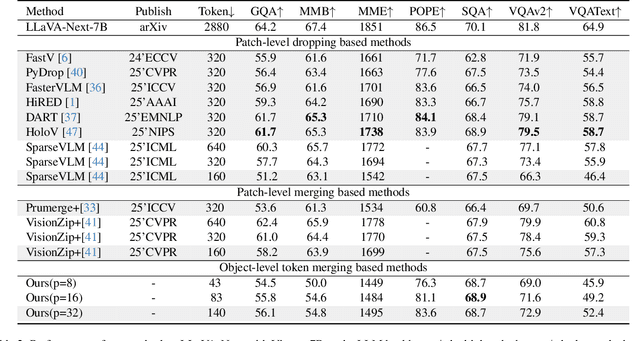
Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated substantial value in unified text-image understanding and reasoning, primarily by converting images into sequences of patch-level tokens that align with their architectural paradigm. However, patch-level tokenization leads to a quadratic growth in image tokens, burdening MLLMs' understanding and reasoning with enormous computation and memory. Additionally, the traditional patch-wise scanning tokenization workflow misaligns with the human vision cognition system, further leading to hallucination and computational redundancy. To address this issue, we propose an object-level token merging strategy for Adaptive Token compression, revealing the consistency with human vision system. The experiments are conducted on multiple comprehensive benchmarks, which show that our approach averagely, utilizes only 10% tokens while achieving almost 96% of the vanilla model's performance. More extensive experimental results in comparison with relevant works demonstrate the superiority of our method in balancing compression ratio and performance. Our code will be available.
Exploiting Inherent Class Label: Towards Robust Scribble Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Scribble-based weakly supervised semantic segmentation leverages only a few annotated pixels as labels to train a segmentation model, presenting significant potential for reducing the human labor involved in the annotation process. This approach faces two primary challenges: first, the sparsity of scribble annotations can lead to inconsistent predictions due to limited supervision; second, the variability in scribble annotations, reflecting differing human annotator preferences, can prevent the model from consistently capturing the discriminative regions of objects, potentially leading to unstable predictions. To address these issues, we propose a holistic framework, the class-driven scribble promotion network, for robust scribble-supervised semantic segmentation. This framework not only utilizes the provided scribble annotations but also leverages their associated class labels to generate reliable pseudo-labels. Within the network, we introduce a localization rectification module to mitigate noisy labels and a distance perception module to identify reliable regions surrounding scribble annotations and pseudo-labels. In addition, we introduce new large-scale benchmarks, ScribbleCOCO and ScribbleCityscapes, accompanied by a scribble simulation algorithm that enables evaluation across varying scribble styles. Our method demonstrates competitive performance in both accuracy and robustness, underscoring its superiority over existing approaches. The datasets and the codes will be made publicly available.
Universal Image Restoration Pre-training via Degradation Classification
Jan 26, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes the Degradation Classification Pre-Training (DCPT), which enables models to learn how to classify the degradation type of input images for universal image restoration pre-training. Unlike the existing self-supervised pre-training methods, DCPT utilizes the degradation type of the input image as an extremely weak supervision, which can be effortlessly obtained, even intrinsic in all image restoration datasets. DCPT comprises two primary stages. Initially, image features are extracted from the encoder. Subsequently, a lightweight decoder, such as ResNet18, is leveraged to classify the degradation type of the input image solely based on the features extracted in the first stage, without utilizing the input image. The encoder is pre-trained with a straightforward yet potent DCPT, which is used to address universal image restoration and achieve outstanding performance. Following DCPT, both convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and transformers demonstrate performance improvements, with gains of up to 2.55 dB in the 10D all-in-one restoration task and 6.53 dB in the mixed degradation scenarios. Moreover, previous self-supervised pretraining methods, such as masked image modeling, discard the decoder after pre-training, while our DCPT utilizes the pre-trained parameters more effectively. This superiority arises from the degradation classifier acquired during DCPT, which facilitates transfer learning between models of identical architecture trained on diverse degradation types. Source code and models are available at https://github.com/MILab-PKU/dcpt.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge